lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Sudovian (also known as Yotvingian, or Jatvingian) was a Western Baltic language of Northeastern Europe. Sudovian was closely related to Old Prussian. It was formerly spoken southwest of the Nemunas river in what is now Lithuania, east of Galindia and north of Yotvingia, and by exiles in East Prussia.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (October 2017) |
| Sudovian | |
|---|---|
| Yotvingian, Jatvingian | |
| Native to | Yotvingia |
| Extinct | 17th century? |
Language family | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xsv |
Linguist List | xsv |
| Glottolog | None |
History
This section does not cite any sources. (November 2019) |
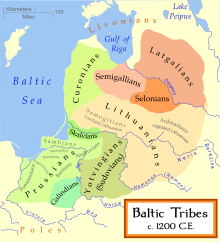
Sudovia and neighboring Galindia were two Baltic tribes or nations mentioned by the Greek geographer Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD as Galíndai and Soudinoí, (Γαλίνδαι, Σουδινοί). Yotvingian and Sudovian are identical in nature, however the Sudovian tribe is commonly grouped with other East Prussian tribes. In reality, the Yotvingian tribe had close linguistic ties to the East Prussian tribes, though were an independent and rather isolated people nonetheless.[citation needed]
Peter of Dusburg, in his 14th-century Chronicon terrae Prussiae, refers to Sudovia and to its inhabitants as Sudovites.
After the district was conquered by the Teutonic Knights, the language died out and its speakers were gradually absorbed by German, Lithuanian and Slavic populations.
The language has six grammatical cases: nominative, vocative, accusative, genitive, dative and locative, and a complex morphology with a variety of moods. It was a frontier dialect of Old Baltic, which preserved many archaic features which had been lost in the Middle Baltic group.
Sudovian was very similar to and mutually intelligible with the archaic Old Prussian language, as stated in the introduction to the 1st Old Prussian Catechism (printed in Königsberg – 1545 – the 1st Baltic language book):
Die Sudawen aber wiewol ihre rede etwas nyderiger wissen sich doch inn diese preüßnische sprach : wie sie alhie im Catechismo gedruckt ist auch wol zuschicken und vernemen alle wort – "But the Sudovians, although their speech is somewhat lower, understand this Prussian language, as it is printed in the Catechism, and they express themselves well and understand every word".
There are also some Sudovian language phrases in "Warhafftige Beschreibung der Sudawen auff Samland sambt ihren Bock heyligen und Ceremonien" – True Description of the Sudovians in Samland together with their goat sanctifications and ceremonies – written in the mid-16th century by Hieronymus Meletius.
- Beigeite beygeyte peckolle.
- Kails naussen gnigethe.
- Kails poskails ains par antres. (a drinking toast)
- Kellewesze perioth, Kellewesze perioth.
- Ocho Moy myle schwante Panike.
John Poliander wrote in 1535 about the Sudovians living near Königsberg, Prussia, that 32 villages used Sudini speech in a 6–7 mile stretch of land of the Samland Corner that bears the name of Sudavia. They spoke a language similar to the Old Prussian language, but they used the term gentaras for amber, not the Samlandish (Old Prussian) term. From him we learn that the Sudovians lived secluded from the Samlandish, that they married within their own tribe, and did not allow intermarriage with the neighbouring Prussian population "even if begged". They stubbornly held to their own traditions, and wore finger and ear rings with bronze bells and silver belts. Nothing was imported from abroad, but everything was produced by local craftsmen. Christoph Hartknoch reported in 1684 that there were still Sudovians there.[citation needed]
The Constit. Synod. Evangel. of 1530 contains the following list of deities who were still worshipped by the Sudavians in Samland: "Occopirmus, Sualxtix, Ausschauts, Autrympus, Potrympus, Bardoayts, Piluuytis, Parcunas, Pecols,..." (Hastings, p 488)
Toponyms from N.E. Poland, N.W. Belarus, and Lithuania also preserve words. Sudovian was influenced by the Gothic language, as was Old Prussian. As did other West Baltic dialects, it preserved the nominative singular neuter case ending – absent from Latvian and Lithuanian. In the declension of nouns, five cases are the same as in Old Prussian: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative. The vocative example "Kails naussen gnigethe." is listed above. The noun declension was very conservative and preserved many archaic features.
The Yotvingian territories of Sudovia and Galindia were later overrun and populated by Slavs around present-day Białystok and Suwałki in north-eastern Poland and nearby Hrodna (formerly Grodno) in Belarus. Some elements of Baltic speech are still retained in the Belarus and Ukraine territory, owing to the sparse indigenous populations and resettlements of refugees from Lithuania. The dialect of Zietela (Belarusian Дзятлава, Russian Дятлово, Yiddish Zietil, Polish Zdzięcioł) was of particular interest. Kazlauskas (1968, p. 285) suggested that the word mėnas ("month") (dative singular mënui) encountered in dialects (Zietela, Lazdijai) and in the writings of Bretkūnas is a remnant of nouns with the stem suffix -s.
Polish-Yotvingian vocabulary
Until the 1970s, Yotvingian was chiefly known from toponyms and medieval Russian sources.[1] But in 1978, a monument with Yotvingian writing was discovered by accident. In Belarus, a young man named Vyacheslav Zinov,[2] an amateur collector, bought a book of Catholic prayers from an old man from Novy Dvor village in the depths of Białowieża Forest, which held a small manuscript titled "Pagan Dialects from Narew" (Pogańskie gwary z Narewu). It was written partly in Polish, and partly in an unspecified, "pagan" language. Unfortunately, Zinov's parents threw away the book. However, before the manuscript was destroyed, Zinov had made notes of it which he sent to Vilnius University in 1983. Even though Zinov's notes were riddled with errors, it has been proven beyond doubt that the notes are indeed a copy of an authentic Yotvingian text.[3][4] According to the first person who analyzed the manuscript, Zigmas Zinkevičius, this short Yotvingian–Polish dictionary (of just 215 words[Note 1]), "Pagan Dialects from Narew", appears to have been written by a Catholic priest[Note 2] in order to preach to locals in their mother tongue. Concerning the language, Zinkevičius put forth three possible versions:
- a Yotvingian dialect under a heavy influence of Lithuanian;
- Lithuanian words over a strong Yotvingian substratum;
- the compiler of the dictionary could not tell Lithuanian from Yotvingian clearly, and may have included words from both. The latter version is indirectly supported by the name of the document: "Dialects", rather than "Dialect".[4] Some scholars did not rule out the possibility of forgery, but there are strong indications it was not.[6]
See also
- Yotvingians / Sudovians
- Sudovian glossary (Narew) on Wiktionary
Notes
- In fact there were 214 words, since one Polish word, "bośian" (Modern Polish, bocian, "stork" was translated three times, with two translations, starkas and gerwe identified, while the third one, aucm was not, whereas to a Russian speaker it is immediately evident that it is a cursive writing for the Russian word "аист" for "stork"; probably a note by Zinov for himself.[5]
- Possibly the priest was a native Belarusian, since some words in the "Polish" part were actually Belarusian
References
- Kapović (2008, p. 96)
- Rakhno, Kostiantyn (24 November 2012). "Terra Sudorum. At one time scattered between the Neman and Western Bug Rivers, the Yotvingians contributed to the development of several Eastern European nations". The Ukrainian Week. Retrieved 11 June 2015.
- Kapović (2008, p. 97)
- Зинкявичюс З. "Польско-ятвяжский словарик?", Балто-славянские исследования, 1983. — Moscow, Наука, 1984, pp. 3—29. (Zinkevičius Z. Lenkų-jotvingių žodynėlis?, Baltistica, XXI(1), 1985; with a photocopy of Zinov's manuscript. Continued in Baltistica, XXI(2), 1985, pp. 184–193); English-language version, expanded: Zinkevičius, Zigmas, "A Polish-Yatvingian vocabulary?" In: Linguistic and Oriental studies from Poznań. 1992, pp. 99–133
- Орёл В.Э., Хелимский Е.А. Наблюдения над балтийским языком польско-«ятвяжского» словарика, Балто-славянские исследования, 1985, Moscow, Наука, 1987, vol. 6, pp. 121—134
- Witczak, Krzysztof Tomasz (2015). ""The Pagan dialects from Narew" in the light of Yatvingian onomastic remnants" (PDF). Baltic from an Indo-European perspective: 43–44. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
Bibliography
- Kapović, Mate (2008), Uvod u indoeuropsku lingvistiku (in Croatian), Zagreb: Matica hrvatska, pp. 96–97, ISBN 978-953-150-847-6
- Catechiſmus jn Peüßniſcher ſprach, Königsberg, Hans Weinreich, 1545, p. 3
- 2nd edition: Catechiſmus jn preüßniſcher ſprach, gecorrigiret vnd dagegen das deüdsche, Königsberg, Hans Weinreich, 1545
- Hartknoch, Christophorus, Alt- und Neues Preussen. Franckfurt & Leipzig, 1684 (Google Books)
- Būga, K., Kalba ir senovė, I, Vilnius, 1922, p. 78
- Būga, K., Lietuvių kalbos žodynas, I, Vilnius, 1924, p. LXXV
- Kazlauskas J., 1968, Lietuvių Kalbos Istorinė Gramatika [Historical Grammar of Lithuanian], Vilnius, 1968, p 285
- Salys, A, Sūduviai [including Sūdovian language], Sūduvių Kampas. Liet. Enciklopedija, XXIX, Boston, USA, 1963, pp 114–126
- Schmalstieg, W. R., Studies in Old Prussian, (1976) University Park and London, pp 17–23, 91–93, ISBN 0-271-01231-5
- Mažiulis, V., Prūsų kalbos paminklai, t. II (1981) Vilnius, pp 62–64, 67–68.
- Mažiulis, V., Prūsų kalbos etimologijos žodynas,t. IV, (1997) Vilnius, pp 166–167, ISBN 5-420-01406-8
- Vidugiris, A., Zietelos Šnektos žodynas [A Dictionary of the Subdialect of Zietela.], Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidybos institutas, 1998
- Vidugiris, A., Mikulėnienė, D, ZIETELOS ŠNEKTOS TEKSTAI. I dalis [Texts of the Zietela Subdialect. Part I], Vilnius, 2005, ISBN 9986-668-73-5 (1 dalis), ISBN 9986-668-74-3 (2 dalys)
- Mikuleniene, D., Concerning the Influence of the Western Balts on the Accentuation System of Western Lithuanian Dialects, Acta Baltico-Slavica, Instytut Slawistyki Polskiej Akademii Nauk, 2006, vol: 30, pp 89–96
- Naktinienė, G., Paulauskienė,A., Vitkauskas, V., Druskininkų tarmės žodynas, Vilnius 1988
- Zinkevičius, Z., Lietuvių kalbos dialektologija, Vilnius 1994
- Z. Zinkevičius. Lietuvių dialektologija, Vilnius 1966
- Zinkevičius, Z, The History of the Lithuanian Language (1996) Vilnius: Mokslas pp 50–53 ISBN 5-420-01363-0
- Zinkevičius Z. Lenkų-jotvingių žodynėlis? – Rinktiniai straipsniai. T. I. Vilnius, 2002. P. 30–60.
- Zinkevičius Z. Nauja apie jotvingių kalbą – Rinktiniai straipsniai. T. I. Vilnius, 2002. P. 61–66.
- Gimbutas, Marija, The Balts, (1963) London : Thames and Hudson, pp 19, 22–23, 83, 112, 126, 139, 141, 147, 159.
- Gerullis, G., Zur Sprache der Sudauer-Jotwinger. Festschrift Bezzen-berger, 1921, p. 44
- Hastings, J., Encyclopaedia of Religion and Ethics: Volume IX, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1917, pp 488
External links
На других языках
[de] Jatwingische Sprache
Jatwingisch (auch Sudauisch, jatw. jātviun/sūdaviun bilā) war eine westbaltische Sprache der Jatwinger (Balten), eines mit den Prußen verwandten Stammes zwischen Weichsel und Memel (Baltikum). Nach der Eroberung des Gebietes durch den Deutschritterorden starb sie aus, die Jatwinger gingen allmählich im deutschen, litauischen (ostbaltischen) und slawischen Element auf.- [en] Sudovian language
[fr] Sudovien
Le sudovien ou yotvingien est une langue éteinte appartenant au groupe balte occidental des langues indo-européennes.[it] Lingua jatvingica
Lo jatvingico (conosciuto anche come sudoviano[1]) era una lingua baltica occidentale nell'Europa nordorientale. Strettamente imparentato con l'antico prussiano, veniva parlato a sud-ovest del fiume Nemunas, in Galindia ed in Sudovia, territori più tardi conosciuti come Prussia orientale e Lituania sudoccidentale. La Sudovia e la Galindia erano due delle dodici originali terre prussiane. Anche se non rappresentavano due lingue separate, sudovico e jatvingico si differenziavano come dialetti già nel X secolo, ed è stato documentato negli scritti. Era una lingua sia molto arcaica, sia molto influenzata dalle lingue germaniche, come tutti gli altri dialetti baltici (come si deriva dal prestito germanico, virdan, "parola", che preserva la desinenza di genere neutro -an, assente dal lettone e dal lituano).[ru] Ятвяжский язык
Ятвяжский язык — язык балтийского племени ятвягов, или судавов (судинов), один из балтийских языков. Не путать со славянским «ятвяжским» микроязыком. Выделяются два ареала, названия которых послужили основой для двух рядов названий всего языка в разных языках: для немцев и литовцев ближе был судавский, для поляков и восточных славян — ятвяжский.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии