lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Transylvanian Saxon (Saxon: Siweberjesch-Såksesch or just Såksesch, German: Siebenbürgisch-Sächsisch or siebenbürgisch-sächsische Sprache, Hungarian: Erdélyi szász nyelv, Romanian: Limba săsească or dialectul săsesc) is the German dialect of the Transylvanian Saxons, a Romanian-German ethnicity from Transylvania, central Romania.[2]
| Transylvanian Saxon | |
|---|---|
| Siweberjesch-Såksesch Såksesch | |
| Native to | Romania[lower-alpha 1] |
| Region | Transylvania (German: Siebenbürgen) |
Native speakers | c. 200,000[1] |
Language family | Indo-European
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | tran1294 |
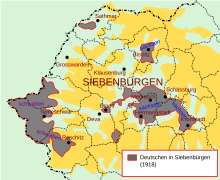 Areas where Transylvanian Saxon was spoken in the Kingdom of Romania in 1918 (the grey-coloured areas to the west denote where Swabian was spoken). | |
 Transylvanian Saxon is classified as Severely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
Background
In terms of comparative linguistics, it pertains to the Moselle Franconian group of West Central German dialects. In this particular regard, it must be mentioned that it shares a consistent amount of lexical similarities with Luxembourgish.[3][4]
The dialect was mainly spoken in Transylvania (contemporary central Romania), by individuals of German, Flemish, and Walloon origins who were settled in the Kingdom of Hungary starting in the 12th century. Over the passing of time, it had been consistently influenced by both Romanian and Hungarian.[5][6] The main areas where Transylvanian Saxon was spoken in Transylvania were southern and northern Transylvania.[7][8]
In the contemporary era, the vast majority of the native speakers have emigrated in several waves, initially to Germany and Austria, but then subsequently to the USA, Canada as well as other Western European countries, managing in the process to preserve (at least temporarily) their specific language there.
Distribution of the dialect in Transylvania
Traditionally, the Transylvanian Saxon dialect was mainly spoken in the rural areas of Transylvania throughout the passing of time, since the arrival of the Transylvanian Saxons in the Carpathian Basin during the High Middle Ages onwards. In the urban settlements (i.e. towns and cities), standard German (i.e. Hochdeutsch) was spoken and written.
Furthermore, the Transylvanian Saxon dialect also varied from village to village where it was spoken (a village could have a slightly different form of Transylvanian Saxon than other; analogous to how English accents vary on a radius of 5 miles in the United Kingdom for example).
Recent history of the dialect (1989–present)
Before the Romanian Revolution of 1989, most of the Transylvanian Saxons were still living in Transylvania. During the communist dictatorship of Nicolae Ceaușescu, many thousands of these Saxons were sold for a total of around $6 million paid to socialist Romania by West Germany.[9]
By 1990, the number of Saxons living in Transylvania had decreased dramatically. Shortly after the fall of Communism, from 1991 to 1994, many Transylvanian Saxons who still remained in Transylvania decided to ultimately emigrate to re-unified Germany, leaving just a minority of approximately 20,0000 Transylvanian Saxons in Romania at the round of the 21st century (or less than 1 percent of the entire population of Transylvania).[10][11]
The number of native Transylvanian Saxon speakers today is estimated at approximately 200,000 persons. Transylvanian Saxon is also the native dialect of the current President of Romania, Klaus Iohannis, by virtue of the fact that he is a Transylvanian Saxon.[12] Additionally, according to the 2011 Romanian census, only 11,400 Transylvanian Saxon were still living in Transylvania at that time.[13]
Alphabet
- A - a
- B - be
- C - ce
- D - de
- E - e
- F - ef
- G - ge
- H - ha
- I - i
- J - jot
- K - ka
- L - el
- M - em
- N - en
- O - o
- P - pe
- Q - ku
- R - er
- S - es
- T - te
- U - u
- V - vau
- W - we
- X - ix
- Y - ipsilon
- Z - zet[14]
Orthography and pronunciation
Vowels
- a - [a/aː]
- au - [aʊ̯]
- å - [ɔː]
- ä - [ɛ/ɛː]
- äi - [eɪ̯]
- e - [ɛ~e~ə/eː]
- ei - [aɪ̯]
- ë - [e]
- i - [ɪ/iː]
- ië - [i]
- o - [ɔ/oː]
- u - [ʊ/uː]
- uë - [u]
- ü/y - [ʏ/yː][15]
Consonants
- b - [b~p]
- c - [k~g̊]
- ch - [x~ʃ]
- ck - [k]
- d - [d~t]
- dsch - [d͡ʒ]
- f - [f]
- g - [g~k~ʃ]
- h - [h~ː]
- j - [j]
- k - [k~g̊]
- l - [l]
- m - [m]
- n - [n]
- ng - [ŋ]
- nj - [ɲ]
- p - [p~b̥]
- pf - [p͡f]
- qv - [kv]
- r - [r~∅]
- s - [s~ʃ~z]
- sch - [ʃ]
- ss - [s]
- t - [t~d̥]
- tsch - [t͡ʃ]
- v - [f/v]
- w - [v]
- x - [ks]
- z - [t͡s][16]
Bibliography
- Siebenbürgisch-Sächsisches Wörterbuch. A. Schullerus, B. Capesius, A. Tudt, S. Haldenwang et al. (in German)
- Band 1, Buchstabe A – C, 1925, de Gruyter, ASIN: B0000BUORT
- Band 2, Buchstabe D – F, 1926, de Gruyter, ASIN: B0000BUORU
- Band 3, Buchstabe G, 1971, de Gruyter, ASIN: B0000BUORV
- Band 4, Buchstabe H – J, 1972
- Band 5, Buchstabe K, 1975
- Band 6, Buchstabe L, 1997, Böhlau Verlag, ISBN 978-3-412-03286-9
- Band 7: Buchstabe M, 1998, Böhlau Verlag, ISBN 978-3-412-09098-2
- Band 8, Buchstabe N - P, 2002, Böhlau Verlag, ISBN 978-3-412-12801-2
- Band 9: Buchstabe Q - R, 2007, Böhlau Verlag, ISBN 978-3-412-06906-3
Notes
- Also spoken in Germany, Austria, several Western European countries, and in North America, more specifically in the United States and Canada.
References
- "Transylvanian Saxon (Siweberjesch Såksesch)". Omniglot. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Victor Rouă (19 August 2015). "A Brief History Of The Transylvanian Saxon Dialect". The Dockyards. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Vu(m) Nathalie Lodhi (13 January 2020). "The Transylvanian Saxon dialect, a not-so-distant cousin of Luxembourgish". RTL. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Stephen McGrath (10 September 2019). "The Saxons first arrived in Romania's Transylvania region in the 12th Century, but over the past few decades the community has all but vanished from the region". BBC Travel. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- "Dictionary of Transylvanian Saxon Dialects". Institute of Social Sciences and Humanities Sibiu. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Gisela Richter (1960). "Zur Bereicherung der siebenbürgisch-sächsischen Mundart durch die rumänische Sprache/On the Enrichment of the Transylvanian-Saxon Dialect by the Romanian Language" (in German). Editura Academiei Române. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Bancu, Ariana. (2020). Two case studies on structural variation in multilingual settings. Proceedings of the Linguistic Society of America. 5. 750. 10.3765/plsa.v5i1.4760.
- Ariana Bancu (March 2020). "Transylvanian Saxon dialectal areas". Two case studies on structural variation in multilingual settings. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Popescu, Karin (12 October 1996). "Vast Corruption Revealed In Ceausescu Visa Scheme". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- "Transylvanian Saxons". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Nationalia (17 November 2014). "Saxon, Lutheran President for Romania: Klaus Iohannis and the "job well done"". Nationalia. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Robert Schwartz (20 October 2015). "Breathing new life into Transylvania's crumbling cultural sites". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- "Table no. 8". Recensământ România (in Romanian). Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- "Transylvanian Saxon". Omniglot. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- "Transylvanian Saxon language". Omniglot. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- "Transylvanian Saxon language". Omniglot. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
External links
- SibiWeb: Die Sprache des siebenbürgisch-sächsischen Volkes von Adolf Schullerus (German)
- Verband der Siebenbürgersachsen in Deutschland: Sprachaufnahmen in siebenbürgisch-sächsischer Mundart - Audiosamples (German, Såksesch)
- Siebenbürgersachsen Baden-Württemberg: Die Mundart der Siebenbürger Sachsen von Waltraut Schuller (German)
- Hörprobe in Siebenbürgersächsisch (Mundart von Honigberg - Hărman) und Vergleich mit anderen Germanischen Sprachen (German)
На других языках
[de] Siebenbürgisch-Sächsisch
Siebenbürgisch-Sächsisch (Eigenbezeichnung: Siweberjesch Såksesch oder einfach Såksesch, rumänisch: săsește, ungarisch: erdélyi szász, landlerisch: Soksisch) ist die Sprache der Siebenbürger Sachsen. Gesprochen wird Siebenbürgisch-Sächsisch von ca. 200.000 Sprechern in Deutschland, Österreich sowie der ursprünglichen Herkunftsregion Siebenbürgen im heutigen Rumänien.- [en] Transylvanian Saxon dialect
[fr] Dialecte saxon de Transylvanie
Le dialecte saxon de Transylvanie (saxon : Siweberjesch-Såksesch or Såksesch, allemand : Siebenbürgisch-Sächsisch ou Siebenbürgisch-Sächsische Sprache, roumain : Limba săsească ou Dialectul săsesc, hongrois : Erdélyi szász nyelv) est un dialecte allemand parlé par les Saxons de Transylvanie[1].[it] Dialetto sassone di Transilvania
Il dialetto sassone di Transilvania (Siweberjesch Såksesch) è un dialetto che deriva dal dialetto mosellano, parlato in Romania.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии