lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Bhojpuri (/ˌboʊdʒˈpʊəri/;[6] ![]() भोजपुरी (help·info)) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bhojpur-Purvanchal region of India and the Terai region of Nepal.[7] It is chiefly spoken in western Bihar, eastern Uttar Pradesh and northwestern Jharkhand.[6] It is an eastern Indo Aryan language and as of 2000[update] is spoken by about 5% of India's population.[8]
भोजपुरी (help·info)) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bhojpur-Purvanchal region of India and the Terai region of Nepal.[7] It is chiefly spoken in western Bihar, eastern Uttar Pradesh and northwestern Jharkhand.[6] It is an eastern Indo Aryan language and as of 2000[update] is spoken by about 5% of India's population.[8]
| Bhojpuri | |
|---|---|
| भोजपुरी • 𑂦𑂷𑂔𑂣𑂳𑂩𑂲 | |
 The word "Bhojpuri" in Kaithi script | |
| Native to | India and Nepal |
| Region | Bhojpur-Purvanchal |
| Ethnicity | Bhojpuriya |
Native speakers | 51 million, partial count (2011 census)[1] (additional speakers counted under Hindi) |
Language family | |
| Dialects |
|
Writing system |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | bho |
| ISO 639-3 | bho |
| Glottolog | bhoj1246 |
| Linguasphere | 59-AAF-sa |
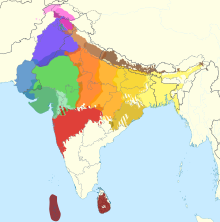
 Bhojpuri-speaking regions of India | |
It is also a recognized minority language in Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, South Africa, Suriname and Trinidad and Tobago.[9][10] Fiji Hindi, an official language of Fiji, is a variant of Awadhi and Bhojpuri spoken by the Indo-Fijians. Caribbean Hindustani, another variant of Bhojpuri is spoken by the Indo-Caribbean people.[11] It has experienced lexical influence from Caribbean English in Trinidad and Tobago and in Guyana. In Suriname, languages that have lexically influenced it include Sranan Tongo Creole, Surinamese Dutch and English. Another dialect is spoken in Mauritius; its use is declining.
Name
The word Bhojpuri is derived from Bhojpur. After the conquest of Chero and Ujjainiya Rajputs in 12th century, who were the descendants of Raja Bhoj from Ujjain, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh captured Shahabad and named their capital Bhojpur (City of Raja Bhoj).[12] The seat of their government was Bhojpur village which was near Dumraon in Buxar. Two villages named Chhotka Bhojpur and Barka Bhojpur still exist in Buxar, where the ruins of their Navratna Fortress still can be seen. Slowly the word Bhojpur became the synonyms of the Shahabad or Arrah region (Today's Bhojpur district, Buxar, Kaimur and Rohtas)[13] and the adjective Bhojpuri or Bhojpuriya extended to mean the language or people of Bhojpur and even beyond it. Apart from Bhojpuri in the Eastern UP and Western Bihar, there were other names also for the language and people, at different places, the Bhojpuriya in Mughal armies were used to called Buxariya.[14] In Bengal, they called Paschhimas (Westerners) and Bhojpuri people also called them Deshwali or Khoṭṭa, in upper provinces like Oudh they called Purabiya. Besides these, Banarasi, Chhaprahiya, and Bangarahi has also used for the language and People. Rahul Sankrityayan has suggested two names for it i.e. Mallika or Malli (due to ancient tribe of Malla) and Kashiki (due to ancient Kashi).[15] The Girmityas who were taken to British colonies called it Hindustani and it became Fiji Hindustani in Fiji and Caribbean Hindustani in Caribbean.
History
Bhojpuri is a descendant of Magadhi Prakrit[16] which started taking in shape during the reign of the Vardhana dynasty. Bāṇabhaṭṭa, in his Harshacharita has mentioned two poets named Isānchandra and Benibhārata who used to write in local language instead of Prakrit and Sanskrit.[17][18] The earliest form of Bhojpuri can be traced in the Siddha Sahitya and Charyapada as early as 8th century A.D.[19][20][21][22]. Between 11th to 14th century A.D. the Folklores like Lorikayan, Sorathi Birjabhar etc. came in to existence.[23] In 15th to 18th century, Kabir and other saints created many Bhajans in Bhojpuri.[21]
Between 1838 and 1917, many Bhojpuriyas were taken to British colonies like Fiji, Mauritius, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago and South Africa, as well as the Dutch colony of Suriname. Music genres based in Bhojpuri folk music like Chutney music, Baithak Gana, Geet Gawanai and Lok Geet took birth in those countries.[24][25]
![Statue named Baba en Maai commemorating the arrival of first Indian couple in Suriname[26]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/Paramaribo_-_Kleine_Combeweg_-_Baba_en_Mai_20160922.jpg/220px-Paramaribo_-_Kleine_Combeweg_-_Baba_en_Mai_20160922.jpg)
In 19th century, notable works like Devakshara Charita, Badmash Darpan were published. Bhikhari Thakur, in 20th century contributed significantly to Bhojpuri literature and theatre with his notable plays like Bidesiya, Beti Bechwa, Gabarghichor and novels like Bindia and Phulsunghi were published. In 1962, the first Bhojpuri film, Ganga Maiyya Tohe Piyari Chadhaibo was released and became the founding stone of the Bhojpuri film industry.
Geographic distribution
The Bhojpuri-speaking region covers the area of 73,000 square kilometres approximately in India and Nepal[27] and borders the Awadhi-speaking region to the west, the Nepali-speaking region to the north, the Magahi and Bajjika-speaking regions to the east and the Magahi and Bagheli-speaking regions to the south.[7] In Nepal, Bhojpuri is a major language.[10] There are a number of Bhojpuri-speaking Muslims in Bangladesh, referred to as Stranded Pakistanis, who migrated there during the Partition of India.

Bhojpuri is spoken by descendants of indentured labourers brought in the 19th and early 20th centuries for work in plantations in British colonies. These Bhojpuri speakers live in Mauritius, Fiji, South Africa, Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, Suriname, Jamaica, and other parts of the Caribbean.[9][10][28]
Classification

Bhojpuri is an Indo-European language and belongs to the Eastern Indo-Aryan group of the Indo-Aryan languages. The Magahi and Maithili languages of Eastern Indo-Aryan group are closest living relatives of Bhojpuri. Odia, Bengali and Assamese are also closely related.[29][30] Bhojpuri along with Magahi and Maithili, are grouped together as the Bihari languages. Together with the other branches of Eastern Indo-Aryan, the Bihari languages are considered to be direct descendants of the Magadhi Prakrit.
Bhojpuri is classified as an Eastern Indo-Aryan Language because it has similar inflexion system to the other languages of the same family such as Bengali, Maithili and Odia. For example, the pronunciation of the vowel a is broad in Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, and sounds like o in Bengali, on moving westwards it becomes less broad but still can be differentiated from the sharp cut a in Middle Indo-Aryan.[clarification needed] In Bhojpuri, the clear cut a and the drawled a, which sounds like aw in the word awl[clarification needed] are present and the contrast between the two gives a different tone to the language.[31] This drawled a is represented by Avagraha (ऽ), for instance, the word dekh'la, you see, is written as देेखऽलऽ.[32] Other property of Eastern Indo Aryan languages is that the adjectives doesn't change with the noun. For instance moṭā feminine form moṭī in Hindi but in Bhojpuri only moṭ is used as in Bengali. The past and future tense in Bhojpuri is formed in same way as other Eastern Indo-Aryan Languages, by adding a suffix stating from -la and -ba respectively to the verb. Form example, I shall See, in Bengali is dekh-bo and in Bhojpuri is dekh-ab.[33]
Some scholars has also divided the East Indo Aryan or Magadhan languages in to three sub-groups viz. Western, Central and Eastern. Bengali, Assamese, Odia belongs to Eastern Magadhan, Maithili and Magahi to Central and Bhojpuri to western.[34][35][36][37] Bhojpuri is classified as Western Magadhan because it has some properties which are peculiar to itself and are not present in other Magadhan Languages. Some striking differences are:[33]
- raürā or raüwā as an honorfic pronoun for second person along with the apne form is used Bhojpuri. apne form is their in other Magadhan Languages but raüwā is totally absent.
- Verb substantive in other Magadhan language is of -acch for but Bhojpuri has -baṭe and hawe.[38][39]
- The simple present is made by Bhojpuri by adding a suffix starting from -la with the verb, but this is totally absent in the other languages of Magadhan group. Hence, he sees, is dēkhe-lā in Bhojpuri but in but dekhait-chhi in Maithili and dekhechhi in Bengali.
Sociolinguistically it is considered to be one of the seven main Hindi dialects.[40]
Dialects
Bhojpuri has several dialects: Southern Standard Bhojpuri, Northern Standard Bhojpuri, Western Standard Bhojpuri,[41] and Nagpuria Bhojpuri.[42][10]
Southern Standard Bhojpuri is prevalent in the Shahabad district (Buxar, Bhojpur, Rohtas, and Kaimur districts) and the Saran region (Saran, Siwan and Gopalganj districts) in Bihar, the eastern Azamgarh (Ballia and Mau(Eastern Part) districts) and Varanasi (eastern part of Ghazipur district) regions in Uttar Pradesh, and in the Palamu division (Palamu and Garhwa districts) in Jharkhand. The dialect is also known as Kharwari. It can be further divided into Shahabadi, Chhaprahiya and Pachhimahi.[43]
Northern Bhojpuri is common in the western Tirhut division (east and west Champaran districts) in Bihar, and Gorakhpur division (Deoria, Kushinagar, Gorakhpur, and Maharajganj districts) and Basti division (Basti, Sidharthanagar, and Sant Kabir Nagar districts) in Uttar Pradesh. It is also spoken in Nepal.[44]
Western Bhojpuri is prevalent in the areas of Varanasi (Varanasi, Chandauli, Jaunpur, and the western part of Ghazipur district), Azamgarh (Azamgarh district,western part of Mau district) and Mirzapur, Sonbhadra, Sant Ravidas Nagar, and Bhadohi districts) in Uttar Pradesh. Banarasi is a local name for Bhojpuri, named after Banaras. Other names for Western Bhojpuri include Purbi and Benarsi.[45]
Nagpuria Bhojpuri is the southernmost popular dialect, found in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand, particularly parts of Palamu, South Chotanagpur and Kolhan divisions. It is sometimes referred to as Sadari.[46][47]
A more specific classification recognises the dialects of Bhojpuri as Bhojpuri Tharu, Domra, Madhesi, Musahari, Northern Standard Bhojpuri (Basti, Gorakhpuri, Sarawaria), Southern Standard Bhojpuri (Kharwari), Western Standard Bhojpuri (Benarsi, Purbi) and Nagpuriya Bhojpuri.
Phonology
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i ɪ | u | ||
| Close-mid | e | ə | o | |
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɔ | ||
| Open | æ | ɑ | ||
| Labial | (Denti-) Alveolar |
Retroflex | (Alveolo-) palatal |
Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɳ | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Stop/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t̪ | ʈ | tɕ | k | |
| voiced | b | d̪ | ɖ | dʑ | ɡ | ||
| aspirated | pʰ | t̪ʰ | ʈʰ | tɕʰ | kʰ | ||
| breathy voiced | bʱ | d̪ʱ | ɖʱ | dʑʱ | ɡʱ | ||
| Fricative | s | h | |||||
| Rhotic | plain | ɾ | ɽ | ||||
| breathy | ɾʱ | ɽʱ | |||||
| Approximant | w ~ ʋ | l | j | ||||
Among the seven languages which are sociolinguistically often counted as Hindi dialects (Haryanvi, Braj, Awadhi, Bhojpuri, Bundeli, Bagheli, and Kannauji),[40] Bhojpuri has the most allophonic variations in vowels.[49]
Bhojpuri has 6 vowel phonemes[16] and 10 vocoids. The higher vowels are relatively tense, and the lower vowels are relatively lax. The language has 31 consonant phonemes and 34 contoids (6 bilabial, 4 apico-dental, 5 apico-alveolar, 7 retroflex, 6 alveo-palatal, 5 dorso-velar, and 1 glottal).[48]
Linguist Robert L. Trammell published the phonology of Northern Standard Bhojpuri in 1971.[48][16] According to him, the syllable system is peak type: every syllable has the vowel phoneme as the highest point of sonority. Codas may consist of one, two, or three consonants. Vowels occur as simple peaks or as peak nuclei in diphthongs. The intonation system involves 4 pitch levels and 3 terminal contours.[48][50]
Grammar
According to George Abraham Grierson, the grammar of Bhojpuri is simpler than other languages of the same family.[33] Nouns in Bhojpuri have three forms: short, long and redundant. The adjectives of nouns do not change with genders. Plurals are made by adding either the suffix -na or ni with the nouns or adding the multitudes such as sabh (all) or lōg (people).
Examples:[33]
| Definition | Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|---|
| House | ghar | gharan |
| Horse | ghoṛā | ghoṛan |
| Boy | laïkā | laïkan/laïka sabh |
| King | rājā | rājā lōg |
Except few instances the Verb forms of Bhojpuri depend only on the subject and the object has no effect on it. Unlike other Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, Bhojpuri has a different verb form for the present tense, which corresponds to the Future forms of Nepali. It is formed by adding the suffix -lā to the present subjunctive. Therefore, for the verb to see the Bhojpuri verb is dekhe and the present form is dhekhelā, which is peculiar to itself and is not found in other languages of the same family like Magahi (dekhaït haï), Maithili (dekhaït achi) and Bengali (dekhechī). The Verbs forms of second person singular (dekh'be; you will see) is considered vulgar in Bhojpuri, plural form (dekhab') is used in general. When it is desired to show respect the first person singular form (dekhab; I will see) is used instead of second person plural (dekhab'). To show plural number the suffix -sa' or -ja is also used with the 2nd and third person forms, thus dekhe-la'-sa' is they see. The present perfect form is made by adding ha' to the past form. Thus, ham dekh'li (I saw) is the past from and its present perfect form is ham dekh'li ha' (I have seen). Past perfect in regular verbs are made by adding the suffix -al to the verb (dekh - dekhal), but in some cases it has irregular forms like kar (kail), mar (mual) etc.[33]
Numerals of Bhojpuri take the classifier gō and ṭhō, which emphasizes the countability and totality both. To show inclusiveness and exclusiveness, Bhojpuri used the suffixes -o and -e as in ham āmo khāïb (I will eat mangoes too) verses ham āme khāïb (I will eat only mangoes). These suffixes can be added to any lexical category such as numerals, adjectives etc.[51]
The auxiliaries in Bhojpuri are formed on five bases viz. ha, ho, hokh, bāṭ, rah. These also act as the Copula. The bāṭ form provides for the tenses and the hokh or ho form provides for the modes, where as rah is the past of other three.[27]
Writing system

Bhojpuri was historically written in Kaithi script,[7] but since 1894 Devanagari has served as the primary script. Kaithi has variants as the locality changes, the three classified varianta are Tirhuti, Magahi and Bhojpuri variants. The Bhojpuri variant is used for writing Bhojpuri.[33] Kaithi is now rarely used for Bhojpuri.

Kaithi script was used for administrative purposes in the Mughal era for writing Bhojpuri, Awadhi, Maithili, Magahi, and Hindustani from at least the 16th century up to the first decade of the 20th century. Government gazetteers[who?] report that Kaithi was used in a few districts of Bihar throughout the 1960s. Bhojpuri residents of India who moved to British colonies in Africa, the Indian Ocean, and the Caribbean in the 19th and early 20th centuries used both Kaithi and Devanagari scripts.[9]

By 1894 both Kaithi and Devanagari became common scripts to write official texts in Bihar. At present almost all Bhojpuri texts are written in Devanagari, even in islands outside of India where Bhojpuri is spoken. In Mauritius, Kaithi script was historically considered informal, and Devanagari was sometimes spelled as Devanagri. In modern Mauritius, the major script is Devanagari.[52]
Politeness
This article or section appears to contradict itself on the number of levels of politeness. (July 2022) |
Bhojpuri syntax and vocabulary reflects a three-tier system of politeness. Any verb can be conjugated through these tiers. The verb to come in Bhojpuri is aana and the verb to speak is bolna. The imperatives come! and speak! can be conjugated in five ways, each marking subtle variation in politeness and propriety. These permutations exclude a host of auxiliary verbs and expressions, which can be added to verbs to add another degree of subtle variation. For extremely polite or formal situations, the pronoun is generally omitted.
| Literary | [teh] āō | [teh] bōl |
|---|---|---|
| Casual and intimate | [tu] āō | [tu] bōl |
| Polite and intimate | [tu] āv' | [tu] bōl' |
| Formal yet intimate | [rau'ā] āīñ | [rau'ā] bōlīñ |
| Polite and formal | [āpne] āīñ | [āp] bōlīñ |
| Extremely formal | āwal jā'e | bōlal jā'e |
Similarly, adjectives are marked for politeness and formality. The adjective your has several forms with different tones of politeness: tum (casual and intimate), "tōhār" (polite and intimate), "t'hār" (formal yet intimate), rā'ur (polite and formal) and āpke (extremely formal). Although there are many tiers of politeness, Bhojpuri speakers mainly use the form tum to address a younger individual and aap for an individual who is older, or holds a higher position in workplace situations.
Status
Greater official recognition of Bhojpuri, such as by inclusion in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, has been demanded.[by whom?][53] In 2018, Bhojpuri was given second-language status in Jharkhand state of India.[54]
Bhojpuri is taught in matriculation and at the higher secondary level in the Bihar School Education Board and the Board of High School and Intermediate Education Uttar Pradesh.[citation needed] It is also taught in various universities in India, such as Veer Kunwar Singh University,[55] Banaras Hindu University,[56] Nalanda Open University,[57] and Dr. Shakuntala Misra National Rehabilitation University.[58]
Literature

Lorikayan, the story of Veer Lorik contains Bhojpuri folklore from Eastern Uttar Pradesh.[59] Bhikhari Thakur's Bidesiya is a play, written as a book. Phool Daliya is a well-known book by Prasiddh Narayan Singh. It comprises poems of veer ras (A style of writing) on the theme of azaadi (Freedom) about his experiences in the Quit India movement and India's struggle with poverty after the country gained independence.
Media
Many Bhojpuri magazines and papers are published in Bihar, Jharkhand, and Uttar Pradesh. Several Bhojpuri newspapers are available locally in North India. Parichhan is a contemporary literary-cultural Maithili-Bhojpuri magazine, published by a Maithili-Bhojpuri academy and the government of Delhi, and edited by Parichay Das. The Sunday Indian, Bhojpuri[60] is a regular national news magazine in Bhojpuri. Aakhar is a monthly online Bhojpuri literature magazine.[61] Other media in Bhojpuri include Lok Lucknow,[62] and the channels Mahuaa TV and Hamar TV. Bhojpuri Wikipedia was launched in 2003.[63] On the 22nd of May 2022, Google Translate added Bhojpuri as one of their languages.[64]
Vocabulary
Bhojpuri vocabularies have similarity with other indo Aryan languages. Here are some examples.
| English | Bhojpuri | Comparable Language |
|---|---|---|
| Near | Niyare | Nere (Punjabi) |
| Pain | Baatha | Batha (Bengali) |
| Hot | Tatal | Tato (Rajasthani, Nepali), Tahta (Punjabi) |
| Daylight | Ghaam | Ghaam (Haryanvi, Nepali) |
| Inside | Bheetar | Bheetar (Bengali, Haryanvi) |
| Watermelon | Hinwana | Indwana (Dogri) |
| To take out | Kadhna | Kadhna (Sindhi, Haryanvi, Rajasthani) |
Weekdays
| English | Bhojpuri (Latin script) | 𑂦𑂷𑂔𑂣𑂳𑂩𑂲 (𑂍𑂰𑂨𑂟𑂲 𑂪𑂱𑂎𑂰𑂆; Kaithi) | भोजपुरी (देवनागरी लिपि; Devanagari) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sunday | Eitwaar | 𑂉𑂞𑂫𑂰𑂩 | एतवार |
| Monday | Somaar | 𑂮𑂷𑂧𑂰𑂩 | सोमार |
| Tuesday | Mangar | 𑂧𑂁𑂏𑂩 | मंगर |
| Wednesday | Budhh | 𑂥𑂳𑂡 | बुध |
| Thursday | Biphey | 𑂥𑂱𑂨𑂤𑂵 | बियफे |
| Friday | Sook | 𑂮𑂴𑂍 | सूक |
| Saturday | Sanichar | 𑂮𑂢𑂱𑂒𑂩 | सनिचर |
Common phrases
| English | Bhojpuri | 𑂦𑂷𑂔𑂣𑂳𑂩𑂲 (Kaithi) | भोजपुरी |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hello | Raam Raam/Parnaam | 𑂩𑂰𑂧 𑂩𑂰𑂧/𑂣𑂩𑂝𑂰𑂧 | राम राम/परणाम |
| Welcome/Please come in | Aain na | 𑂄𑂆𑂁 𑂢𑂰 | आईं ना |
| How are you? | Ka haal ba?/Kaisan hava? | 𑂍𑂰 𑂯𑂰𑂪 𑂥𑂰?/𑂍𑂆𑂮𑂢 𑂯𑂫ऽ? | का हाल बा?/कइसन हवऽ? |
| I'm good. And you? | Hum theek baani. Aur rauwa?/Hum theek hañi. Aur aap? | 𑂯𑂧 𑂘𑂱𑂍 𑂥𑂰𑂢𑂲𑃀 𑂃𑂇𑂩 𑂩𑂈𑂫𑂰?/𑂯𑂧 𑂘𑂱𑂍 𑂯𑂖𑂱𑃀 𑂃𑂇𑂩 𑂄𑂣? | हम ठीक बानी। अउर रउवा?/हम ठीक हञि। अउर आप? |
| What is your name? | Tohaar naav ka ha?/Raur naav ka ha? | 𑂞𑂷𑂯𑂰𑂩 𑂢𑂰𑂀𑂫 𑂍𑂰 𑂯ऽ?/𑂩𑂰𑂈𑂩 𑂢𑂰𑂀𑂫 𑂍𑂰 𑂯ऽ? | तोहार नाँव का ह?/राउर नाँव का ह? |
| My name is ... | Hamar naav ... ha | 𑂯𑂧𑂰𑂩 𑂢𑂰𑂀𑂫 ... 𑂯ऽ | हमार नाँव ... ह |
| What's up? | Kaa hot aa? | 𑂍𑂰 𑂯𑂷𑂞𑂰? | का होताऽ? |
| I love you | Hum tohse pyaar kareni/Hum tohra se pyaar kareni | 𑂯𑂧 𑂞𑂷𑂯 𑂮𑂵 𑂣𑂹𑂨𑂰𑂩 𑂍𑂩𑂵𑂢𑂲/𑂯𑂧 𑂞𑂷𑂯𑂩𑂰 𑂮𑂵 𑂣𑂹𑂨𑂰𑂩 𑂍𑂩𑂵𑂢𑂲 | हम तोहसे प्यार करेनी/हम तोहरा से प्यार करेनी |
NUMBER
English। Bhojpuri
1 - One १= ek - एक
2= Two २= du - दु
3= Three ३= teen =तीन
4= four ४= char= चार
5= five ५= pan = पान
6= six ६= chhav= छव
7= seven। ७= sat= सात
8=eight ८= aath= आठ
9= nine ९= nav = नव
10= ten १०= das= दस
100= one hundred १००= ek say = एक सव
500= five hundred ५००= pan say = पान सव
1000= one thousand १०००= ek hajar = एक हजार
Example text
The following is Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in four languages:
- Bhojpuri (Kaithi) – 𑂃𑂢𑂳𑂒𑂹𑂓𑂵𑂠 १: 𑂮𑂥𑂯𑂱 𑂪𑂷𑂍𑂰𑂢𑂱 𑂄𑂔𑂰𑂠𑂵 𑂔𑂢𑂹𑂧𑂵𑂪𑂰 𑂄𑂇𑂩 𑂋𑂎𑂱𑂢𑂱𑂨𑂷 𑂍𑂵 𑂥𑂩𑂰𑂥𑂩 𑂮𑂧𑂹𑂧𑂰𑂢 𑂄𑂋𑂩 𑂃𑂡𑂱𑂍𑂰𑂩 𑂣𑂹𑂩𑂰𑂣𑂹𑂞 𑂯𑂫𑂵𑂾 𑂋𑂎𑂱𑂢𑂱𑂨𑂷 𑂍𑂵 𑂣𑂰𑂮 𑂮𑂧𑂕-𑂥𑂴𑂕 𑂄𑂇𑂩 𑂃𑂁𑂞:𑂍𑂩𑂝 𑂍𑂵 𑂄𑂫𑂰𑂔 𑂯𑂷𑂎𑂞𑂰 𑂄𑂋𑂩 𑂯𑂳𑂢𑂍𑂷 𑂍𑂵 𑂠𑂷𑂮𑂩𑂰 𑂍𑂵 𑂮𑂰𑂟 𑂦𑂰𑂆𑂒𑂰𑂩𑂵 𑂍𑂵 𑂥𑂵𑂫𑂯𑂰𑂩 𑂍𑂩𑂵 𑂍𑂵 𑂯𑂷𑂎𑂪𑂰𑂿
- Bhojpuri (Devanagari) – अनुच्छेद १: सबहि लोकानि आजादे जन्मेला आउर ओखिनियो के बराबर सम्मान आओर अधिकार प्राप्त हवे। ओखिनियो के पास समझ-बूझ आउर अंत:करण के आवाज होखता आओर हुनको के दोसरा के साथ भाईचारे के बेवहार करे के होखला।[65]
- Hindi – अनुच्छेद १: सभी मनुष्यों को गौरव और अधिकारों के मामले में जन्मजात स्वतन्त्रता और समानता प्राप्त हैं। उन्हें बुद्धि और अन्तरात्मा की देन प्राप्त है और परस्पर उन्हें भाईचारे के भाव से बर्ताव करना चाहिये।[66]
- Sarnámi Hindustani (a dialect of Caribbean Hindustani) – Aadhiaai 1: Sab djanne aadjádi aur barabar paidaa bhailèn, iddjat aur hak mê. Ohi djanne ke lage sab ke samadj-boedj aur hierdaai hai aur doesare se sab soemmat sè, djaane-maane ke chaahin.[67]
- English – Article 1: All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.[68]
See also
- Culture of Bhojpuri Region
- Bhojpuri cinema
Footnotes
References
- "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues – 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- Oozeerally, Shameem (March 2013). "The Evolution of Mauritian Bhojpuri: an Ecological Analysis - Mauritius Institute of Education". Retrieved 1 September 2020.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Rambilass, B. "NAITALI - SOUTH AFRICAN BHOJPURI" (PDF). indiandiasporacouncil.org. Retrieved 1 September 2020.
- Sudhir Kumar Mishra (22 March 2018). "Bhojpuri, 3 more to get official tag". The Telegraph.
- "New chairman of Bhojpuri Academy | Patna News - Times of India". The Times of India.
- Bhojpuri entry, Oxford Dictionaries Archived 8 December 2015 at the Wayback Machine, Oxford University Press
- Bhojpuri Ethnologue World Languages (2009)[circular reference]
- William J. Frawley, International Encyclopedia of Linguistics, Volume 1, ISBN 0-19-513977-1, Oxford University Press, Bhojpuri, page 481
- Rajend Mesthrie, Language in indenture: a sociolinguistic history of Bhojpuri-Hindi in South Africa, Routledge, 1992, ISBN 978-0415064040, pages 30–32
- Bhojpuri Archived 25 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine Language Materials Project, University of California, Los Angeles, United States
- Hindustani, Caribbean Archived 13 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine Ethnologue (2013)
- Journol of Asiatic Society of Bengal. 1871. pp. 111–129.
- Rennel, James (1781). Bengal Atlas.
- Irvine, William (1903). The Army of the Indian Moghuls. London. pp. 168–169.
- Tiwari, Udai Narayan. The Origin and Development of Bhojpuri. Kolkata: The Asiatic society.
- Verma, Manindra K. (2003), Bhojpuri, In Cardona et al. (Editors), The Indo-Aryan Languages, 515–537. London: Routledge
- Tiwari, Arjun (2014). Bhojpuri Sāhitya ke itihāsa. Varanasi: Vishwavidyala Prakashan. p. 35.
- Cowell, Edward Byles (1897). The Harsa-carita of Bana. London: Royal Asiatic Society. p. 32.
- Tiwari, Arjun. Bhojpuri Sahtiya Ke Itihas.
- Tahmid, Syed Md. "Buddhist Charyapada & Bengali Identity".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Jain, Dinesh (26 July 2007). The Indo-Aryan Langauages. p. 519. ISBN 978-1135797119.
- Pandey, Narmadeshwar Sahay. Comprehensive History of Bihar (Bhojpuri Language and literature of Bihar).
- Prasad, Vishwanatha. Yathopaari.
- "The legacy of Indian migration to European colonies". The Economist. 2 September 2017. Retrieved 2 September 2017.
- "Indian Arrival Day". www.nalis.gov.tt. Archived from the original on 12 February 2017. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- Olga van der Klooster & Michel Bakker, Architectuur en bouwcultuur in Suriname (2009). KIT Publishers. ISBN 978-90-6832-531-7. Blz. 329-330.
- Jain, Dinesh (2007). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. ISBN 978-1135797102.
- "Forced Labour". The National Archives, Government of the United Kingdom. 2010. Archived from the original on 4 December 2016.
- Dept, West Bengal (India) Information and Public Relations (1976). Introducing West Bengal. Department of Information and Public Relations, Government of West Bengal.
- Tuṅga, Sudhāṃśu Śekhara (1995). Bengali and Other Related Dialects of South Assam. Mittal Publications. ISBN 978-81-7099-588-3.
- Pandey, Shruti (2003). A Comparative Study of Bhojpuri and Bengali. Vishwavidyalaya Prakashan. p. 122. ISBN 978-81-7124-343-3.
- Other proposed methods to represent the drawled "a" sound are, देख'ल', देखःलः and देखअलअ.[citation needed]
- Grierson, G.A. (1902). Linguistic Survey of India. Vol V. Part II.
- Varmā, Śīlā (1985). The Structure of the Magahi Verb. Manohar. p. 6.
- International Journal of Dravidian Linguistics: IJDL. Department of Linguistics, University of Kerala. 2008.
- The New Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica. 1983. ISBN 978-0-85229-400-0.
- The History and Culture of the Indian People. G. Allen & Unwin. 1951. p. 358.
- Study, Indian Institute of Advanced (1969). Transactions. R. Nivas.
- Bihar in Folklore Study: An Anthology. Indian Publications. 1971.
- Diwakar Mishra and Kalika Bali, A COMPARATIVE PHONOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE DIALECTS OF HINDI Archived 1 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine, ICPhS XVII, Hong Kong, 17–21 August 2011, pp 1390
- Parable of the prodigal son in Benares Bhojpuri Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, A Recording in May 1920 by Rajaji Gupta, Linguistic Survey of India, Digital South Asia Library, University of Chicago, USA
- Parable of the prodigal son in Nagpuria Bhojpuri Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, A Recording in 1920 by Shiva Sahay Lal, Linguistic Survey of India, Digital South Asia Library, University of Chicago, USA
- Map of Southern Standard Bhojpuri Archived 1 March 2014 at archive.today Digital Library of Language Relationships (2012)
- Shaligram Shukla (1981), Bhojpuri Grammar, Georgetown University School of Language, ISBN 978-0878401895
- Western Standard Bhojpuri Archived 1 March 2014 at archive.today Digital Library of Language Relationships (2012)
- Monika Horstmann (1969), Sadari, Indologia Berolinensis, Otto Harrassowitz – Wiesbaden, Germany, pp 176–180
- Thiel-Horstmann, M. (1969). "Sadani : a Bhojpuri dialect spoken in Chotanagpur". undefined.
- Trammell, Robert L. (1971). "The Phonology of the Northern Standard Dialect of Bhojpuri". Anthropological Linguistics. 13 (4): 126–141. JSTOR 30029290.
- Diwakar Mishra and Kalika Bali, A COMPARATIVE PHONOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE DIALECTS OF HINDI Archived 1 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine, ICPhS XVII, Hong Kong, 17–21 August 2011, pp 1390–1393
- Shukla, Shaligram (1981), Bhojpuri Grammar, Washington, D. C., Georgetown University Press
- Jain, Dinesh; Cardona, George (2007). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. ISBN 9781135797119.
- Sarita Boodho, Bhojpuri traditions in Mauritius, Mauritius Bhojpuri Institute, 1999, ISBN 978-9990390216, pages 47–48 and 85–92
- "Chidambaram speaks a surprise". Chennai, India. The Hindu. 17 May 2012. Archived from the original on 20 May 2012. Retrieved 5 June 2012.
- "Jharkhand gives second language status to Magahi, Angika, Bhojpuri and Maithili". Avenue Mail. 21 March 2018. Archived from the original on 28 March 2019. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- "Bhojpuri". Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- "Banaras Hindu University, Faculty of Arts, bhojpuri addhyan kendra Varanasi". www.bhu.ac.in. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- "Bhojpuri in NOU" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 May 2017. Retrieved 6 June 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Auty, Robert (4 December 1969). Traditions of heroic and epic poetry. ISBN 9780900547720. Retrieved 27 February 2014.
- "Today Bhojpuri Newspaper Update Headlines India- The Sunday Indian Online Magazine – The Sunday Indian". www.thesundayindian.com. Archived from the original on 30 January 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- "आखर भोजपुरी पत्रिका Aakhar Bhojpuri Magazine". Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 25 February 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - A Study on the Usage of Internet by Working Women of Vadodara City for Performing Their Household Responsibilities. Anchor Academic Publishing. 2016. ISBN 978-3960675518.
- https://www.indiatoday.in/technology/news/story/google-translate-gets-24-new-languages-including-assamese-bhojpuri-sanskrit-1948298-2022-05-11
- "Universal Declaration of Human Rights – Bhojpuri" (PDF). United Nations (in Bhojpuri). 23 April 2019. p. 1. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- "Universal Declaration of Human Rights – Hindi" (PDF). United Nations (in Hindi). 1 July 2015. p. 1 (orig p. 2). Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- "Universal Declaration of Human Rights – Sarnámi Hindustani" (PDF). United Nations. (in Sarnámi Hindustani). 9 December 2013. p. 2. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- "Universal Declaration of Human Rights – English" (PDF). United Nations. 6 November 2019. p. 2. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
Further reading
- Rajathi, J and Perumalsamy, P (2021). Linguistic Description of Bhojpuri Mother Tongue Spoken in Bihar, New Delhi: Office of the Registrar General.
External links
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Bhojpuri, United Nations Information Centre, India (1998)
- Archived open-access recordings of Bhojpuri from Kaipuleohone
- English-Bhojpuri Machine Translation System
- Bhojpuri. Linguistic Survey of India.
На других языках
[de] Bhojpuri
Bhojpuri (भोजपुरी Bhojpurī [.mw-parser-output .IPA a{text-decoration:none}ˈbʱoːdʒpʊriː]) ist eine hauptsächlich im östlichen Nordindien gesprochene Sprache der indoarischen Sprachfamilie. Sie gehört zur Gruppe der Bihari-Sprachen, die mit dem Hindi nah verwandt sind.- [en] Bhojpuri language
[es] Idioma bhoshpuri
El bhhōjapurī, bhoyapuri o bhoshpuri es una lengua bihari hablada en el noreste de la India en el occidente del estado de Bihar, la parte norte de Jharkhand, y la región Purvanchal de Uttar Pradesh, así como el sur de Nepal. También es hablado en Guyana, Surinam, Fiyi, Trinidad y Tobago, Mauricio y Sudáfrica.[it] Lingua bhojpuri
La lingua bhojpuri è una lingua parlata in alcuni stati del centro nord e dell'est dell'India: è diffusa nella parte occidentale del Bihar, nel nord-ovest del Jharkhand e nella regione Purvanchal dell'Uttar Pradesh, insieme alla contigua regione del Terai nepalese[1]. Il Bhojpuri è parlato anche in Guyana, Suriname, nelle Figi, in Trinidad e Tobago e nelle Mauritius[2].[ru] Бходжпури
Бходжпури (भोजपुरी, Bhojpuri) — индоарийский язык, распространённый в индийских штатах Бихар, Джаркханд, а также в частях штата Уттар-Прадеш. Кроме того, на нём говорят меньшинства в Гайане, Суринаме, а также на островах Тринидад и Тобаго и на Маврикии. Из-за близкого родства к хинди, некоторые лингвисты рассматривают бходжпури как его диалект. На Фиджи сложился новый язык — фиджийский хинди — благодаря смешению диалектов бходжпури и хинди.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии