lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
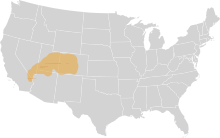
Colorado River Numic (also called Ute /ˈjuːt/, Southern Paiute /ˈpaɪjuːt/, Ute–Southern Paiute, or Ute-Chemehuevi /tʃɛmɪˈweɪvi/), of the Numic branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family, is a dialect chain that stretches from southeastern California to Colorado.[2] Individual dialects are Chemehuevi, which is in danger of extinction, Southern Paiute (Moapa, Cedar City, Kaibab, and San Juan subdialects), and Ute (Central Utah, Northern, White Mesa, Southern subdialects). According to the Ethnologue, there were a little less than two thousand speakers of Colorado River Numic Language in 1990, or around 40% out of an ethnic population of 5,000.[3]
| Colorado River Numic | |
|---|---|
| Southern Paiute | |
| Native to | United States |
| Region | Nevada, California, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico |
| Ethnicity | 6,200 Chemehuevi, Southern Paiute and Ute (2007)[1] |
Native speakers | 920 (2007)[1] 20 monolinguals (1990 census)[1] |
Language family | Uto-Aztecan
|
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | ute |
| Glottolog | utes1238 |
| ELP | Ute |
 | |
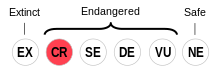 Chemehuevi is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
The Southern Paiute dialect has played a significant role in linguistics, as the background for a famous article by linguist Edward Sapir and his collaborator Tony Tillohash on the nature of the phoneme.[4]
Dialects
The three major dialect groups of Colorado River are Chemehuevi, Southern Paiute, and Ute, although there are no strong isoglosses. The threefold division is primarily one of culture rather than strictly linguistic. There are, however, three major phonological distinctions among the dialects:
- In Southern Paiute and Ute, initial /h/ has been lost: Chemehuevi /hipi/ 'drink', other dialects /ipi/ 'drink'.
- In Ute, nasal-stop clusters have become voiceless geminate stops: Ute /pukku/ 'horse, pet', other dialects /puŋku/.
- In Ute, the mid back round vowel /o/ has been fronted to /ö/: Ute /söö-/ 'lungs', other dialects /soo-/.
There are no strong isoglosses between Southern Paiute and Ute for the changes but an increasing level of change, as one moves from Kaibab Southern Paiute (0% of nasal-stop clusters have changed) to Southern Ute (100% of nasal-stop clusters have changed).
Phonology
Consonant and vowel charts for the westernmost and easternmost dialects are given.[5][6]
Consonants
| labial | dental | palatal | velar | glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | labial | ||||||
| plosive | p | t | ts | k | kʷ | ʔ | |
| fricative | β | s | ɣ | ɣʷ | h | ||
| rhotic | ɾ | ||||||
| nasal | plain | m | n | ŋ | ŋʷ | ||
| glottalized | mˀ | nˀ | ŋˀ | ||||
| glide | plain | w | j | ||||
| glottalized | wˀ | jˀ | |||||
| labial | dental | palatal | velar | glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | labial | |||||
| plosive | p | t | tʃ | k | kʷ | ʔ |
| fricative | β | s | ɣ | ɣʷ | ||
| rhotic | ɾ | |||||
| nasal | m | n | ||||
| glide | w | j | ||||
Vowels
| front | central | back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | |||
| high | i | ɯ | u | |
| mid | o | |||
| low | ɑ | |||
| front | central | back | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | unrounded | rounded | ||
| high | i | ɯ | u | ||
| mid | ø | ||||
| low | ɑ | ||||
Vowels can be long or short. Short unstressed vowels can be devoiced.
Morphology
The Colorado River Numic language is an agglutinative language, in which words use suffix complexes for a variety of purposes with several morphemes strung together.
References
- Colorado River Numic at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Mithun (1999:542)
- "Ethnologue report for language code:ute". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- Sapir, Edward (1933). "La réalité psychologique des phonèmes (The psychological reality of phonemes)". Journal de Psychologie Normale et Pathologique (in French).
- Press, Margaret L. (1979). Chemehuevi: A Grammar and Lexicon. University of California Press.
- Givon, T. (2011). Ute Reference Grammar. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
Bibliography
- Bunte, Pamela A. (1979). "Problems in Southern Paiute Syntax and Semantics," Indiana University Ph.D. dissertation.
- Charney, Jean O. (1996). A Dictionary of the Southern Ute Language. Ignacio, Colorado: Ute Press.
- Givón, Talmy (2011). Ute Reference Grammar. Culture and Language Use Volume 3. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company.
- Laird, Carobeth (1976). The Chemehuevis. Banning, CA: Malki Museum Press.
- Mithun, Marianne (1999). Languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Press, Margaret L. (1979). Chemehuevi, A Grammar and Lexicon. University of California Publications in Linguistics Volume 92. Berkeley, CA. University of California Press.
- Sapir, Edward (1930). Southern Paiute, a Shoshonean Language. Reprinted in 1992 in: The Collected Works of Edward Sapir, X, Southern Paiute and Ute Linguistics and Ethnography. Ed. William Bright. Berlin: Mouton deGruyter.
- Sapir, Edward (1931). Southern Paiute Dictionary. Reprinted in 1992 in: The Collected Works of Edward Sapir, X, Southern Paiute and Ute Linguistics and Ethnography. Ed. William Bright. Berlin: Mouton deGruyter.
External links
- A Preliminary Analysis of Southern Ute with a Special Focus on Noun Phrases - also contains phonology information
- Chemehuevi language overview at the Survey of California and Other Indian Languages
- A Chemehuevi Language Archive - 1970s Fieldwork and Analysis by Margaret L. Press
- OLAC resources in and about the Ute-Southern Paiute language
- Collected Works of Edward Sapir, Vol. X: Southern Paiute and Ute Linguistics and Ethnography
- Ute Dictionary
На других языках
- [en] Colorado River Numic language
[es] Idioma ute
El ute o paiute meridional es un complejo dialectal[1] de lenguas uto-aztecas desde el sudeste de Arizona hasta Colorado. Los dialectos o variantes individuales de esta lengua son el chemehuevi, que está en peligro de extinción, el paiute meridional propiamente dicho y el ute propiamente dicho.[fr] Ute (langue)
L'ute ou païute du sud est une gamme dialectale de la branche des langues numiques, de la famille des langues uto-aztèques, qui s'étend du Sud-Est de la Californie au Colorado. Les différents dialectes sont le chemehuevi (qui est en danger d'extinction), le païute du Sud (sous-dialectes : Moapa, Cedar City, Kaibab, et San Juan), et l'ute (sous-dialectes : Central Utah, Nord, White Mesa, Sud).[ru] Юте (язык)
Юте — индейский язык, относится к южной группе нумийской ветви юто-ацтекской семьи языков. Представляет собой группу диалектов, распространённых на обширной территории от юго-восточной Калифорнии до Колорадо. Согласно данным Ethnologue, имеется менее 2000 носителей языка, тогда как численность этноса составляет 5000 человек. Имеет агглютинативный строй.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии