lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Tagish was a language spoken by the Tagish or Carcross-Tagish, a First Nations people that historically lived in the Northwest Territories and Yukon in Canada. The name Tagish derives from /ta:gizi dene/, or "Tagish people", which is how they refer to themselves, where /ta:gizi/ is a place name meaning "it (spring ice) is breaking up.[3]
| Tagish | |
|---|---|
| Tā̀gish | |
| Native to | Canada |
| Ethnicity | Tagish people |
| Extinct | 2008, with the death of Lucy Wren[1][2] |
Language family | Dené–Yeniseian?
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | tgx |
| Glottolog | tagi1240 |
| ELP | Tagish |
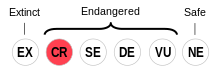 Tagish is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
The language is a Northern Athabaskan language, closely related to Tahltan and Kaska. The three languages are often grouped together as Tahltan-Kaska-Tagish; the three languages are considered dialects of the same language by some.[4] As of 2004, there was only 1 native fluent speaker of Tagish documented: Lucy Wren (Agaymā/Ghùch Tlâ).[5] She died in 2008.[6]
Classification
Tagish is among many other languages within the large language family of Na-Dene languages,[7] which includes another group of indigenous North American languages called the Athabaskan languages.[8] The Northern Athabaskan languages are often considered to be part of a complex of languages entitled Tagish-Tahltan-Kaska. The languages in this complex have an extremely similar lexicon and grammar but differ in systems of obstruents.[4] Known alternatively as Dene K'e, Tagish is also closely related to the neighboring languages Tahltan, Kaska, and Southern Tutchone.[9]
History
The culture of the Tagish people has its roots in both the coastal Indian cultures and those from the interior (Tlingit and Athabaskan languages, Athapaskan respectively).[5] Trade and travel across the Chilkoot pass contributed to the mixing of these cultures. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Tlingit-speaking peoples began to move in from the coast and intermarry with the native Tagish-speaking population. By the time outsiders first made contact in the 1880s, the majority of the people were bilingual, and the Tlingit language had replaced Tagish as the language of the majority.[5]
Tagish became less common partially because native traditions were domesticated and suppressed in writing by the colonial administration.[10] The most significant impact on the decline of nearly every native language in Canada came when aboriginal children were forced to attend residential schools where they were forbidden to speak their own languages.[11]
After the Yukon Gold Rush in 1898, English became the majority language of the area. As the majority of children attended the English-only Chooutla Anglican school nearby, fluency in the native languages began to be lost. Language courses began to be reintroduced in the 1970s, but the programs had little funding and were not comparable to the French or English programs present. More recently, political awareness has led to movements to gain constitutional provisions for the language, as well as a greater focus on in-school programs, language conferences, and public awareness.[9] For example, beginning in 2004, Southern Tutchone and Tagish languages were being revitalized and protected through an on-line approach called FirstVoices.
The federal government signed an agreement giving the territory $4.25 million over five years to "preserve, develop and enhance aboriginal languages",[12] however Tagish was not one of the offered native language programs. Ken McQueen stated that despite efforts, the language will likely become extinct after the last fluent Tagish speaker dies.[13]
Tagish on First Voices
FirstVoices is an indigenous language computer database and web-based teaching and development tool.[14] Tagish was one of the first to be added to the FirstVoices digital multimedia archive of endangered indigenous languages.[9] Resources on the site include sound files of name pronunciation, word lists, and some children's books written in the language. This language documentation is intended to create a holistic platform where identity, oral tradition, elders' knowledge and the centrality of the land can all be intertwined.[15] On the Tagish FirstVoices page, there are a total of 36 words and 442 phrases archived and sound recordings of the alphabet. To provide a cultural context, there are also a community slide show and art gallery section. This website includes greetings from a multitude of elders complete with contact information about the website's contributors.[16]
Notable people
Angela Sidney was a prominent activist for the use and reclamation of her Tagish language and heritage in the southern Yukon Territory. Born in 1902, her heritage was Tagish on her father's side and Tlingit on her mother's side. Sidney's accomplishments include working with Julie Cruikshank, documenting and authoring traditional stories[17] as well as becoming a member of the Order of Canada in 1986. Sidney died in 1991.[18]
Lucy Wren was the last known fluent speaker. She was actively involved in the recordings and stories used on the First Voices website including the "Our Elders Statement" before passing in 2008.[19] This work by Lucy Wren has been continued by her son Norman James as he works to record more language and culture of the Tagish and Tlingit people for the Yukon Native Language Centre and the First Voices website.[20]
Geographic Distribution
The Tagish people make their territory in southern Yukon Territory and northern British Columbia in Canada,[3] most specifically at Tagish, which lies between Marsh Lake and Tagish Lake, and Carcross, located between Bennett and Nares Lake.[5] The language was used most frequently in the Lewes and Teslin plateaus.
Phonology
The Tagish language includes aspiration, glottalization, nasal sounds, resonance, and tones.[21]
Tagish is characterized by the simplest stem-initial consonant system of the Northern Athabaskan languages, has a conservative vowel system and conserves stem-final consonants. Final glottalization is lost. Constricted vowels are pronounced with low tone.[21]
The Tagish language includes nouns, verbs, and particles. Particles and nouns are single, sometimes compounded, morphemes, but the difference is that nouns can be inflected and particles cannot. Verbs are the most complex class in this language because their stemmed morphemes have many prefixes which indicate inflectional and derivational categories.[22]
The total inventory of phonemes present in Tagish includes:[23]
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Velar | Glottal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | sibilant | lateral | ||||||
| Plosive | voiceless | t | t͡s | t͡ɬ | t͡ʃ | k | ʔ | |
| aspirated | tʰ | t͡sʰ | t͡ɬʰ | t͡ʃʰ | kʰ | |||
| ejective | tʼ | t͡sʼ | t͡ɬʼ | t͡ʃʼ | kʼ | |||
| prenasal | ᵐb | ⁿd | ||||||
| Nasal | m | n | ||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | s | ɬ | ʃ | x | h | ||
| voiced | z | ɮ | ʒ | ɣ | ||||
| Approximant | j | w | ||||||
Vowels
The short vowels /i, e, a, o, u/; as well as their long counterparts /iː, eː, aː, oː, uː/.[24]
Tone
High tone is marked with (v́) on short vowels and (v́v) on long vowels while low tones remain unmarked[25]
Vocabulary
Some women's names contain the nasalized prefix Maa which translates directly to "mother of."[25]
Writing System
The language makes use of the Latin writing system.[26] The Tagish alphabet, as seen in how it is written, is present in the table below.
| Tagish Alphabet | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consonants | Stops and Affricates | d | dl | dz | j | g | ||
| t | tl | ts | ch | k | ||||
| t' | tl' | ts' | ch' | k' | ' | |||
| Fricatives | ł | s | sh | x | h | |||
| l | z | zh | ÿ | |||||
| Nasals | m | n | ||||||
| mb | nd | |||||||
| Glides | w | y | ||||||
| Vowels | Short | i | e | a | o | u | ||
| Long | ī | ē | ā | ō | ū | |||
Nasal vowels are denoted by a hook as follows: (ᶏ).
See also
- Tagish
- Tahltan
References
- "Lucy Wren • Biography". Archived from the original on 2011-05-24.
- Tagish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Yinka Déné Language Institute. (2006). The Tagish Language. https://www.ydli.org/langs/tagish.htm
- Alderete, J., Blenkiron, A., &Thompson, J. E. (2014). Some notes on stem phonology and the development of affricates in Tahltan (Northern Athabaskan). Ms., Simon Fraser University and Northwest Community College.
- Greenaway, J. (2006, November 08). Tagish First Voices Project. http://www.firstvoices.com/en/Tagish/welcome
- "Carcross elder steps forward to continue language work of mother and sister". Yukon News. 2015-04-01. Retrieved 2021-05-05.
- Na-Dene Language Family. (2016). Salem Press Encyclopedia
- Olson, Tamara. (1999). The Na-Dene Languages. Brigham Young University. Retrieved from http://linguistics.byu.edu/classes/Ling450ch/reports/na-dene.html
- Moore, Patrick; Hennessy, Kate (2006). "New Technologies and Contested Ideologies: The Tagish FirstVoices Project". The American Indian Quarterly. 30 (1): 119–137. doi:10.1353/aiq.2006.0006. JSTOR 4138916. S2CID 144741485. ProQuest 216858891.
- Remie, Cornelius H. W. (2002). "Narrative and Knowledge in the Yukon Territory: A Review Article". Anthropos. 97 (2): 553–557. JSTOR 40466054.
- Unrau, Jason (8 April 2010). "Parties at odds over preserving languages". Whitehorse Star. p. 4. ProQuest 362432339.
- MacQueen, Ken (10 September 1989). "Native tongue was a sin, punishment was the strap". The Gazette. p. A4. ProQuest 431847503.
- MacQueen, Ken (6 September 1989). "The Tagish language is Angela Sidney, age 87, and only Angela Sidney". Southam News. p. 1. ProQuest 460878484.
- "Protecting the past with the future". Whitehorse Star. 7 November 2005. p. 5. ProQuest 362290009.
- Moore, Patrick; Hennessy, Kate (2006). "New Technologies and Contested Ideologies: The Tagish FirstVoices Project". The American Indian Quarterly. 30 (1): 119–137. doi:10.1353/aiq.2006.0006. JSTOR 4138916. S2CID 144741485. ProQuest 216858891.
- "Tagish First Voices".
- Ruppert, James (2001). "Tagish". Our Voices: Native Stories of Alaska and the Yukon: 169–186.
- "Angela Sidney". Retrieved 2017-11-12.
- Wren, Lucy. "Our Elders Statement". Retrieved 2017-11-12.
- "Yukon News".
- Krauss, M. E., & Golla, V. K. (1978). Northern Athapaskan languages. In Handbook of North American Indians: Subarctic (Vol. 6, pp. 67-85). Government Printing Office 1978.
- Helm, June. (1981). Handbook of North American Indians: Subarctic. Smithsonian Institution
- McClellan, C. (1978). Tagish. In Handbook of North American Indians: Subarctic (Vol. 6, pp. 481-492). Government Printing Office 1978.
- Aboriginal Language Services (1994). Tagish Literacy Workshop. Tagish, Yukon.
- Cruikshank, Julie; Sidney, Angela; Smith, Kitty; Ned, Annie (1992). Life Lived Like a Story: Life Stories of Three Yukon Native Elders. UBC Press. ISBN 978-0-7748-0413-4.[page needed]
- "YNLC•Tagish". Archived from the original on 2008-04-17. Retrieved 2008-05-25.
External links
- Yukon Native Language Centre's introduction to the Tagish Language
- OLAC resources in and about the Tagish language
- The Tagish First Voices Project. http://www.firstvoices.com/en/Tagish/welcome
- Word list. http://www.firstvoices.com/en/Tagish/words
- Phrases. http://www.firstvoices.com/en/Tagish/phrase-books
- Audio files of First Words. http://www.firstvoices.com/en/Tagish
- Audio files, word lists, and other resources at Glottlog. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/tagi1240
- List of English-Tagish word lists. Renato, F. B. (2014, March 21). Freelang Tagish-English dictionary. Retrieved from http://www.freelang.net/dictionary/tagish.php
- Cruikshank, Julie (1992). "Images of Society in Klondike Gold Rush Narratives: Skookum Jim and the Discovery of Gold". Ethnohistory. 39 (1): 20–41. doi:10.2307/482563. JSTOR 482563.
- Cruikshank, Julie (1990). "Getting the Words Right: Perspectives on Naming and Places in Athapaskan Oral History". Arctic Anthropology. 27 (1): 52–65. JSTOR 40316196.
- Cruikshank, Julie (1981). "Legend and Landscape: Convergence of Oral and Scientific Traditions in the Yukon Territory". Arctic Anthropology. 18 (2): 67–93. JSTOR 40316002.
- The Endangered Languages Project. http://www.endangeredlanguages.com/lang/1448
На других языках
- [en] Tagish language
[fr] Tagish (langue)
Le tagish (autonyme : Tā̀gish) est la langue parlée par les Tagishs du Yukon. Il fait partie des langues athapascanes septentrionales. Il est presque éteint, une poignée de gens le parle. Le kaska et le tahltan sont des langues proches, et sont parfois considérés comme étant des variétés d’une seule langue avec le tagish.[it] Lingua tagish
La lingua tagish è la lingua parlata dal popolo Tagish dello Yukon nel Canada nord-occidentale.[ru] Тагиш (язык)
Язык тагиш (тагиш, Tā̀gish khwáan) — вымерший язык народа тагиш, был распространён в Канаде, в территории Юкон. Относится к атабаскским языкам языковой семьи на-дене. Последний носитель языка умер в 2008 году[1].Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии