lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Alyutor or Alutor is a language of Russia that belongs to the Chukotkan branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2021) |
| Alyutor | |
|---|---|
| nəməlʔu | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Kamchatka |
| Ethnicity | Alyutors |
Native speakers | 25, 5% of ethnic population (2010 census)[1] |
Language family | Chukotko-Kamchatkan
|
| Dialects |
|
Writing system | Cyrillic script |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | alr |
| Glottolog | alut1245 |
| ELP | Alutor |
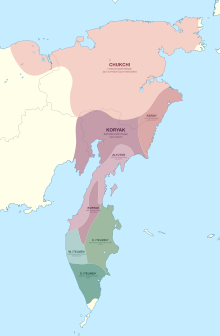 Pre-contact distribution of Alyutor (light purple) and other Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages | |
 Alutor is classified as Severely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
Sociolinguistic situation
The Alutor are the indigenous inhabitants of the northern part of the Kamchatka Peninsula. The language is unwritten and moribund; in the 1970s residents of the chief Alutor village of Vyvenka under the age of 25 did not know the language. In recent years the Vyvenka village school has started teaching the language. Until 1958 the language was considered the "village" (settled) dialect of the Koryak language, but it is not intelligible with traditionally nomadic varieties of Koryak. The autonym [ˈnəməlʔən] means "villager".
Orthography
| А а | Б б | В в | Вʼ вʼ | Г г | Гʼ гʼ | Ғ ғ | Д д |
| Е е | Ә ә | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й | К к |
| Ӄ ӄ | Л л | М м | Н н | Ӈ ӈ | О о | П п | Р р |
| С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш |
| Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Typology
Alutor is a polysynthetic language.
ŋan(.ina)
that+3PL
ulʲlʲaʔu.tku=ʔuttə-k
walk.into.woods.masked=stick-LOC
na-n.illitə-tkə-ni-na…
LOW.A-hang-IPF-3.SG.A+3P-3PL.P
'Those things on a stick, which wear masks, hung ... '[dubious ] Unknown glossing abbreviation(s) (help);
The morphology is agglutinative, with extensive prefixes and suffixes.
qəlʲippə
bread+NOM+SG
tətu-kki
eat.with.something-CVB
ɣeqə⟩masla⟨ta
ASSOC⟩butter⟨ASSOC
n-ə-mal-qin.
good
'Bread (eaten) with butter is excellent.'
The argument structure is ergative.
ən-an(nə)
he-ERG
ɣəmmə
me+ABS
ina-ɣal-i.
1SG.P-walk.past-3SG.A
'He walked past me.'
The word order is variable, and it is difficult to say which typology is basic. The verb-absolutive orders AVO and VAO are perhaps most common.
tita·qa
once
qutkinʲnʲaqu-nak
(name)-ERG+SG
maŋ.ki·ʔana
somewhere
ɣa⟩laʔu⟨lin
RES⟩see⟨RES+3SG.P
ʔənnə-ʔən.
fish-ABS+SG
'Once Qutkinnyaqu saw a fish somewhere.'
ɣa⟩nvə⟨lin
RES⟩poke⟨RES+3SG.P
qutkinʲnʲaqu-nak
(name)-ERG+SG
təlɣə-lŋən
finger-ABS+SG
ŋan.tiŋ.
there
'Qutkinnyaqu stuck his finger there.'
Phonology
Vowels
Alyutor has six vowels, five of which may be long or short. The schwa /ə/ cannot be long.
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i iː | u uː | |
| Mid | e eː | ə | o oː |
| Open | a aː |
Consonants
There are 18 consonants in Alyutor.[2]
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | palatalized | |||||||
| Nasal | m | n | nʲ | ŋ | ||||
| Plosive | p | t | k | q | ʔ | |||
| Fricative | v | s | ɣ | ʕ | ||||
| Approximant | w | l | lʲ | j | ||||
| Trill | r | |||||||
Stress
Stress is generally on the second syllable of the word. However, it cannot fall on an open syllable containing the vowel schwa or on the last syllable, so in two-syllable words stress is transferred to the first syllable, as long as that syllable is not open and doesn't contain the schwa. In cases where it is an open syllable containing the schwa, a third syllable is added to the end of the word and the second syllable is stressed[3] E.g /ˈmə.tan/ -> /məˈtan.nə/ 'mosquito'
Examples: /ˈmi.məl/ 'water', /qə.ˈla.vul/ 'husband', /pə.ˈla.kəl.ŋən/ 'a mukluk (boot)', /ˈta.wə.ja.tək/ 'to feed' /ˈɣəl.ɣən/ 'skin'.
Syllable structure
All Alyutor syllables begin with a single consonant. If the vowel is short, including a schwa, they may also close with a single consonant. Consonant clusters are not permitted in the word initial or word final positions. The schwa is used to brake disallowed clusters.
Examples are /ˈvi.tak/ 'to work', /ˈtil.mə.til/ 'eagle', /ˈʔitʔən/ 'parka'.
Alyutor word boundaries always coincide with syllable boundaries.
Morphology
Alyutor has the following parts of speech: nouns, adjectives, numerals, pronouns, verbs, participles, adverbs, postpositions, conjunctions, and particles.
Nouns
Nouns are inflected for number, case, definiteness, and grammatical person.
There are three grammatical numbers: singular, dual and plural.
There are eleven cases: absolutive, ergative, locative, dative, lative, prolative, contractive, causative, equative, comitative, and associative.
Number and case are expressed using a single affix. A suffix is used for all cases except the comitative and associative, which are expressed using circumfixes. There are two declensions, taught as three noun classes. The first class are nonhuman nouns of the first declension. Number is only distinguished in the absolutive case, though verbal agreement may distinguish number when these nouns are in the ergative. The second class are proper names and kin terms for elders. They are second declension, and distinguish number in the ergative, locative, and lative cases, as well as the absolutive. The third class are the other human nouns; they may be either first or second declension.
| 1st declension | 2nd declension | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| singular | dual | plural | singular | dual | plural | |
| absolutive | (stem) |
-t/-ti |
-w/-wwi |
(stem) |
-nti |
-w/-wwi |
| ergative | -a/-ta | -ənak |
-ətək | |||
| locative | -k/-ki | -ənak |
-ətək | |||
| dative | -ŋ | -ənaŋ |
-ətək | |||
| lative [clarification needed] |
-kəŋ | — | ||||
| prolative | -jpəŋ/-ɣəpəŋ (-e ~ -i) | |||||
| contactive | -jit ~ -jita | |||||
| causative | -kjit ~ -kjita | |||||
| equative | -u/-nu | -u/-ənu | ||||
| comitative | ɣa⟩…⟨a/-ta |
awən⟩…⟨ma | ||||
| associative | ɣeqə⟩…⟨a/-ta |
— | ||||
Case roles
- The absolutive case is the citation form of a noun. It is used for the argument ("subject") of an intransitive clause and the object of a transitive clause, for "syntactic possessives",[clarification needed] and for the vocative.
- The ergative is used for the agent ("subject") of a transitive verb, as an instrumental case, and as the argument of an antipassive clause.
- The locative is used for position and direction (essive and lative cases), as well as arguments which are "driven away" [clarification needed]
- The dative is used for recipients, benefactors, directional objects (allative case), and subjects of experiential verbs
- Lative is used for motion toward a goal
- Prolative is used for movement along and movement from (perlative and elative cases)
- Equative is used with the meanings 'like X', 'as X', usually with verbs like 'to become', 'to turn into', 'to work as,' etc.
- Contactive is used for objects that make contact
- Causative is used for noun phrases that cause or motivate an action
- Comitative is used for ... [clarification needed]
- Associative is used for ... [clarification needed]. It is only attested in the declension of nouns of the first declension, usually inanimate.
Grammatical person
Grammatical first and second person suffixes on nouns are used to equate a noun with participants in the discourse. They only appear in the absolutive, with an intervening j on nouns ending in a vowel and an i on nouns ending in a consonant.
| singular | dual | plural | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person | -j-ɣəm | -muri | -muru |
| 2nd person | -j-ɣət | -turi | -turu |
- …ʡopta am-ʡujamtawilʔ-ə-muru "yes we the people"
- japlə=q ʡujamtawilʔ-iɣəm "and I'm a man"
Numerals
Alyutor has simple numerals for the numbers one to five, ten, and twenty. All other numbers are compounds based on these numerals.
| ənnan | one |
| ŋitaq | two |
| ŋəruqqə | three |
| ŋəraqqə | four |
| məlləŋin | five |
| ənnanməlləŋ(in) | six (one-five) |
| ŋitaqməlləŋ(in) | seven (two-five) |
| ŋəruqməlləŋ(in) | eight (three-five) |
| ŋəraqməlləŋ(in) | nine (four-five) |
| mənɣətkin | ten |
| mənɣətək ənnan | eleven |
| qəlikkə | twenty (a score) |
| qəlikək ənnan | twenty one |
| ŋəraqmənɣətkin | forty (four tens) |
| ŋəraqmənɣətkin ŋəraqqə | forty four |
| ŋitaqməlləŋin mənɣətkin | seventy (seven tens) |
| mənɣətək mənɣətkin | hundred (ten tens) |
Verbs
There are finite (conjugated) and non-finite verbs. There are several conjugations.
Polypersonal conjugation
Finite verbs agree in person and number with their nuclear arguments; agreement is through both prefixes and suffixes. Transitive verbs agree with both arguments (ergative and absolutive), whereas intransitive verbs agree with their sole (absolutive) argument.
Verbs distinguish two aspects, perfective, the bare stem, and imperfective, using the suffix -tkə / -tkəni. There are five moods, indicative, imperative, optative, potential (marked by the circumfix ta…(ŋ)), and conjunctive (prefix ʔ-/a-).
Monopersonal conjugation
Monopersonal verbs[clarification needed] include two conjugations, one with the third-person singular in ɣa-...-lin, and the other in n-...-qin.
Impersonal conjugation
For impersonal forms of conjugation include verbal predicate (formed with the circumfix a…ka) and imperative (formed by circumfix ɣa…a/ta). Non-finite forms Impersonal forms include the verbal predicate[clarification needed] with the circumfix a…ka, and the imperative in ɣa…a/ta.
Non-finite forms
These include the infinitive, supine, gerunds, and participles.
References
- Alyutor at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Nagayama, Yukari (2003). Ocherk grammatiki aljutorskogo jazyka. Osaka: Osaka Gakuin University.
- http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/~nedoluzko/2018/docs/phonology_2018.pdf [bare URL PDF]
Bibliography
- Kibrik, A.E., S.V. Kodzasov, I.A. Murav'eva. 2000. Jazyk i fol'klor aljutorcev. Moscow: IMLI RAN Nasledie. ISBN 5-9208-0035-6
- Nagayama, Yukari. 2003. Ocherk grammatiki aljutorskogo jazyka (ELPR Publication Series A2-038). Osaka: Osaka Gakuin University.
External links
На других языках
- [en] Alyutor language
[fr] Alioutor
L’alioutor (ou alutor) est une langue paléo-sibérienne de la famille des langues tchouktches-kamtchadales, parlée dans le Nord du Kamtchatka.[ru] Алюторский язык
Алю́торский язы́к относится к чукотско-корякской ветви чукотско-камчатской семьи языков.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
