lingvo.wikisort.org - Alphabet
The Azerbaijani alphabet (Azerbaijani: Azərbaycan əlifbası, آذربایجان الفباسی, Азəрбајҹан әлифбасы) has three versions which includes the Perso-Arabic, Latin, and Cyrillic alphabets.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2020) |

North Azerbaijani, the official language of Republic of Azerbaijan, is written in a modified Latin alphabet. This superseded previous versions based on Cyrillic and Arabic scripts after the fall of Soviet Union.
In Iran, where Iranian Azerbaijanis make up the second largest ethnic group after ethnic Persians, a modified Persian script is widely used to write the South Azerbaijani language.
Azerbaijanis of Dagestan and other parts of Russia still use the Cyrillic script.[1][better source needed]
Latin Azerbaijani alphabet
The Azerbaijani Latin alphabet consists of 32 letters.
| Majuscule forms (uppercase/capital letters) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Ç | D | E | Ə | F | G | Ğ | H | X | I | İ | J | K |
| Q | L | M | N | O | Ö | P | R | S | Ş | T | U | Ü | V | Y | Z |
| Minuscule forms (lowercase/small letters) | |||||||||||||||
| a | b | c | ç | d | e | ə | f | g | ğ | h | x | ı | i | j | k |
| q | l | m | n | o | ö | p | r | s | ş | t | u | ü | v | y | z |
History
From the nineteenth century there were efforts by some intellectuals like Mirza Fatali Akhundov and Mammad agha Shahtakhtinski to replace the Arabic script and create a Latin alphabet for Azeri. In 1929, a Latin alphabet was created by Soviet Union sponsored Yeni türk əlifba komitəsi (New Turkic Alphabet Committee; Јени түрк əлифба комитəси) in Baku which hoped that the new alphabet would divide the Azerbaijanis in the USSR from those living in Iran.[2] An additional reason for the Soviet regime's encouragement of a non-Arabic script was that they hoped the transition would work towards secularizing Azerbaijan's Muslim culture and since language script reform, proposed as early as the 19th century by Azeri intellectuals (e.g. Mirza Fatali Akhundov), had previously been rejected by the Azeri religious establishment on the grounds that Arabic script, the language of the Koran, was "holy and should not be tampered with"[3] there was some historical basis for the reform which received overwhelming support at the First Turcological Congress in Baku during 1926 where the reform was voted for 101 to 7. The Azeri poet Samad Vurgun declared "Azerbaijani people are proud of being the first among Oriental nations that buried the Arabic alphabet and adopted the Latin alphabet. This event is written in golden letters of our history"[4] As a result, in the Soviet Union in 1926 the Uniform Turkic Alphabet was introduced to replace the varieties of the Arabic script in use at the time.[5] In 1939 Joseph Stalin ordered that the Azeri script used in the USSR again be changed, this time to the Cyrillic script in order to sever the Soviet Azerbaijani Turks' ties with the Turkish people in the Republic of Turkey.[6]
At the same time that the leaders of the Soviet Union were attempting to isolate the Soviet population of Azeri speakers from the neighboring populations in Persia and Turkey, the Persian government of the Azeri speaking Qajar dynasty was overthrown by Reza Shah (1925–41) who quickly established the Pahlavi dynasty and banned the publication of texts in Azeri.
When the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991 and Azerbaijan gained its independence, one of the first laws passed in the new Parliament was the adoption of a new Latin-script alphabet.
- From 1929 until 1939 (old alphabet defined using the Latin script):
- Aa, Bʙ, Cc, Çç, Dd, Ee, Əə, Ff, Gg, Ƣƣ, Hh, Ii, Ьь, Jj, Kk, Qq, Ll, Mm, Nn, Ꞑꞑ, Oo, Ɵɵ, Pp, Rr, Ss, Şş, Tt, Uu, Vv, Xx, Уy, Zz, Ƶƶ
- From 1939 until 1958 (first version of the alphabet defined using the Cyrillic script):
- Аа, Бб, Вв, Гг, Ғғ, Дд, Ее, Әә, Жж, Зз, Ии, Йй, Кк, Ҝҝ, Лл, Мм, Нн, Оо, Өө, Пп, Рр, Сс, Тт, Уу, Үү, Фф, Хх, Һһ, Цц, Чч, Ҹҹ, Шш, Ыы, Ээ, Юю, Яя, ʼ (apostrophe)
- From 1958 until 1991 (simplified version of the alphabet defined using the Cyrillic script and the letter Јј borrowed from Latin):
- Аа, Бб, Вв, Гг, Ғғ, Дд, Ее, Әә, Жж, Зз, Ии, Ыы, Јј, Кк, Ҝҝ, Лл, Мм, Нн, Оо, Өө, Пп, Рр, Сс, Тт, Уу, Үү, Фф, Хх, Һһ, Чч, Ҹҹ, Шш, ʼ (apostrophe)
- From 1991 until 1992 (first version of the modern alphabet defined using the Latin script):
- Aa, Ää, Bb, Cc, Çç, Dd, Ee, Ff, Gg, Ğğ, Hh, Xx, Iı, İi, Jj, Kk, Qq, Ll, Mm, Nn, Oo, Öö, Pp, Rr, Ss, Şş, Tt, Uu, Üü, Vv, Yy, Zz
- Since 1992 (current version of the modern alphabet defined using the Latin script, replacing Ää with the historic Əə for better sorting):
- Aa, Bb, Cc, Çç, Dd, Ee, Əə, Ff, Gg, Ğğ, Hh, Xx, Iı, İi, Jj, Kk, Qq, Ll, Mm, Nn, Oo, Öö, Pp, Rr, Ss, Şş, Tt, Uu, Üü, Vv, Yy, Zz
The Azerbaijani alphabet is the same as the Turkish alphabet, except for Әə, Xx, and Qq, the letters for sounds which do not exist as separate phonemes in Turkish. When compared to the historic Latin alphabet: Ğğ has replaced the historic Ƣƣ ; the undotted Iı has replaced the historic I with half-oval Ьь (consequently the lowercase form of B was changed from small capital ʙ to the usual b); the dotted İi has replaced the historic soft-dotted Ii; Jj has replaced the historic Ƶƶ; Öö has replaced the historic Ɵɵ; Üü has replaced the historic Yy; and Yy has replaced the historic Jј. The letters are named a, be, ce, çe, de, e, ə, fe, ge, ğe, he, xe, ı, i, je, ke/ka, qe, el, em, en, o, ö, pe, er, es, şe, te, u, ü, ve, ye, ze. W is named ikiqat ve.
Schwa (Ə)
When the new Latin script was introduced on December 25, 1991, A-umlaut (Ä ä) was selected to represent the sound /æ/. However, on May 16, 1992, it was replaced by the grapheme schwa (Ə ə), used previously. Although use of Ä ä (also used in Tatar, Turkmen, and Gagauz) seems to be a simpler alternative as the schwa is absent in most character sets, particularly Turkish encoding, it was reintroduced; the schwa had existed continuously from 1929 to 1991 to represent Azeri's most common vowel, in both post-Arabic alphabets (Latin and Cyrillic) of Azerbaijan.
Perso-Arabic Azerbaijani alphabet
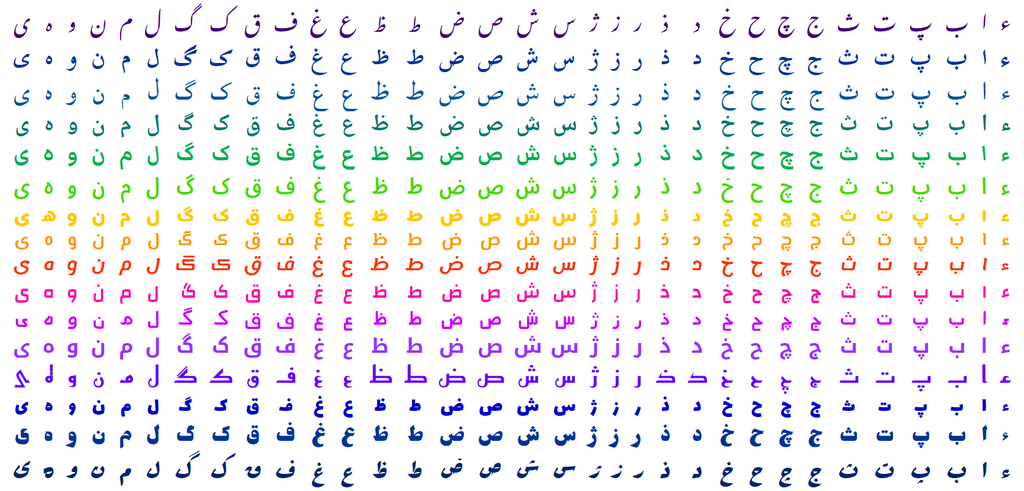
Here is the modified Persian script that is currently used by Iranian Azerbaijanis:
| ی ه و ن م ل گ ک ق ف غ ع ظ ط ض ص ش س ژ ز ر ذ د خ ح چ ج ث ت پ ب ا ء | ||
 |
Font: | |
| • | Noto Nastaliq Urdu | |
| • | Scheherazade | |
| • | Lateef | |
| • | Noto Naskh Arabic | |
| • | Markazi Text | |
| • | Noto Sans Arabic | |
| • | Baloo Bhaijaan | |
| • | El Messiri SemiBold | |
| • | Lemonada Medium | |
| • | Changa Medium | |
| • | Mada | |
| • | Noto Kufi Arabic | |
| • | Reem Kufi | |
| • | Lalezar | |
| • | Jomhuria | |
| • | Rakkas | |
| The alphabet in 16 fonts: Noto Nastaliq Urdu, Scheherazade, Lateef, Noto Naskh Arabic, Markazi Text, Noto Sans Arabic, Baloo Bhaijaan, El Messiri SemiBold, Lemonada Medium, Changa Medium, Mada, Noto Kufi Arabic, Reem Kufi, Lalezar, Jomhuria, and Rakkas. | ||
Comparison of Azerbaijani alphabets
National anthem
This section contains the national anthem of Azerbaijan, in the current Latin, Cyrillic, Jaŋalif, Georgian, and Arabic alphabets.
| 1992-present | 1991-1992 | 1958-1991 (still used in Dagestan) | 1939-1958 | 1933-1939 | 1929-1933 | until 1929 (still used in Iranian Azerbaijan) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transliteration
The Arabic, Latin, and Cyrillic alphabets each have a different sequence of letters. The table below is ordered according to the latest Latin alphabet:
| Arabic | Latin | Cyrillic | Latin | IPA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –1929 | 1922–1933 | 1933–1939 | 1939–1958 | 1958–1991 | 1991–1992 | 1992–Present | |
| آ-ا | A a | [ɑ] | |||||
| ب | B b | B ʙ | Б б | B b | [b] | ||
| ج | C c | Ç ç | Ҹ ҹ | C c | [dʒ] | ||
| چ | Ç ç | C c | Ч ч | Ç ç | [tʃ] | ||
| د | D d | Д д | D d | [d] | |||
| ائ | E e | Е е, Э э1 | Е е | [e] | |||
| ه-ٱ-اَ | Ə ə | Ä ä | Ə ə | [æ] | |||
| ف | F f | Ф ф | F f | [f] | |||
| گ | Ƣ ƣ | G g | Ҝ ҝ | G g | [ɟ] | ||
| غ | G g | Ƣ ƣ | Ғ ғ | Ğ ğ | [ɣ] | ||
| ح, ه | H h | Һ һ | H h | [h] | |||
| خ | X x | [x] | |||||
| اؽ | Į į | Ь ь | Ы ы | I ı | [ɯ] | ||
| ای | I i | И и | İ i | [ɪ] | |||
| ژ | Ƶ ƶ | Ж ж | J j | [ʒ] | |||
| ک | Q q | K k | К к | K k | [c], [ç], [k] | ||
| ق | K k | Q q | Г г | Q q | [ɡ] | ||
| ل | L l | Л л | L l | [l] | |||
| م | M m | М м | M m | [m] | |||
| ن | N n | Н н | N n | [n] | |||
| وْ | O o | [o] | |||||
| ؤ | Ɵ ɵ | Ö ö | [œ] | ||||
| پ | P p | П п | P p | [p] | |||
| ر | R r | Р р | R r | [r] | |||
| ث, س, ص | S s | С с | S s | [s] | |||
| ش | Ɜ ɜ | Ş ş | Ш ш | Ş ş | [ʃ] | ||
| ت, ط | T t | Т т | T t | [t] | |||
| ۇ | Y y | U u | У у | U u | [u] | ||
| ۆ | U u | У y | Ү ү | Ü ü | [y] | ||
| و | V v | В в | V v | [v] | |||
| ی | J j | Й й | Ј ј | Y y | [j] | ||
| یا | ЈА ја | Я я | ЈА jа | YA ya | [jɑ] | ||
| یئ | ЈE јe | Е е1 | ЈЕ је | YE ye | [je] | ||
| ئ | E e | [e] | |||||
| یوْ | ЈO јo | Йо йо | ЈО јо | YO yo | [jo] | ||
| یۇ | JY jy | ЈU јu | Ю ю | ЈУ ју | YU yu | [ju] | |
| ذ, ز, ض, ظ | Z z | З з | Z z | [z] | |||
1 – in the beginning of a word and after vowels
The Azeri Arabic alphabet also contains the letter ڴ. Originally ڴ stood for the sound [ŋ], which then merged with [n]. Initial versions of the Azeri Latin alphabet contained the letter Ꞑꞑ, which was dropped in 1938.
The letter Цц, intended for the sound [ts] in loanwords, was used in Azerbaijani Cyrillic until 1951. In Azerbaijani, like in most Turkic languages, the sound [ts] generally becomes [s].
Sources
- Hatcher, Lynley. 2008. Script change in Azerbaijan: acts of identity. International Journal of the Sociology of Language 192:105–116.
References
- "Archive of issues of the newspaper Dərbənd (Дәрбәнд)".
- Script change in Azerbaijan: acts of identity, Lynley Hatcher, International Journal of the Sociology of Language. Volume 2008, Issue 192, Pages 105–116, ISSN (Online) 1613-3668, ISSN (Print) 0165-2516, doi:10.1515/IJSL.2008.038, July 2008, page 106, http://www.degruyter.com/dg/viewarticle.fullcontentlink:pdfeventlink/$002fj$002fijsl.2008.2008.issue-192$002fijsl.2008.038$002fijsl.2008.038.pdf?t:ac=j$002fijsl.2008.2008.issue-192$002fijsl.2008.038$002fijsl.2008.038.xml
- Alakbarov, Farid (2000). Mirza Fatali Akhundov: alphabet reformer before his time. Azer-baijan International, 8(1), 53
- Wright, Sue (2004), Language Policy and Language Planning, Basingstokes: Palgrave MacMillan.
- Clement, Victoria (2005). The politics of script reform in Soviet Turkmenistan: alphabet and national identity formation. Unpublished doctoral thesis, Ohio State University, cited in "Script change in Azerbaijan: acts of identity", Lynley Hatcher, International Journal of the Sociology of Language. Volume 2008, Issue 192, Pages 105–116, ISSN (Online) 1613-3668, ISSN (Print) 0165-2516, doi:10.1515/IJSL.2008.038, July 2008, page 106, http://www.degruyter.com/dg/viewarticle.fullcontentlink:pdfeventlink/$002fj$002fijsl.2008.2008.issue-192$002fijsl.2008.038$002fijsl.2008.038.pdf?t:ac=j$002fijsl.2008.2008.issue-192$002fijsl.2008.038$002fijsl.2008.038.xml
- Script change in Azerbaijan: acts of identity, Lynley Hatcher, International Journal of the Sociology of Language. Volume 2008, Issue 192, Pages 105–116, ISSN (Online) 1613-3668, ISSN (Print) 0165-2516, doi:10.1515/IJSL.2008.038, July 2008, page 106, http://www.degruyter.com/dg/viewarticle.fullcontentlink:pdfeventlink/$002fj$002fijsl.2008.2008.issue-192$002fijsl.2008.038$002fijsl.2008.038.pdf?t:ac=j$002fijsl.2008.2008.issue-192$002fijsl.2008.038$002fijsl.2008.038.xml
External links
- Source: azeri.org
- Turned e in Azerbaijani
- Azerbaijani alphabet (with video)
На других языках
- [en] Azerbaijani alphabet
[ru] Азербайджанская письменность
Азербайджа́нский алфави́т (азерб. Azərbaycan əlifbası) — алфавит азербайджанского языка. В азербайджанском языке существуют три официальные алфавитные системы: в Азербайджане — на латинице, в Иране — на арабице, в России (Дагестан) — на кириллице.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии