lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
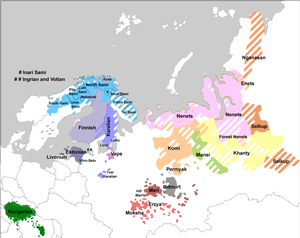
The Erzya language (эрзянь кель, eŕźań keĺ, pronounced [ˈerʲzʲanʲ ˈkelʲ]), also Erzian or historically Arisa, is spoken by approximately 300,000 people in the northern, eastern and north-western parts of the Republic of Mordovia and adjacent regions of Nizhny Novgorod, Chuvashia, Penza, Samara, Saratov, Orenburg, Ulyanovsk, Tatarstan and Bashkortostan in Russia. A diaspora can also be found in Armenia and Estonia, as well as in Kazakhstan and other states of Central Asia. Erzya is currently written using Cyrillic with no modifications to the variant used by the Russian language. In Mordovia, Erzya is co-official with Moksha and Russian.
| Erzya | |
|---|---|
| eŕźań keĺ | |
| эрзянь кель | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Mordovia, Nizhny Novgorod, Chuvashia, Ulyanovsk, Samara, Penza, Saratov, Orenburg, Tatarstan, Bashkortostan |
| Ethnicity | 610,000 (553,000 in Russia, 2010 census) |
Native speakers | 36 726 (2010 census)[1] (2010 census)[2] 430,000 Mordvin in Russia per 2010 census.[3] The 1926 census found that approximately 2/3 of ethnic Mordvins were Erzya, and the figure might be similar today[4] |
Language family | |
Writing system | Cyrillic |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Mordovia (Russia) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | myv |
| ISO 639-3 | myv |
| Glottolog | erzy1239 |
| ELP | Erzya |
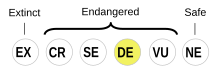 Erzya is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |

The language belongs to the Mordvinic branch of the Uralic languages. Erzya is a language that is closely related to Moksha but has distinct phonetics, morphology and vocabulary.
Phonology
Consonants
The following table lists the consonant phonemes of Erzya together with their Cyrillic equivalents.[5]
| Labial | Alveolar | (Palato-) alveolar |
Velar | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | pal. | |||||
| Nasal | /m/ м | /n/ н | /nʲ/ нь | /ŋ/ (н) | ||
| Plosive | voiceless | /p/ п | /t/ т | /tʲ/ ть | /k/ к | |
| voiced | /b/ б | /d/ д | /dʲ/ дь | /ɡ/ г | ||
| Affricate | voiceless | /t͡s/ ц | /t͡sʲ/ ць | /t͡ʃ/ ч | ||
| Fricative | voiceless | /f/ ф | /s/ с | /sʲ/ сь | /ʃ/ ш | /x/ х |
| voiced | /v/ в | /z/ з | /zʲ/ зь | /ʒ/ ж | ||
| Trill | /r/ р | /rʲ/ рь | ||||
| Approximant | /l/ л | /lʲ/ ль | /j/ й | |||
Note on romanized transcription: in Uralic studies, the members of the palatalized series are usually spelled as ń, ť, ď, ć, ś, ź, ŕ, ľ, while the postalveolar sounds are spelled č, š, ž (see Uralic Phonetic Alphabet).
Minimal pairs between /n/ and /ŋ/ include:
- /janɡa/ "along the path", in which the alveolar /n/ of the stem is retained before the prolative case ending /ɡa/, vs. /jaŋɡa/, the connegative form of the verb /jaŋɡams/ "to break"
- /jonks/ "good", subject or object complement in /ks/ translative, vs. /joŋks/ "direction; area". See Rueter 2010: 58.
Vowels
Erzya has a simple five-vowel system.[6]
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| High | i | u |
| Mid | e | o |
| Low | a | |

The front vowels /i/ and /e/ have centralized variants [ï] and [ë] immediately following a plain alveolar consonant, e.g. siń [sïnʲ] "they", seń [sënʲ] "blue".
Vowel harmony
As in many other Uralic languages, Erzya has vowel harmony. Most roots contain either front vowels (/i/, /e/) or back vowels (/u/, /o/). In addition, all suffixes with mid vowels have two forms: the form to be used is determined by the final syllable of the stem. The low vowel (/a/), found in the comparative case -шка (ška) "the size of" and the prolative -ка/-га/-ва (ka/ga/va) "spatial multipoint used with verbs of motion as well as position" is a back vowel and not subject to vowel harmony.
The rules of vowel harmony are as follows:
- If the final syllable of the word stem contains a front vowel, the front form of the suffix is used: веле (veĺe) "village", велесэ (veĺese) "in a village"
- If the final syllable of the word stem contains a back vowel, and it is followed by plain (non-palatalized) consonants, the back form of the suffix is used: кудо (kudo) "house", кудосо (kudoso) "in a house"
However, if the back vowel is followed by a palatalized consonant or palatal glide, vowel harmony is violated and the "front" form of the suffix is used: кальсэ (kaĺse) "with willow", ойсэ (ojse) "with butter". Likewise, if a front-vowel stem is followed by a low back vowel suffix, subsequent syllables will contain back harmony: велеванзо (veĺevanzo) "throughout its villages"
Thus the seeming violations of vowel harmony attested in stems, e.g. узере (uźere) "axe", суре (suŕe) "thread (string)", are actually due to the palatalized consonants /zʲ/ and /rʲ/.
One exception to front-vowel harmony is observed in palatalized non-final /lʲ/, e.g. асфальтсо (asfaĺtso) "with asphalt".
Morphology
Like all other Uralic languages, Erzya is an agglutinative language which expresses grammatical relations by means of suffixes.
Nouns
Nouns are inflected for case, number, definiteness and possessor. Erzya distinguishes twelve cases (here illustrated with the noun мода moda "ground, earth"). Number is systematically distinguished only with definite nouns; for indefinite nouns and nouns with a possessive suffix, only nominative case has a distinct plural.[6][5]
| Case | Indefinite | Definite | 1st person sg. possessive | 2nd person sg. possessive | 3rd person sg. possessive | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| singular | plural | singular | plural | singular | plural | singular/plural | singular | plural | |
| nominative | мода moda | мода-т moda-t | мода-сь moda-ś | мода-тне moda-ťńe | мода-м moda-m | мода-н moda-n | мода-т moda-t | мода-зo moda-zo | мода-нзo moda-nzo |
| genitive | мода-нь moda-ń | мода-нть moda-ńť | мода-тне-нь moda-ťńe-ń | ||||||
| dative/allative | мода-нень moda-ńeń | мода-нтень moda-ńťeń | мода-тне-нень moda-ťńe-ńeń | ||||||
| inessive | мода-со moda-so | мода-сонть moda-sońť | мода-тне-сэ moda-ťńe-se | мода-со-н moda-so-n | мода-со-т moda-so-t | мода-со-нзo moda-so-nzo | |||
| elative | мода-сто moda-sto | мода-стонть moda-stońť | мода-тне-стэ moda-ťńe-ste | мода-сто-н moda-sto-n | мода-сто-т moda-sto-t | мода-сто-нзo moda-sto-nzo | |||
| illative | мода-с moda-s | мода-нтень moda-ńťeń | мода-тне-с moda-ťńe-s | мода-з-oн moda-z-on | мода-з-oт moda-z-ot | мода-з-oнзo moda-z-onzo | |||
| prolative | мода-ва moda-va | мода-ванть moda-vańť | мода-тне-ва moda-ťńe-va | мода-ва-н moda-va-n | мода-ва-т moda-va-t | мода-ва-нзo moda-va-nzo | |||
| ablative | мода-до moda-do | мода-донть moda-dońť | мода-тне-дe moda-ťńe-ďe | мода-до-н moda-do-n | мода-до-т moda-do-t | мода-до-нзo moda-do-nzo | |||
| lative | мода-в moda-v | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| translative | мода-кс moda-ks | мода-ксонть moda-ksońť | мода-тне-кс moda-ťńe-ks | мода-кс-oн moda-ks-on | мода-кс-oт moda-ks-ot | мода-кс-oнзo moda-ks-onzo | |||
| abessive | мода-втомо moda-vtomo | мода-втомонть moda-vtomońť | мода-тне-втеме moda-ťńe-vťeme | мода-втомо-н moda-vtomo-n | мода-втомо-т moda-vtomo-t | мода-втомо-нзo moda-vtomo-nzo | |||
| comparative | мода-шка moda-ška | мода-шканть moda-škańť | мода-тне-шка moda-ťńe-ška | мода-шка-н moda-ška-n | мода-шка-т moda-ška-t | мода-шка-нзo moda-ška-nzo | |||
Plural possessors follow the pattern of second person singular possessors.
| Case | 1st pers. pl. poss. | 2nd pers. pl. poss. | 3rd pers. pl. poss. |
|---|---|---|---|
| singular/plural | singular/plural | singular/plural | |
| nominative | мода-нoк moda-nok | мода-нк moda-nk | мода-ст moda-st |
| inessive (...) |
мода-со-нoк moda-so-nok (...) | мода-со-нк moda-so-nk (...) | мода-со-ст moda-so-st (...) |
Verbs
Erzya verbs are inflected for tense and mood, and are further conjugated for person of subject and object.[5][6] Traditionally, three stem types are distinguished: a-stems, o-stems and e-stems. A-stems always retain the stem vowel a in the non-third person present tense forms, and in the third person first past tense forms (e.g. pala-ś "kissed"). With many o-stems and e-stems, the stem vowel is dropped in these forms (e.g. o-stem van-ś "watched", e-stem ńiľ-ś "swallowed"), but there also o- and e-stem verbs which retain the vowel (udo-ś "slept", piďe-ś "cooked"). Rueter (2010) therefore divides verb stems into vowel-retaining stems and vowel-dropping stems.[7]
In indicative mood, three tenses are distinguished: present/future, first past, second (=habitual) past.
| present/future tense | first past tense | second past tense | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-stem | o-stem | e-stem | a-stem | e-stem | a-stem | ||
| 1sg | мора-н mora-n |
ван-ан van-an |
пил-ян piľ-an |
сод-ы-нь sod-i-ń |
мер-и-нь meŕ-i-ń |
моры-линь mori-ľiń | |
| 2sg | мора-т mora-t |
ван-ат van-at |
пил-ят piľ-at |
сод-ы-ть sod-i-ť |
мер-и-ть meŕ-i-ť |
моры-лить mori-ľiť | |
| 3sg | мор-ы mor-i |
ван-ы van-i |
пил-и piľ-i |
содa-сь soda-ś |
мер-сь meŕ-ś |
моры-ль mori-ľ | |
| 1pl | мора-тано mora-tano |
ван-тано van-tano |
пиль-тяно piľ-ťano |
сод-ы-нек sod-i-ńek |
мер-и-нек meŕ-i-ńek |
моры-линек mori-ľińek | |
| 2pl | мора-тадо mora-tado |
ван-тадо van-tado |
пиль-тядо piľ-ťado |
сод-ы-де sod-i-ďe |
мер-и-де meŕ-i-ďe |
моры-лиде mori-ľiďe | |
| 3pl | мор-ыть mor-iť |
ван-ыть van-iť |
пил-ить piľ-iť |
содa-сть soda-śť |
мер-сть meŕ-śť |
моры-льть mori-ľť | |
| infinitive | мора-мс mora-ms |
вано-мс vano-ms |
пиле-мс piľe-ms |
сода-мс soda-ms |
мере-мс meŕe-ms |
мора-мс mora-ms | |
| 'sing' | 'watch' | 'swallow' | 'know' | 'say' | 'sing' | ||
The third person singular form in present tense is also used as present participle. The second past tense is formed by adding the past tense copula -ľ to the present participle.
The other mood categories are:
- conditional (-ińďeŕa + present suffixes)
- conjunctive (-v(o)ľ + past suffixes)
- conditional-conjunctive (-ińďeŕa-v(o)ľ + past suffixes)
- desiderative (-ikseľ + past suffixes)
- optative (zo + present suffixes)
- imperative (-k/-do)
| conditional | conjunctive | conditional-conjunctive | desiderative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1sg | ярс-ындеря-н jars-ińďeŕa-n |
ярсa-влинь jarsa-vľiń |
ярс-ындеря-влинь jars-ińďeŕa-vľiń |
мор-ыксэлинь mor-ikseľiń |
| 2sg | ярс-ындеря-т jars-ińďeŕa-t |
ярсa-влить jarsa-vľiť |
ярс-ындеря-влить jars-ińďeŕa-vľiť |
мор-ыксэлить mor-ikseľiť |
| 3sg | ярс-ындеря-й jars-ińďeŕa-j |
ярсa-воль jarsa-voľ |
ярс-ындеря-воль jars-ińďeŕa-voľ |
мор-ыксэль mor-ikseľ |
| 1pl | ярс-ындеря-тано jars-ińďeŕa-tano |
ярсa-влинек jarsa-vľińek |
ярс-ындеря-влинек jars-ińďeŕa-vľińek |
мор-ыксэлинек mor-ikseľińek |
| 2pl | ярс-ындеря-тадо jars-ińďeŕa-tado |
ярсa-влиде jarsa-vľiďe |
ярс-ындеря-влиде jars-ińďeŕa-vľiďe |
мор-ыксэлиде mor-ikseľiďe |
| 3pl | ярс-ындеря-йть jars-ińďeŕa-jť |
ярсa-вольть jarsa-voľť |
ярс-ындеря-вольть jars-ińďeŕa-voľť |
мор-ыксэльть mor-ikseľť |
| infinitive | ярса-мс jarsa-ms |
ярса-мс jarsa-ms |
ярса-мс jarsa-ms |
мора-мс mora-ms |
| 'eat' | 'eat' | 'eat' | 'sing' |
Writing
Cyrillic alphabet
The modern Erzya alphabet is the same as for Russian:[5]
А
/a/Б
/b/В
/v/Г
/ɡ/Д
/d/Е
/je/Ё
/jo/Ж
/ʒ/З
/z/И
/i/Й
/j/К
/k/Л
/l/М
/m/Н
/n/О
/o/П
/p/Р
/r/С
/s/Т
/t/У
/u/Ф
/f/Х
/x/Ц
/t͡s/Ч
/t͡ʃ/Ш
/ʃ/Щ
/ʃt͡ʃ/Ъ
/-/Ы
/ɨ/Ь
/◌ʲ/Э
/e/Ю
/ju/Я
/ja/
The letters ф, х, щ and ъ are only used in loanwords from Russian. The pre-1929 version of the Erzya alphabet included the additional letter Cyrillic ligature En Ge (Ҥ ҥ) in some publications, (cf. Evsevyev 1928).
In combination with the alveolar consonants т, д, ц, с, з, н, л, and р, vowel letters are employed to distinguish between plain and palatalized articulations in a similar way as in Russian: а, э, ы, о, у follow plain alveolars, while я, е, и, ё, ю follow palatalized alveolars, e.g. та /ta/, тэ /te/, ты /ti/, то /to/, ту /tu/ vs. тя /tʲa/, те /tʲe/, ти /tʲi/, тё /tʲo/, тю /tʲu/. If no vowel follows, palatalization is indicated by ь, e.g. ть /tʲ/. Following non-alveolar consonants, only а, е, и, о, у occur, e.g. па /pa/, пе /pe/, пи /pi/, по /po/, пу /pu/.
Latin alphabet
A Latin alphabet was officially approved by the government of Nizhne-Volzhskiy Kray in 1932, but it was never used:[8]
- a в c ç d ә e f g y i j k l m n o p r s ş t u v x z ƶ ь
A modern version of Latin alphabet exists:[9]
- a b c č ć d d́ e f g h i j k l ĺ m n ń o p r ŕ s š ś t t́ u v y z ž ź
| Cyrillic | Latin |
| a | a |
| б | b |
| в | v |
| г | g |
| д | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — d́ |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — d | |
| e | at the beginning of a word — je |
| after a vowel — je | |
| after a consonant — e | |
| ë | at the beginning of a word — jo |
| after a vowel — jo | |
| after a consonant — o | |
| ж | ž |
| з | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — ź |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — z | |
| и | at the beginning of a word — i |
| after a consonant — i | |
| after a vowel — ji | |
| й | j |
| к | k |
| л | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — ĺ |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — l | |
| м | m |
| н | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — ń |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — n | |
| o | o |
| п | p |
| p | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — ŕ |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — r | |
| c | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — ś |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — s | |
| т | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — t́ |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — t | |
| у | u |
| ф | f (only in loanwords) |
| x | h (only in loanwords) |
| ц | before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — ć |
| not before e,ë,и,ь,ю,я — c | |
| ч | č |
| ш | š |
| щ | št́ (only in loanwords) |
| ъ | - |
| ы | i |
| ь | - |
| э | e |
| ю | at the beginning of a word — ju |
| after a vowel — ju | |
| after a consonant — u | |
| я | at the beginning of a word — ja |
| after a vowel — ja | |
| after a consonant — a |
See also
- Erzya people
- Erzya literature
- Erzyan Mastor
Bibliography
- A.I. Bryzhinskiy, O.V. Pashutina, Ye.I. Chernov. Писатели Мордовии Биобиблиографический справочник. Saransk: Mordovskoye Knizhnoye Izdatelystvo, 2001. ISBN 5-7595-1386-9.
- Vasilij D'omin. Сюконян тенк... Эрзянь писательде ёвтнемат. Saransk, 2005. ISBN 5-7595-1665-5.
- Ksenija Djordjevic & Jean-Leo Leonard. Parlons Mordve. Paris: L'Harmattan, 2006, ISBN 2-296-00147-5.
- Makar E. Evsev'ev. Основы мордовской грамматика, Эрзянь грамматика. С приложением образцов мокшанских склонений и спряжений. Москва: Центральное издательство народов СССР, 1928.
- Jack Rueter. Adnominal Person in the Morphological System of Erzya. Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran Toimituksia 261. Helsinki: Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura, 2010, ISBN 978-952-5667-23-3 [print], ISBN 978-952-5667-24-0 [online].
- D.V. Tsygankin. Память запечатленная в слове: Словарь географических названий республики Мордовия. Saransk, 2005. ISBN 5-7493-0780-8.
References
- Официальная публикация итогов Всероссийской переписи населения 2010 года. Т. 1. Численность и размещение населения // Федеральная служба государственной статистики
- Erzya at Ethnologue (24th ed., 2021)
- "Population of the Russian Federation by Languages (in Russian)" (PDF). gks.ru. Russian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
- Jack Rueter (2013) The Erzya Language. Where is it spoken? Études finno-ougriennes 45
- Saarinen, Sirkka. "Erzya e-learning course" (PDF). Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München. Retrieved 2019-03-05.
- Zaicz, Gábor (1998). "Mordva". In Abondolo, Daniel (ed.). The Uralic Languages. London: Routledge. pp. 184–218.
- Rueter, Jack (2010). Adnominal Person in the Morphological System of Erzya. Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran Toimituksia 261. Helsinki: Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura.
- Г. Аитов (1932). Новый алфавит. Великая революция на востоке (in Russian). Саратов: Нижневолжское краевое изд-во. p. 61—64.
- Aasmäe, Niina. An introductory course of the Erzya language. Tartu Ülikool.
External links
 Media related to Erzya language at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Erzya language at Wikimedia Commons
- Finno-Ugric Electronic Library by the Finno-Ugric Information Center in Syktyvkar, Komi Republic (interface in Russian and English, texts in Mari, Komi, Udmurt, Erzya and Moksha languages):
- Erzjanj Mastor – The society for preserving the Erzya language (in Erzya and Russian)
- https://web.archive.org/web/20061029185215/http://www.info-rm.com/er/index.php News in the Erzya and Moksha Mordvinian languages
- Эрзянский язык
- Erzya – Finnish/English/German/Russian dictionary (robust finite-state, open-source)
- Erzya studies reference bibliography under construction.
- Russian-Moksha-Erzya Dictionary
- Russian-Erzya Dictionary
На других языках
[de] Ersjanische Sprache
Das Ersja-Mordwinische (ersjanisch э́рзянь ersjan’) ist einer der beiden Hauptdialekte der mordwinischen Sprache, die zur wolgafinnischen Gruppe der finno-ugrischen Sprachen gehört. Es wird auch Ersa-Mordwinisch geschrieben.[1] Gesprochen wird diese Sprache in den nördlichen Teilen der Republik Mordwinien.- [en] Erzya language
[es] Idioma erzya
El erzya (э́рзянь кель, érzyañ kel) es un idioma urálico hablado por 500.000 personas al norte, este y noroeste de la República de Mordovia y las regiones adyacentes de Nizhni Nóvgorod, Chuvasia, Penza, Samara, Sarátov, Oremburgo, Uliánovsk, Tartaristán y Baskortostán en Rusia. También se habla en la diáspora —en Armenia, Estonia, Kazajistán y otras antiguas repúblicas soviéticas centroasiáticas— a causa de la emigración de sus hablantes a estas áreas. El erzya se escribe en alfabeto cirílico sin modificaciones de la variante usada en el idioma ruso. En Mordovia, el erzya es cooficial con el moksha y el ruso.[fr] Erzya
L'erzya ou erza (autonyme : эрзянь кель (erzänʹ kelʹ)) est l'une des deux langues mordves avec le mokcha. Il est parlé dans le nord, l'est et le nord-ouest de la République de Mordovie et les régions voisines de Nijni Novgorod, de la Tchouvachie, de Penza, Samara, Saratov, Orenbourg, Oulianovsk, du Tatarstan et du Bachkortostan en Russie. Il existe également une diaspora en Arménie, Estonie, au Kazakhstan et dans les autres nouveaux états indépendants d'Asie centrale. En Mordovie, l'erzya a le statut de langue officielle au même titre que le mokcha et le russe.[it] Lingua erza
La lingua erza[1][2] (nome nativo эрзянь кель o erzjan' kel') è una lingua mordvina parlata in Russia, nella regione del Volga.[ru] Эрзянский язык
Эрзя́нский язы́к (также эрзя-мордовский[3]; самоназвание — эрзянь кель) — финно-угорский язык финно-волжской группы мордовской подгруппы, язык эрзян, один из трёх государственных языков Республики Мордовия, наряду с мокшанским и русским.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии