lingvo.wikisort.org - Alphabet
The Ol Onal is an alphabetic writing script of Bhumij language, spoken by Bhumij peoples.[1] Ol Onal script was created between 1981 and 1992 by Ol Guru Mahendra Nath Sardar. Ol Onal script is used to write Bhumij language in some parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Orissa, and Assam.[2][3]
| Ol Onal script | |
|---|---|
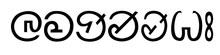 Bhumij written in Ol Onal script | |
| Script type | Alphabet
|
| Creator | Mahendra Nath Sardar |
Time period | 1981 to current |
| Direction | Left to Right |
| Region | Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Assam (India) |
| Languages | Bhumij language[a] |
| Related scripts | |
Sister systems | Santali script, Mundari Bani Others: Odia script, Devnagari script, Bengali Script |
[a] The Bhumij language often considered as a dialect of Mundari language. | |
History
The Ol Onal script was created in between 1981 and 1992 by Ol Guru Mahendra Nath Sardar for the Bhumij language.


Bhumij community had no written language and knowledge was transmitted orally from one generation to other. Later researchers started to use Devanagari, Bengali, and Odia scripts to document the Bhumij language. However, Bhumijs did not have their own script. His invention of the Ol Onal script enriched the cultural identity of the tribal Bhumij community. He wrote many text books in the Ol Onal script.
Language
Bhumij is the language of the Munda subfamily of the Austroasiatic languages, related to Ho, Mundari and Santali, spoken mainly in the Indian states Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. It is spoken by around 100,000 people in India.[4]
See also
- Bhumij
- Bhumij language
References
- "Ol Onal". Omniglot.
- "Non-Scheduled Indian Languages Resources".[failed verification]
- "Tribals demand official status for Bhumij language". Times of India. 17 March 2016.
- "Bhumij language and alphabet". omniglot.com. Retrieved 2022-04-19.
External links
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии