lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Udmurt is a Permic language spoken by the Udmurt people who are native to Udmurtia. As a Uralic language, it is distantly related to languages such as Finnish, Estonian, Mansi, Khanty, and Hungarian. The Udmurt language is co-official with Russian within Udmurtia.
| Udmurt | |
|---|---|
| Удмурт кыл Udmurt kyl | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Udmurtia |
| Ethnicity | Udmurts |
Native speakers | 324,000 in the Russian Federation, ethnic population: 554,000, total users in all countries: 335,730 (2010 census)[1] |
Language family | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Russia
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | udm |
| ISO 639-3 | udm |
| Glottolog | udmu1245 |
| ELP | Udmurt |
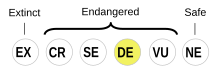 Udmurt is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |
It is written using the Cyrillic alphabet with the addition of five characters not used in the Russian alphabet: Ӝ/ӝ, Ӟ/ӟ, Ӥ/ӥ, Ӧ/ӧ, and Ӵ/ӵ. Together with the Komi and Permyak languages, it constitutes the Permic grouping of the Uralic family. Among outsiders, it has traditionally been referred to by its Russian exonym, Votyak. Udmurt has borrowed vocabulary from neighboring languages, mainly from Tatar and Russian.

In 2010, as per the Russian census, there were around 324,000 speakers of the language in the country, out of the ethnic population of roughly 554,000.[2] Ethnologue estimated that there were 550,000 native speakers (77%) out of an ethnic population of 750,000 in the former Russian SFSR (1989 census),[3] a decline of roughly 41% in 21 years.
Dialects
Udmurt varieties can be grouped in three broad dialect groups:
- Northern Udmurt, spoken along the Cheptsa River
- Southern Udmurt
- Besermyan, spoken by the strongly Turkified Besermyans
A continuum of intermediate dialects between Northern and Southern Udmurt is found, and literary Udmurt includes features from both areas. Besermyan is more sharply distinguished.[citation needed]
The differences between the dialects are regardless not major and mainly involve differences in vocabulary, largely attributable to the stronger influence of Tatar in the southern end of the Udmurt-speaking area. A few differences in morphology and phonology still exist as well; for example:
- Southern Udmurt has an accusative ending -ыз /-ɨz/, contrasting with northern -ты /-tɨ/.
- Southwestern Udmurt distinguishes an eighth vowel phoneme /ʉ/.
- Besermyan has /e/ in place of standard Udmurt /ə/ (thus distinguishing only six vowel phonemes), and /ɵ/ in place of standard Udmurt /ɨ/.
Orthography
Udmurt is written using a modified version of the Russian Cyrillic alphabet:
| Cyrillic | Latin | IPA | Letter name | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| А а | A a | [a] | а | |
| Б б | B b | [b] | бэ | |
| В в | V v | [v] | вэ | |
| Г г | G g | [ɡ] | гэ | |
| Д д | D d Ď ď | [d] [dʲ~ɟ] before е, ё, и, ю, я, ь | дэ | |
| Е е | JE je E e | [je] [ʲe] after coronals д, т, з, с, л, н | е | |
| Ё ё | JO jo O o | [jo] [ʲo] after д, т, з, с, л, н | ё | |
| Ж ж | Ž ž | [ʒ] | жэ | |
| Ӝ ӝ | DŽ dž | [dʒ] | ӝэ | Д + Ж |
| З з | Z z Ź ź | [z] [ʑ] before е, ё, и, ю, я, ь | зэ | |
| Ӟ ӟ | Đ đ | [dʑ] | ӟе | Дь + Зь |
| И и | I i | [i] [ʲi] after д, т, з, с, л, н | и | |
| Ӥ ӥ | I i | [i] when preceded by д, т, з, с, л, н | точкаен и, точкаосын и ("dotted i") | Like Komi і. Non-palatalized form of и. |
| Й й | J j | [j] | вакчи и ("short i") | |
| К к | K k | [k] | ка | |
| Л л | Ł ł L l | [ɫ] [ʎ] before е, ё, и, ю, я, ь | эл | |
| М м | M m | [m] | эм | |
| Н н | N n Ň ň | [n] [ɲ] before е, ё, и, ю, я, ь | эн | |
| О о | O o | [o] | о | |
| Ӧ ӧ | Õ õ | [ɜ~ə] | ӧ | |
| П п | P p | [p] | пэ | |
| Р р | R r | [r] | эр | |
| С с | S s Ś ś | [s] [ɕ] before е, ё, и, ю, я, ь | эс | |
| Т т | T t Ť ť | [t] [tʲ~c] before е, ё, и, ю, я, ь | тэ | |
| У у | U u | [u] | у | |
| Ф ф | F f | [f] | эф | In loanwords. |
| Х х | H h | [x] | ха | In loanwords. |
| Ц ц | C c | [ts] | цэ | In loanwords. |
| Ч ч | Ć ć | [tɕ] | чэ | Ть + Сь |
| Ӵ ӵ | Č č | [tʃ] | ӵэ | Т + Ш |
| Ш ш | Š š | [ʃ] | ша | |
| Щ щ | ŠČ šč | [ɕ(ː)] | ща | In loanwords. |
| Ъ ъ | – | – | чурыт пус ("hard sign") | Distinguishes palatalized consonants (/dʲ tʲ zʲ sʲ lʲ n/) from unpalatalized consonants followed by /j/ if followed by vowel; for example, /zʲo/ and /zjo/ are written зё (źo) and зъё (zjo), respectively. |
| Ы ы | Y y | [ɨ~ɯ] | ы | |
| Ь ь | – | [ʲ] | небыт пус ("soft sign") | |
| Э э | E e | [e] | э | |
| Ю ю | JU ju | [ju] [ʲu] after д, т, з, с, л, н | ю | |
| Я я | JA ja | [ja] [ʲa] after д, т, з, с, л, н | я |
Phonology
Unlike other Uralic languages such as Finnish and Hungarian, Udmurt does not distinguish between long and short vowels and does not have vowel harmony.
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
(Alveolo-) palatal |
Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | tʲ | k | |
| voiced | b | d | dʲ | ɡ | ||
| Affricate | voiceless | (t͡s) | t͡ʃ | t͡ɕ | ||
| voiced | (d͡z) | d͡ʒ | d͡ʑ | |||
| Fricative | voiceless | (f) | s | ʃ | ɕ | (x) |
| voiced | v | z | ʒ | ʑ | ||
| Approximant | j | |||||
| Lateral | l | ʎ | ||||
| Trill | r | |||||
The consonants /f x t͡s/ are restricted to loanwords, and are traditionally replaced by /p k t͡ɕ/ respectively. As in Hungarian, Udmurt exhibits regressive voicing and devoicing assimilations (the last element determines the assimilation), but with some exceptions (mostly to distinguish minimal pairs by voicing).[4]
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Round | |||
| Close | i | ɨ | u | |
| Mid | e | ə | o | |
| Open | a | |||
Grammar

Udmurt is an agglutinating language. It uses affixes to express possession, to specify mode, time, and so on.
No gender distinction is made in nouns or personal pronouns.
Cases
Udmurt has fifteen cases: eight grammatical cases and seven locative cases.
There is no congruency between adjectives and nouns in neutral Udmurt noun phrases; in other words, there is no adjective declension as in the inessive noun phrase бадӟым гуртын ("in a big village"; cf. Finnish inessive phrase isossa kylässä, in which iso "large" is inflected according to the head noun).
| Udmurt cases | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Suffix | Example | Translation |
| Grammatical | |||
| nominative | – | гурт /gurt/ | village |
| genitive | -лэн /ɫen/ | гуртлэн /gurtɫen/ | of a village / village's |
| accusative | -эз/-ез/-ты/-ыз /ez/jez/tɨ/ɨz/ | гуртэз /gurtez/ | village (as an object) |
| ablative | -лэсь /ɫeɕ/ | гуртлэсь /gurtɫeɕ/ | from a village |
| dative | -лы /ɫɨ/ | гуртлы /gurtɫɨ/ | to a village |
| instrumental | -эн/-ен/-ын /en/jen/ɨn/ | гуртэн /gurten/ | by means of a village |
| abessive | -тэк /tek/ | гурттэк /gurtːek/ | without a village |
| adverbial | -я /jɑ/ | гуртъя /gurtjɑ/ | in a village way |
| Locative cases* | |||
| inessive | -ын /ɨn/ | гуртын /gurtɨn/ | in a village |
| illative | -э/-е/-ы /e/je/ɨ/ | гуртэ /gurte/ | into a village (or house) |
| elative | -ысь /ɨɕ/ | гуртысь /gurtɨɕ/ | from a village |
| egressive | -ысен /ɨɕen/ | гуртысен /gurtɨɕen/ | starting from a village |
| terminative | -озь /oʑ/ | гуртозь /gurtoʑ/ | end up at a village |
| prolative | -этӥ/-етӥ/-ытӥ/-тӥ /eti/jeti/ɨti/ti/ | гуртэтӥ /gurteti/ | along a village |
| allative | -лань /ɫɑɲ/ | гуртлань /gurtɫɑɲ/ | towards a village |
*Of all the locative cases, personal pronouns can only inflect in the allative (also called approximative).
Plural
There are two types of nominal plurals in Udmurt. One is the plural for nouns -ос/-ëс and the other is the plural for adjectives -эсь/-есь.
Nominal plural
The noun is always in plural. In attributive plural phrases, the adjective is not required to be in the plural:
| Attributive plural | |
|---|---|
| Udmurt | English |
| чебер(есь) нылъëс | (the) beautiful girls |
The plural marker always comes before other endings (i.e. cases and possessive suffixes) in the morphological structure of plural nominal.
| Morphological order | |
|---|---|
| Udmurt | English |
| нылъëслы | to the girls |
| гуртъëсазы | to/in their villages |
Predicative plural
As in Hungarian and Mordvinic languages, if the subject is plural, the adjective is always plural when it functions as the sentence's predicative:
| Attributive plural | |
|---|---|
| Udmurt | English |
| нылъëс чебересь | the girls are beautiful |
| толъёс кузесь | the winters are cold |
Udmurt pronouns are inflected much in the same way that their referent nouns are. However, personal pronouns are only inflected in the grammatical cases and cannot be inflected in the locative cases.
Pronouns
Personal pronouns
Udmurt personal pronouns are used to refer to human beings only. However, the third person singular can be referred to as it. The nominative case of personal pronouns are listed in the following table:
| Personal pronouns | |
|---|---|
| Udmurt | English |
| Singular | |
| мон /mon/ | I |
| тон /ton/ | you |
| со /so/ | she or he or it |
| Plural | |
| ми /mi/ | we |
| тӥ /ti/ | you |
| соос /soːs/ | they |
Interrogative pronouns
Udmurt interrogative pronouns inflect in all cases. However, the inanimate interrogative pronouns 'what' in the locative cases have the base form кыт-. The nominative case of interrogative pronouns are listed in the following table:
| Interrogative pronouns (nominative case) | |
|---|---|
| Udmurt | English |
| Singular | |
| ма /mɑ/ | what |
| кин /kin/ | who |
| Plural | |
| маос /mɑos/ | what |
| кинъëс /kinjos/ | who |
Verbs
Udmurt verbs are divided into two conjugation groups, both having the infinitive marker -ны.
There are three verbal moods in Udmurt: indicative, conditional and imperative. There is also an optative mood used in certain dialects. The indicative mood has four tenses: present, future, and two past tenses. In addition there are four past tense structures which include auxiliary verbs. Verbs are negated by use of an auxiliary negative verb that conjugates with personal endings.
The basic verbal personal markers in Udmurt are (with some exceptions):
| Personal endings of verbs | |
|---|---|
| Person | Ending |
| Singular | |
| 1st | -Ø |
| 2nd | -д |
| 3rd | -з |
| Plural | |
| 1st | -мы |
| 2nd | -ды |
| 3rd | -зы |
| Example conjugation: тодыны (conjugation I) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Person | Udmurt | English |
| Singular | ||
| 1st | тодӥсько* | I know |
| 2nd | тодӥськод* | you know |
| 3rd | тодэ | he/she knows |
| Plural | ||
| 1st | тодӥськомы | we know |
| 2nd | тодӥськоды | you know |
| 3rd | тодо | they know |
*The present tense in Udmurt in all but the third person, is marked with -(ӥ)сько-/-(и)сько-.
Syntax
Udmurt is an SOV language.
Lexicon
Depending on the style, about 10 to 30 percent of the Udmurt lexicon consists of loanwords. Many loanwords are from the Tatar language, which has also strongly influenced Udmurt phonology and syntax.

The Udmurt language, along with the Tatar language, influenced the language of the Udmurt Jews, in the dialects of which the words of Finno-Ugric and Turkic origin there were recorded.[5][6][7][8]
Media in Udmurt
Eurovision runners-up Buranovskiye Babushki, a pop group composed of Udmurt grandmothers, sing mostly in Udmurt.[9]
The romantic comedy film Berry-Strawberry, a joint Polish-Udmurt production, is in the Udmurt language.
In 2013 the film company "Inwis kinopottonni" produced a film in the Udmurt language called Puzkar ("nest").[10]
The Bible was first completely translated into Udmurt in 2013.[11]
Bibliography
- Csúcs, Sándor (1998). Udmurt. In Daniel Abondolo (ed.), The Uralic Languages: London: Routledge. pp. 276–304.
- Kel'makov, Valentin; Sara Hännikäinen (2008). Udmurtin kielioppia ja harjoituksia (in Finnish) (2nd ed.). Helsinki: Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura. ISBN 978-952-5150-34-6.
- Moreau, Jean-Luc (2009). Parlons Oudmourte. Paris: L'Harmattan. ISBN 978-2-296-07951-9.
References
- Udmurt at Ethnologue (23rd ed., 2020)
- "Udmurt". Endangered Languages Project. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- Ethnologue code=UDM Archived October 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- "2. Фонетика". Удмуртология. Retrieved 3 April 2022.
- Altyntsev A.V., "The Concept of Love in Ashkenazim of Udmurtia and Tatarstan", Nauka Udmurtii. 2013. № 4 (66), pp. 131–132. (Алтынцев А.В., "Чувство любви в понимании евреев-ашкенази Удмуртии и Татарстана". Наука Удмуртии. 2013. №4. С. 131–132: Комментарии.) (in Russian)
- Goldberg-Altyntsev A.V., "A short ethnographic overview of the Ashkenazic Jews' group in Alnashsky District of Udmurt Republic". Die Sammlung der wissenschaftlichen Arbeiten der jungen jüdischen Wissenschaftler. Herausgegeben von Artur Katz, Yumi Matsuda und Alexander Grinberg. München, Dachau, 2015. S. 51.
- Гольдберг-Алтынцев А.В., "Краткий этнографический обзор группы ашкеназских евреев в Алнашском районе Удмуртской Республики / пер. с англ. яз. А.Й. Каца." Jewish studies in the Udmurt Republic: Online. Part 1. Edited by A. Greenberg. February 27, 2015 published. P. 3. (in Russian)
- Goldberg-Altyntsev A.V., "Some characteristics of the Jews in Alnashsky District of Udmurt Republic." The youth. The creativity. The science. Edited by V. Cox, A. Katz and A. Greenberg. Trenton, 2014, p. 28. (גאלדבערג-אלטינצעוו א.ו., ". איניגע באזונדערהייטן פון די יידן אין אלנאשסקער רייאן פון ודמורטישע רעפובליק" The youth. The creativity. The science. = Die Jugend. Die Kreativität. Die Wissenschaft. = נוער. יצירתיות. מדע Edited by V. Cox, A. Katz and A. Greenberg. Trenton, 2014. P. 28.) (in Yiddish)
- Omelyanchuk, Olena (7 March 2012). "Buranovskiye Babushki to represent Russia in Baku". European Broadcasting Union. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Пузкар (удмурт кино)".
- "First Bible in Udmurt – arrives this week!". United Bible Societies. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
External links
 Media related to Udmurt language at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Udmurt language at Wikimedia Commons
- Udmurtology: Udmurt Language, History and Culture(in Russian)
- Literature
- The First Udmurt Forum(in Russian)
- Udmurt State University (has Udmurt Language Program for English speakers)
- Udmurt language, alphabet and pronunciation
- Vladimir Napolskikh. Review of Eberhard Winkler, Udmurt, München 2001 (Languages of the World. Materials 212)
- Udmurt – Finnish/Komi Zyrian dictionary (robust finite-state, open-source)
- Learning Udmurt words
- BGN/PCGN romanization tool for Udmurt
На других языках
[de] Udmurtische Sprache
Die udmurtische Sprache (älter auch wotjakische Sprache; Selbstbezeichnung удмурт кыл – udmurt kyl) gehört zum permischen Zweig der finno-ugrischen Sprachen und wird in Udmurtien im westlichen Uralgebiet von etwa 464.000 Menschen, den Udmurten, gesprochen. Die Selbstbezeichnung Udmurt geht wahrscheinlich zurück auf ein Wort, das „Wiesenmensch“ bedeutete.[1]- [en] Udmurt language
[es] Idioma udmurto
El idioma udmurto o votiaco (удмурт кыл udmurt kyl) es una lengua fino-úgrica hablada por los udmurtos, nativos de la república rusa de Udmurtia. Unos 340 000 hablantes —339 800 personas según datos de 2010— usan esta lengua.[1][fr] Oudmourte
L'oudmourte (Удмурт кыл), ou votiak, est une langue parlée par les Oudmourtes en Russie. Elle forme, avec le komi, la branche permienne des langues ouraliennes.[it] Lingua udmurta
La lingua udmurta o udmurto (nome nativo Удмурт кыл, Udmurt kyl; in russo удмуртский язык, udmurtskij jazyk), chiamata anche votiaco,[1][2] è una lingua uralica parlata in Russia.[ru] Удмуртский язык
Удму́ртский язы́к (удм. Удмурт кыл) — один из языков пермской ветви финно-угорских языков уральской языковой семьи. Национальный язык удмуртов и бесермян. Носители языка проживают в Удмуртии, Башкортостане, Татарстане, Марий Эл, Пермском крае, Кировской и Свердловской областях России.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии