lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Tundra Nenets is a Uralic language spoken in European Russia and North-Western Siberia. It is the largest and best-preserved language in the Samoyedic group.[2]: 1–2
| Tundra Nenets | |
|---|---|
| Nenec, Nenetsy, Nentse, Yurak, Yurak Samoyed | |
| Native to | Northern Russia |
| Ethnicity | Nenets |
Native speakers | 21,900 (2010)[1] |
Language family | |
Writing system | Cyrillic |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | tund1255 |
| ELP | Tundra Nenets |
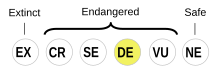 Tundra Nenets is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
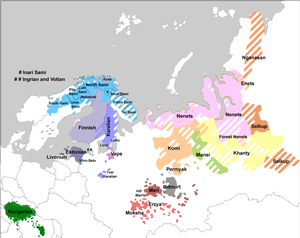
Tundra Nenets is closely related to the Nganasan and Enets languages, and more distantly to Selkup. Tundra Nenets and its sister language, Forest Nenets, are sometimes considered dialects of a single Nenets language, though there is low mutual intelligibility between the two. In spite of the large area in which Tundra Nenets is spoken, the language is very uniform with few dialectal differences.[3]: 13
Geographically, the Tundra Nenets territory spans the Nenets District of the Arkhangelsk Province, as well as parts of the Komi Republic, the Yamal-Nenets District in the Tyumen Province, and the Ust-Yeniseisk region of the Taimyr District in the Krasnoyarsk Region. This territory has been in constant growth over the past millennium, as Tundra Nenets settlers moved further east and engaged with other groups of Enets.[2]: 3
A 2010 census reported 44,640 Nenets, 49% of whom were speakers of the Nenets language. However, while the population of Nenets has been growing in the past few decades, the language itself has been in a decline, as many children are now educated in Russian-language schools and many other ethnic groups have begun settling in Tundra Nenets territories.[2]: 5–6 The language is classified as 6b (Threatened), indicating that it is still spoken by all age generations, but the number of speakers in decreasing.[4]
Tundra Nenets is spoken primarily within family circles and in traditional economic activities, such as hunting and herding reindeer. The language has no official status within the Russian Federation. In the mid 1930s, an orthography based on the Cyrillic script was developed, which is taught in local schools. However, many Tundra Nenets speakers are primarily literate in Russian. Nonetheless, there is a small amount of Tundra Nenets literature, as well as radio and television broadcasts.[2]: 7–8
Phonology
The syllable structure of Tundra Nenets is generally CV(C), and syllables with initial, medial or final consonant clusters of more than two consonants are not allowed. Words normally do not begin with a vowel, except in western dialects of the language, mostly due to the loss of /ŋ/, so the standard Tundra Nenets word ŋarka ('big') is found as arka in western varieties.[5]
Vowels
The number of vowel phonemes in Tundra Nenets is 10, which have 17 distinct allophones governed by palatality, which dominates whole sequences of vowels and consonants.[6] Vowel frontness is not segmentally contrastive.
Monophthong vowels are present in the chart below. Phonemes are marked in bold, with their palatal (on the left) and non-palatal (on the right) allophones marked underneath using the International Phonetic Alphabet.
| Unrounded | Rounded | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | Long | /í/ [(ʲ)iː], [ɨː] |
/ú/ [(ʲ)ʉː], [uː] |
| Short | /i/ [(ʲ)i], [ɨ] |
/u/ [(ʲ)ʉ], [u] | |
| Mid | Tense | /e/ [(ʲ)eː], [ɤː] |
/o/ [(ʲ)ɵː], [oː] |
| Lax | /°/ [ə] |
||
| Open | Tense | /a/ [(ʲ)aː], [ɑː] |
|
| Lax | /ø/ [(ʲ)ɐ], [ʌ] |
||
There is also a vowel ⟨æ⟩, which is interchangeably realized as [æ͡e̘] or [æː]. This and the long close vowels only occur in word-initial syllables.
Vowel reduction
In much of the literature on Tundra Nenets and its sister dialect, Forest Nenets, a so-called reduced vowel is mentioned. This reduced vowel was thought to have two distinct qualities depending on whether it was found in a stressed or unstressed position. In stressed position it was transcribed as ⟨ø⟩ and represented a reduced variant of an underlying vowel, and in unstressed position it was transcribed as ⟨â⟩ and represented a reduced variant of /a/. Recently, however, it has become clear that the reduced vowels are in fact short vowels, counterparts to their respective long vowels. Today ⟨â⟩ should simply be replaced by ⟨a⟩, while ⟨ø⟩ simply represents a short vowel, although it is not specified which short vowel in this orthography.[7]
Consonants
The number of consonant phonemes in Tundra Nenets is 27.[8] All labial and coronal consonants other than the semivowels /w/ and /j/ have plain and palatalized counterparts.
| Bilabial | Coronal | Velar | Glottal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | Pala. | Plain | Pala. | ||||
| Nasal | m | mʲ | n | nʲ | ŋ | ||
| Stop | Voiceless | p | pʲ | t | tʲ | k | ʔ |
| Voiced | b | bʲ | d | dʲ | |||
| Affricate | Voiceless | ts | tsʲ | ||||
| Fricative | Voiceless | s | sʲ | x | |||
| Approximant | Semivowel | w[lower-alpha 1] | j | w[lower-alpha 1] | |||
| Lateral | l | lʲ | |||||
| Trill | r[lower-alpha 2] | rʲ | |||||
- Eastern dialects realize this as the pure bilabial [β].[9]
- The trill [r] may be uvular [ʀ] or a uvular fricative [ʁ] for some speakers.
All consonants can be found word-internally between vowels, but their occurrence in other positions is strongly limited.[10]
- Only the 16 consonants shown on darker gray background may occur word-initially.
- Syllable-finally, most consonant contrasts are not found, and only six consonants occur: /b/, /ʔ/, /m/, /n ~ ŋ/, /l/, /r/.
Sandhi
Tundra Nenets has a phonological process of sandhi: the simplification of consonant clusters, both within words (in e.g. inflection) and between words. This allows considering some of the consonant phonemes secondarily derived from underlying consonant clusters.[11]
- Fortition of fricatives: when preceded by a consonant, the fricatives /s/, /sʲ/, /x/ become the affricates / stops /ts/, /tsʲ/, /k/ respectively.
- A syllable-final glottal stop /ʔ/ is lost before any obstruent consonants.
- A word-final non-labial nasal /n/ is lost when followed by a sonorant, and becomes a glottal stop utterance finally. Within a word, the cluster /nj/ may occur.
As the citation form of a noun is the bare stem, a word ending in a glottal stop in isolation can thus underlyingly end either in a plain glottal stop, or in a nasal. The latter is sometimes called a "nasalizable glottal stop", and is in the orthography of the language written differently from the former.
Syllable structure
Tundra Nenets has a (C)V(C) syllable structure, and the minimal word is CV. Thus, there are no word initial or word final consonant clusters, nor are there any three-consonant clusters. Moreover, syllables with zero onset typically cannot occur word-initially, but in Western dialects, the word-initial ŋ is lost, giving some vowel-initial words. For example, the Eastern dialect ŋəno 'boat' becomes əno in the Western dialect.[2]: 27 Word-internally, zero onset syllables only occur when ə or ° follow another vowel. For example, such vowel clusters can occur when forming the finite stem: me° 'he takes (3SG)' gives meə-s'° 'he took (3SG.PST).'[2]: 27–28
Stress
Tundra Nenets displays bisyllabic trochaic feet that are aligned to the left. Primary stress falls on the initial syllable. Secondary stress falls on subsequent odd syllables and on even-position syllables preceding a syllable with °, excluding the final syllable,[2]: 28 as illustrated in the following examples where ´ indicates primary stress on a vowel and ` indicates secondary stress on the preceding vowel:
méŋa-xə`yu-n°
take-DU.OBJ-1SG[2]: 28
méŋa-xə`yu-nə`-s'°
take-DU.OBJ-1SG-PAST[2]: 28
mé-nake`-x°yu`-n'ə-s'°
take-PROB-DU.OBJ-1SG-PAST[2]: 28
Morphology
Typical of the Uralic language family, Tundra Nenets has an agglutinating morphological structure with a wide variety of suffixes. There is no prefixation. The two primary word classes are nouns and verbs. Other word classes include adjectives, pronouns, numerals, adverbs, postpositions, conjunctions, particles, and interjections.[2]: 8–9
A noun can contain up to five morphemes, including the root, a derivational suffix, a possessive suffix, a number suffix, and a case suffix. A verb can contain up to six or seven morphemes, including the root, one or two derivational suffixes, a tense suffix, a mood suffix, a subject agreement suffix, and an object agreement suffix. Although the morphology is predominately agglutinating, there are some suffixes that express multiple meanings, as well as periphrastic clausal negation and some auxiliary verbs.[2]: 8–9
Derivational affixes
Tundra Nenets contains a few nominal derivational affixes that can be used to denote a cause, express an instrument, or refer to a location of action. For example, the noun xərwa-bco 'wish' can be derived from the verb xərwa- 'to want'.[2]: 31 There are also several mixed categories of nouns that have a syntactic distribution of a different word-class, yet share other properties with nouns. For example, the proprietive suffix -sawey° can be used to derive nouns with the meaning 'with X, having X', as in yī-sawey° 'intelligent' (from yī 'mind').[2]: 32
Tundra Nenets has two verbal aspectual classes, perfective and imperfective. There are several derivational aspectual suffixes which can change the aspectual class of a verb. For example, imperfectivizing suffixes can be used to express durative, frequentative, multiplicative, and iterative meanings, such as in tola-bə 'to keep counting' (from tola- 'to count').[2]: 45 There are also denominal verbs with the meaning 'to use as X, to have as X', which are formed from the accusative plural stem, such as in səb'i-q' 'to use as a hat' (from səwa 'hat').[2]: 46
Inflectional affixes
Nouns are inflected for number (singular, dual, plural), case (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, locative, ablative, prolative), and possessive, which can indicate the person and number of the possessor.[2]: 9 For example, the following noun is inflected for similative case and third person plural number.
numke-rəxa-q
star-SIM-3PL
'like stars'[2]: 73
Verbs are inflected for agreement, tense, and mood. Present tense is unmarked, but Tundra Nenets distinguishes inflectionally the past, future, habitual, and future-in-the-past tenses. There are sixteen moods, which include the imperative, hortative, optative, conjunctive, necessitative, interrogative, probabilitative, obligative, potential, and inferential.[2]: 9 For example, the verb below is inflected for subjunctive mood, first person singular agreement, and past tense.
Clitics
Clitics undergo the same phonological processes and stress assignment as affixes. They can attach to an affirmative finite verb, a negative auxiliary, or a non-verbal final predicate, and follow any other inflection,[2]: 116 as shown with the following exclamative clitic:[2]: 117
Particles
Particles are primarily used for discourse. Common particles include yekar°q 'it is unknown', ŋod'°q 'hardly', tǣr'i 'just, very', and məs'iq 'maybe, perhaps.'[2]: 53 An example is given below:
Compounding
There are some lexical noun-noun compounds in Tundra Nenets. As shown in the following example, the first element in the compound can always be modified and take a number.[2]: 167
Suppletion
A few irregular verbs show suppletion. The most frequent suppletive verbs are xǣ- ‘to go, to depart’, ŋǣ- ‘to be’, to- ‘to come’, ta- ‘to bring, to give’ and the negative auxiliary nʹi-. Some common suppletive forms for these verbs are given in the table below.[2]: 25
| to go/depart | to be | to come | to bring, give | negative auxiliary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3SG | xəya | ŋa | to° | ta° | nʹī |
| CONNEG | xanʹ°q | ŋaq (~ŋǣq) | tuq | taq | - |
| IMPF PART | xǣn(ʹ)a | ŋǣda | tona | tada~tana | nʹinʹa |
| IMP 2SG | xanʹ°q | ŋaq | tuq | taq | nʹon° |
| FUT 3SG | xan°tə° | ŋǣŋu | tūtə° | tətə° | - |
Syntax
Basic word order
Tundra Nenets is predominantly a head-final SOV language.[2]: 9 Verb finality is the primary constraint on word order.[2]: 213 Below are examples of the basic word order for a transitive and intransitive sentence.
məy°mpə-da
cheerful-IMPF.PART
Wera
Wera
Maša-m
Masha-ACC
pad°ta°-da
draw-3SG > SG.OBJ
‘Cheerful Wera drew Masha.’[2]: 197
However, although most simple sentences have SOV order, a more general trend is for the informationally new element to be immediately preverbal and to be preceded by the informationally old element. So, it is possible to have sentences where the direct object precedes the subject,[2]: 214 as illustrated below:
Possessee + possessor
The possessor precedes the thing being possessed.[2]: 142
Adjective (comparative) + standard
Comparative adjectives follow their standards, which take the ablative case.[2]: 174
t’uku°
This
pəni°
coat
taki°
that
pəne-xəd°
coat-ABL
səwa(-rka)
good-COMP
‘This coat is better than that one.’[2]: 174
Determiner + noun phrase
The determiner precedes the noun phrase.[2]: 141–142
Orthography
The alphabet of Tundra Nenets is based on Cyrillic, with the addition of three letters: Ӈ ӈ, ʼ, and ˮ.
Vowels
The palatalized and plain vowel allophones are distinguished in the original orthography[3]: 36–37
| phonemic transcription | a | e | o | i | u | æ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyrillic | Plain | а | э | о | ы | у | э |
| Palatalized | я | е | ё | и | ю | ||
The Cyrillic orthography does not distinguish the reduced vowel from a, nor the long ī and ū from their short counterparts i and u. ǣ is not found in a palatalized environment, and thus does not show up in the chart. The schwa, [ə], has no direct counterpart in the Cyrillic orthography and is in most cases not written. However, it may sometimes appear as ⟨а⟩, ⟨я⟩, ⟨ы⟩, ⟨ӗ⟩ or ⟨ŏ⟩. For example, xad°, ('snowstorm') is written as хад, and nix° ('power') is written as ныхы.[3]: 34–35
Consonants
The consonants in the Cyrillic orthography can be seen in the chart below. Note that palatalized consonants are not included.[3]: 38
| phonemic transcription | /m/ | /p/ | /b/ | /w/ | /n/ | /t/ | /d/ | /ts/ | /s/ | /j/ | /l/ | /r/ | /ŋ/ | /k/ | /x/ | /ʔ/ | /ʔ/ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyrillic | м | п | б | в | н | т | д | ц | с | й | л | р | ӈ | к | х | ˮ | ʼ |
The letter ⟨ˮ⟩ marks a "plain" glottal stop, while ⟨ʼ⟩ marks a glottal stop derived from a word-final n. As in Russian, the consonants are palatalized using the soft sign, ⟨ь⟩. For example, the palatalized consonant m' is represented with ⟨мь⟩ in Cyrillic unless it is followed by a palatalizing vowel, such as ⟨ё⟩, so that m'o is written as ⟨мё⟩.[3]: 38
Sample text
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
Ет
Et
хибяри
xibjari
ненэць
nenėc’
соямарианта
sojamarianta
хуркари
xurkari
правада
pravada
тнява,
tnjava,
ӈобой
ṇoboj
ненээя
nenėėja
ниду
nidu
нись
nis’
токалба,
tokalba,
ӈыбтамба
ṇybtamba
илевату
ilevatu
тара.
tara.
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.[12]
References
- Daniel Abondolo, 1998. The Uralic Languages, p. 517.
- Nikolaeva, Irina (2014). A grammar of Tundra Nenets. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton. ISBN 9783110320640. OCLC 958355161.
- Salminen, Tapani. (1997). Tundra Nenets inflection. Helsinki: Suomalais-ugrilainen seura. ISBN 952515002X. OCLC 37350558.
- "Nenets". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2019-05-12.
- Salminen 1997, pp. 35–36.
- Salminen 1997, pp. 36–37.
- Salminen, Tapani (1993). On identifying basic vowel distinctions in Tundra Nenets. Finnisch-Ugrische Forschungen. Vol. 51. Helsinki: Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura. pp. 177–187.
- Salminen 1997, pp. 37–38.
- Burkova, Svetlana (2022). "Nenets". The Oxford Guide to the Uralic Languages. Oxford Guides to the World's Languages (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 680.
- Salminen 1997, pp. 40–41.
- Salminen 1997, pp. 43–44.
- Nenets language, alphabet and pronunciation
На других языках
[de] Tundra-Nenzische Sprache
Das Tundra-Nenzische ist ein Dialekt der nenzischen Sprache. Er unterscheidet sich ausreichend vom Wald-Nenzischen Dialekt, sodass er von einigen Sprachforschern als eigene Sprache aufgefasst wird.- [en] Tundra Nenets language
[fr] Nénètse de la toundra
Le nénètse de la toundra est une langue samoyède parlée par approximativement 25 000 personnes, principalement en Sibérie, entre la péninsule de Kanine et le Ienisseï, et l'un des deux principaux dialectes nénètse[2]. Comme son nom l'indique, il est étroitement apparenté au nénètse des forêts, parlé par un plus petit nombre de locuteurs[2]. Comme ce dernier, il s'écrit traditionnellement à l'aide d'une variation de l'alphabet cyrillique.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии