lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
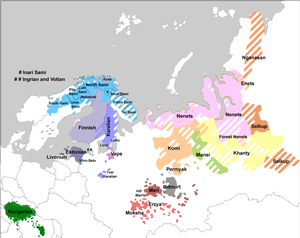
Selkup language is the language of the Selkups, belonging to the Samoyedic group of the Uralic language family. It is spoken by some 1,570 people (1994 est.) in the region between the Ob and Yenisei Rivers (in Siberia). The language name Selkup comes from the Russian "cелькупский язык" (selkupsky yazyk), based on the native name used in the Taz dialect, шӧльӄумыт әты šöľqumyt әty, lit. forest-man language. Different dialects use different names.
| Selkup | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| Ethnicity | Selkup people |
Native speakers | 1,000 (2010 census)[1] |
Language family | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | sel |
| ISO 639-3 | sel |
| Glottolog | selk1253 |
| ELP | |
 Northern Selkup is classified as Severely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
Selkup is fractured in an extensive dialect continuum whose ends are no longer mutually intelligible. The three main varieties are the Taz (Northern) dialect (тазовский диалект, tazovsky dialekt), which became the basis of the Selkup written language in the 1930s, Tym (Central) dialect (тымский диалект, tymsky dialekt), and Ket dialect (кетский диалект, ketsky dialekt). It is not related to the Ket language.
Phonology
There are 25 vowel and 16 consonant phonemes in the Taz dialect.
| Labial | Dental | Palatal(ized) | Velar | Uvular | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasals | m | n | nʲ | ŋ | [ɴ] |
| Plosives | p | t | tʲ | k | q |
| Fricatives | s | ʃʲ | |||
| Trills | r | [ʀ] | |||
| Laterals | l | lʲ | |||
| Approximant | w | j |
- Voicing is not phonemic. Stops and fricatives may be voiced between vowels or after sonorant consonants.
- The palatalized stop and fricative /tʲ/, /ʃʲ/ are most typically rendered as an alveolo-palatal affricate [tɕ] and fricative [ɕ]. Depending on the speaker, the former can be also realized as the stop [tʲ], the latter as a non-palatalized fricative, postalveolar [ʃ] or retroflex [ʂ].
- Before front vowels, palatalized variants of other consonants are also found.
- [ɴ] and [ʀ] are allophones of /q/ when occurring before nasals and liquids, respectively.
- The non-coronal stops /p/, /k/, /q/ have optional fricative allophones [f], [x], [χ] when occurring before /s/ or /ʃʲ/.
| Front | Central | Back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | |||
| Tense | Close | i, iː | y, yː | ɨ, ɨː | u, | uː |
| Mid | e, eː | ø, øː | ɘ, ɘː | o, oː | ||
| Open | æ, æː | a, aː | ||||
| Lax | Close | ɪ, ɪː | [ɪ̈ ~ ə] | |||
| Mid | ɛ, ɛː | ɔː | ||||
- Vowel length is phonemic. /ɔː/ alone, deriving from proto-Selkup */aː/, has no short counterpart.
- The tenseness contrast, an innovation of northern Selkup, is independent of length (e.g. /i/, /iː/, /ɪ/, /ɪː/ all contrast).
- The full range of vowel quality contrasts is only possible in the initial syllable of a word: in later syllables, /e/ /ø/ /ɘ/ /y/ /ɨ/ of either length do not occur, nor does long /uː/. (Shown on a darker gray background.)
- The non-phonemic lax central vowel [ɪ̈ ~ ə] only occurs in unstressed non-first syllables; it is normally treated equivalent with short tense /ɨ/.
Selkup has a syllable structure (C)V(C). Word-initial /ŋ/ and word-final /tʲ/ or /w/ do not occur. Various consonant clusters and geminate consonants such as /nt/, /rm/, /ʃʲʃʲ/ may occur, though many potential combinations occurring morphologically are simplified.
Stress in Selkup is marginally phonemic. Generally the rightmost long vowel in a word is stressed, or otherwise the first syllable, but certain suffixes with short vowels may acquire stress, leading to minimal pairs such as [ˈtɕɛlʲtɕalqo] "to stamp down" vs. [tɕɛlʲˈtɕalqo] "to stamp once".
References
- Selkup at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Helimski 1998, pp. 551–552.
Works cited
- Helimski, Eugene (1998). "Selkup". In Abondolo, David (ed.). The Uralic Languages. London: Routledge. pp. 548–579. ISBN 0-415-08198-X.
External links
- Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia: The Selkup Language
- The Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire: The Selkups
- Audio of a man telling a story in Selkup
На других языках
[de] Selkupische Sprache
Die selkupische Sprache (früher auch Ostjak-Samojedisch oder Wald-Samojedisch genannt) ist eine der samojedischen Sprachen. Diese bilden gemeinsam mit den finno-ugrischen Sprachen die uralische Sprachfamilie. Selkupisch ist die einzige noch existierende südsamojedische Sprache. Sie wird vom Volk der Selkupen in der Region zwischen den Flüssen Ob und Jenissei gesprochen. Die Zahl der Muttersprachler wird mit rund 1.500 angegeben (etwa die Hälfte des selkupischen Volkes). Im täglichen Umgang setzt sich jedoch immer mehr das Russische durch. Bis zur vierten Klasse wird an manchen Schulen noch in Nord-Selkupisch unterrichtet.- [en] Selkup language
[es] Idioma selkup
El selkup es una lengua urálica hablada por el pueblo siberiano de los selkup que pertenece al grupo de las lenguas samoyedas, como el idioma nenezo. Es hablado por unas 1.570 personas (est. en 1994, 10000 según Ethnologue[1]) en la región situada entre los ríos Obi y Yenisei.[fr] Selkoupe
Le selkoupe (anciennement, ostyak samoyède) est une langue ouralienne, dernière survivante du groupe des langues samoyèdes du Sud. Il est parlé en Russie, en Sibérie, par 1 570 des 3 600 membres de l'ethnie selkoupe.[it] Lingua selcupa
La lingua selcupa[1] o selkup[2] (in russo селькупский язык) è una lingua samoieda parlata in Russia all'est dei Monti Urali.[ru] Селькупский язык
Сельку́пский язы́к (устар. название остяко-самоедский язык) — язык селькупов, относящийся к самодийским языкам. Число говорящих — около 1 тыс. человек. Распространён на северо-востоке и востоке Западной Сибири.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии