lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
Western Pennsylvania English, known more narrowly as Pittsburgh English or popularly as Pittsburghese, is a dialect of American English native primarily to the western half of Pennsylvania, centered on the city of Pittsburgh, but potentially appearing in some speakers as far north as Erie County, as far west as Youngstown, Ohio, and as far south as Clarksburg, West Virginia.[1][2] Commonly associated with the white working class of Pittsburgh, users of the dialect are colloquially known as "Yinzers".
| Western Pennsylvania English | |
|---|---|
| Pittsburgh English, Pittsburghese | |
| Region | Western Pennsylvania |
Language family | Indo-European
|
Early forms | |
Writing system | English alphabet |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | west2919 |
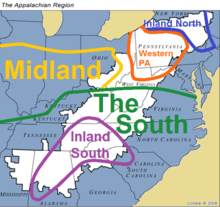 Appalachia (in white) overlaid with dialect regions defined by the 2006 ANAE. Western Pennsylvania English can be seen in orange. | |

Overview
Scots-Irish, Pennsylvania German, Polish,[3] Ukrainian[4] and Croatian[5] immigrants to the area all provided certain loanwords to the dialect (see "Vocabulary" below). Many of the sounds and words found in the dialect are popularly thought to be unique to Pittsburgh, but that is a misconception since the dialect resides throughout the greater part of western Pennsylvania and the surrounding areas.[6][7] Central Pennsylvania, currently an intersection of several dialect regions, was identified in 1949 by Hans Kurath as a subregion between western and eastern Pennsylvania,[8][9] but some scholars have more recently identified it within the western Pennsylvania dialect region.[9][10] Since Kurath's study, one of western Pennsylvania's defining features, the cot–caught merger, has expanded into central Pennsylvania,[11] moving eastward until being blocked at Harrisburg.[12] Perhaps the only feature whose distribution is restricted almost exclusively to the immediate vicinity of Pittsburgh is /aʊ/ monophthongization in which words such as house, down, found, and sauerkraut are sometimes pronounced with an "ah" sound, instead of the more standard pronunciation of "ow", rendering eye spellings such as hahs, dahn, fahnd, and sahrkraht.
Speakers of Pittsburgh English are sometimes called "Yinzers" in reference to their use of the second-person plural pronoun "yinz." The word "yinzer" is sometimes heard as pejorative, indicating a lack of sophistication, but the term is now used in a variety of ways.[13] Older men are more likely to use the accent than women "possibly because of a stronger interest in displaying local identity...."[14]
Phonology
A defining feature of Western Pennsylvania English is the cot–caught merger, in which /ɑ/ (as in ah) and /ɔ/ (as in aw) merges to a rounded vowel: [ɔ~ɒ]. As in most other American dialects, the father–bother merger also occurs.[6][7][15] Therefore, cot and caught are both pronounced [kʰɔt~kʰɒt]; Don and dawn are both [dɔn~dɒn]. While the merger of the low back vowels is also widespread elsewhere in the United States, the rounded realizations of the merged vowel around [ɒ] is less common, except in Canada, California and Northeastern New England.[6][7]
The /oʊ/ sound as in oh begins more fronted in the mouth, as in the American South or in Southern England. Therefore, go is pronounced [ɡɜʊ]. Similarly, /u/ as in food and rude is fronted and often diphthongized, as in much of the American South, Midland, and West.
The diphthong /aʊ/, as in ouch or mouth, is monophthongized to [aː] in some environments (sounding instead like ah), namely: before nasal consonants (downtown [daːnˈtʰaːn] and found [faːnd]), liquid consonants (fowl, hour) and obstruents (house [haːs], out, cloudy).[6][7][15] The monophthongization does not occur, however, in word-final positions (how, now), and the diphthong then remains [aʊ].[16] That is one of the few features, if not the only one, restricted almost exclusively to western Pennsylvania in North America, but it can sometimes be found in other accents of the English-speaking world, such as Cockney and South African English.[6][7] The sound may be the result of contact from Slavic languages during the early 20th century.[7] Monophthongization also occurs for the sound /aɪ/, as in eye, before liquid consonants,[6][7][15][17] so that tile is pronounced [tʰɑːɫ]; pile is pronounced [pʰɑːɫ]; and iron is pronounced [ɑːɹn]. That phenomenon allows tire to merge with the sound of tar: [tʰɑːɹ].
An epenthetic (intruding) /r/ sound may occur after vowels in a few words, such as water pronounced as [ˈwɔɹɾɚ], and wash as [wɔɹʃ].[6][7]
A number of vowel mergers occur uniquely in Western Pennsylvania English before the consonant /l/. The pair of vowels /i/ and /ɪ/ may merge before the /l/ consonant,[6][7][15][18] cause both steel and still to be pronounced as something like [stɪɫ]. Similarly, /u/, /oʊ/, and /ʊ/ may merge before /l/, so that pool, pull, and pole may merge to something like [pʰʊɫ]. On the /il/~/ɪl/ merger, Labov, Ash and Boberg (2006) note "the stereotype of merger of /ɪl ~ il/ is based only on a close approximation of some forms, and does not represent the underlying norms of the dialect."[19] The /i/~/ɪ/ merger is found in western Pennsylvania,[6][7][15][18] as well as parts of the southern United States, including Alabama, Texas and the west (McElhinny 1999). On the other hand, the /u/~/ʊ/ merger is consistently found only in western Pennsylvania. The /i/~/ɪ/ merger towards [ɪ] may also appear before /ɡ/: eagle then sounds to outsiders like iggle.[6][7][15] The vowel /ʌ/ (as in uh) before /l/, may lower into the vowel of the cot–caught merger mentioned above, so that mull can sound identical to mall/maul: [mɔɫ].
L-vocalization is also common in the Western Pennsylvania dialect; an /l/ then sounds like a /w/ or a cross between a vowel and a "dark" /l/ at the end of a syllable.[6][7][20] For example, well is pronounced as [wɛw]; milk as [mɪwk] or [mɛwk]; role as [ɹʊw]; and cold as [ˈkʰʊwd]. The phenomenon is also common in African-American English.
Western Pennsylvania English speakers may use falling intonation at the end of questions,[6][7][21] for example, in "Are you painting your garage?" (with pitch rising in intonation up to just before the last syllable and then falling precipitously).[21] Such speakers typically use falling pitch for yes-no questions for which they already are quite sure of the answer. A speaker uttering the above example is simply confirming what is already thought: yes, the person spoken to is painting his/her garage. It is most common in areas of heavy German settlement, especially southeastern Pennsylvania,[21] hence its nickname, the "Pennsylvania Dutch question", but it is also found elsewhere in Pennsylvania, including Pittsburgh[6][7][21] (Maxfield 1931; Layton 1999; Wisnosky 2003; Johnstone, Andrus and Danielson 2006). It is of German origin.[21]
Vocabulary
This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2021) |

- babushka - (n.) headscarf[3][22]
- buggy - (n.) shopping cart[23]
- baby buggy - (n.) baby carriage
- the 'Burgh - (n.) Pittsburgh[7][24]
- beal - (v.) to fester or suppurate[3]
- bealed - (adj.) usually of an ear: infected or abscessed[3]
- belling - (n.) noisy celebration or mock serenade for newlyweds; a shivaree[3]
- berm - (n.) edge of the road, curb: an accepted alternative to "shoulder of the road"[3]
- carbon oil - (n.) kerosene[25]
- chipped ham - (n.) very thinly sliced chopped ham loaf for sandwiches (from a local brand name)[6][7] (see chipped chopped ham)
- city chicken - (n.) cubes of pork loin and/or veal on a short wooden skewer, breaded, then fried or baked[26][27]
- cupboard - (n.) closet[28]
- craw - (n.) crawfish[3]
- cruds, crudded milk, or cruddled milk - (n.) cottage cheese[29][30]
- diamond - (n.) town square[28]
- dippy - (adj.) appropriate for dipping into, such as gravy, coffee, egg yolks, etc.[31]
- doll baby - (n.) complimentary term for an attractively childlike girl or woman (reversal of "baby doll")
- drooth - (n.) drought[3][32]
- dupa - (n.) parental term (of Polish origin) for a child's backside
- feature - (v.) to think about, understand, or imagine
- grinnie - (n.) chipmunk[33]
- gumband - (n.) rubber band;[6][7][31] elastic fastener[28]
- gutchies; or undergutchies (n.) term used to describe undergarments of any variety.
- hap - (n.) comfort; or, comforter or quilt:[29][34]
- hoagie - (n.) a sub (i.e., submarine sandwich; used throughout Pennsylvania)[31]
- jag - (v.) to prick, stab, or jab;[35] to tease[36] (often, jag off or jag around)[37][35]
- jimmies - (n.) sprinkles[38]
- jumbo - (n.) bologna lunch meat[6][7][35][39]
- "Kennywood's open" - idiom used to inform someone that their fly is open ("Kennywood" referring to the Kennywood amusement park in West Mifflin, Pennsylvania)
- Klondike - (n.) ice cream bar (from a local brand name)[28]
- kolbusy or kolbassi - (n.) variant pronunciation of kielbasa[35] (/kʊlˈbɑsi/)[40]
- monkey ball - (n.) fruit of the Maclura pomifera or monkey ball tree[41]
- n'at (/əˈnæt/) - et cetera; and so on; a "general extender";[6][7] literally, a contraction of "and (all) that"[42][43]
- neb - (v.) to pry into a conversation or argument intrusively or impertinently[35] (this term and its derivatives are common to Pennsylvania, but especially southwestern Pennsylvania, from Scots-Irish English)
- onion snow - (n.) early spring snow[28]
- redd up (also ret, rid, ridd, or redd out) - (v.) to tidy up, clean up, or clean out (a room, house, cupboard, etc.); to clean house, tidy up (hence v bl. redding up house-cleaning; tidying up)[44][45][46][47][48]
- reverend - (adj.) extreme;[28] extraordinary, powerful[32]
- slippy - (adj.) slippery (from Scots-Irish English)[6][7]
- spicket - (n.) alternate pronunciation of spigot, specifically an outdoor faucet used to connect to a garden hose[49]
- Stillers - (n.) alternate pronunciation of the Pittsburgh Steelers[50]
- sweep - (v.) to vacuum
- sweeper - (n.) vacuum cleaner (also used in Ohio and Indiana; from carpet sweeper)
- tossle cap - (n.) knit hat designed to provide warmth in cold weather
- trick - (n.) a job shift (as used in West-Central Pennsylvania)[51]
- yins, yinz, yunz, you'uns, or youns - (pronoun) plural of you (second-person personal plural pronoun from Scots-Irish English)[6][7][29][52][13][53][54]
Grammar
- All to mean all gone: When referring to consumable products, the word all has a secondary meaning: all gone. For example, the phrase the butter's all would be understood as "the butter is all gone." This likely derives from German.[55]
- "Positive anymore": In addition to the normal negative use of anymore it can also, as in the greater Midland U.S. dialect, be used in a positive sense to mean "these days" or "nowadays".[56] An example is "I wear these shoes a lot anymore". While in Standard English anymore must be used as a negative polarity item (NPI), some speakers in Pittsburgh and throughout the Midland area do not have this restriction.[53] This is somewhat common in both the Midland regions (Montgomery 1989) and in northern Maryland (Frederick, Hagerstown, and Westminster), likely of Scots-Irish origin (Montgomery 1999).
- Reversed usage of leave and let:[6][7][57] Examples of this include "Leave him go outside" and "Let the book on the table". Leave is used in some contexts in which, in standard English, let would be used; and vice versa. Used in Southwestern Pennsylvania and elsewhere, this is either Pennsylvania German or Scots-Irish.[57]
- "Need, want, or like + past participle":[6][7][58] Examples of this include "The car needs washed", "The cat wants petted", and "Babies like cuddled". More common constructions are "The grass needs cutting" or "The grass needs to be cut" or "Babies like cuddling" or "Babies like to be cuddled"; "The car needs washing" or "The car needs to be washed"; and "The cat wants petting" or "The cat wants to be petted." Found predominantly in the North Midland region, this is especially common in southwestern Pennsylvania (Murray, Frazer and Simon 1996; Murray and Simon 1999; Murray and Simon 2002). Need + past participle is the most common construction, followed by want + past participle, and then like + past participle. The forms are "implicationally related" to one another (Murray and Simon 2002). This means the existence of a less common construction from the list in a given location entails the existence of the more common ones there, but not vice versa. The constructions "like + past participle" and "need + past participle" are Scots-Irish (Murray, Frazer, and Simon 1996; Murray and Simon 1999; Montgomery 2001; Murray and Simon 2002). While Adams[57] argues that "want + past participle" could be from Scots-Irish or German, it seems likely that this construction is Scots-Irish, as Murray and Simon (1999 and 2002) claim. like and need + past participle are Scots-Irish, the distributions of all three constructions are implicationally related, the area where they are predominantly found is most heavily influenced by Scots-Irish, and a related construction, "want + directional adverb", as in "The cat wants out", is Scots-Irish.[29][53]
- "Punctual whenever": "Whenever" is often used to mean "at the time that" (Montgomery 2001). An example is "My mother, whenever she passed away, she had pneumonia." A punctual descriptor refers to the use of the word for "a onetime momentary event rather than in its two common uses for a recurrent event or a conditional one". This Scots-Irish usage is found in the Midlands and the South.
See also
- Jagoff
- Midland American English
- Pennsylvania Dutch English
- Philadelphia accent
- Pittsburgh Dad
- Regional vocabularies of American English
- Yinztagram
References
- Labov, Ash & Boberg (2006:130, 133)
- "Do You Speak American . Sea to Shining Sea . American Varieties . Pittsburghese - PBS". PBS.
- Cassidy, F. G., ed. (1985). Dictionary of American Regional English, Vol. I: A-C. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-20511-6.
- Wolowyna, Oleh (January 9, 2000). "Demographic, social, cultural characteristics of persons of Ukrainian ancestry in Chicago". The Ukrainian Weekly No. 2, Vol. LXVIII. Retrieved May 16, 2008. (based on 1990 US Census)
- LeMay, Michael C. (2012-12-10). Transforming America: Perspectives on U.S. Immigration [3 volumes]: Perspectives on U.S. Immigration. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 9780313396441.
- Johnstone, Barbara; Baumgardt, Dan (2004). ""Pittsburghese" Online: Vernacular Norming in Conversation". American Speech. 79 (2): 115–145. doi:10.1215/00031283-79-2-115. JSTOR 40281107. S2CID 3861413.
- Johnstone, Barbara; Bhasin, Neeta; Wittkofski, Denise (2002). ""Dahntahn" Pittsburgh: Monophthongal /aw/ and Representations of Localness in Southwestern Pennsylvania". American Speech. 77 (2): 148–166. doi:10.1215/00031283-77-2-148. JSTOR 40281028. S2CID 2783229.
- Kurath, Hans (1949). A Word Geography of the Eastern United States. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 9780472085323. Retrieved 21 October 2012.
- Salvucci, Claudio (1999). "Linguistic Geography of Pennsylvania". Evolution Publishing. Retrieved 2012-10-21.
- Thomas, Charles (1958). An Introduction to the Phonetics of American English. Ronald Press. Retrieved 21 October 2012.
- Labov, Ash & Boberg (2006:66)
- Labov, Ash & Boberg (2006:123)
- Johnstone, Barbara (2011). "Place, language, and semiotic order. Paper presented at Urban Symbolic Landscapes conference, Helsinki, Finland, May 3, 2011".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Questions and Answers: Who Uses Pittsburgh Speech the Most?". Pittsburgh Speech and Society. University Library System, University of Pittsburgh. Retrieved 16 May 2013.
- Gagnon, C. L. (1999). Language attitudes in Pittsburgh: 'Pittsburghese' vs. standard English. Master's thesis. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh.
- Kortmann, Bernd and Edgar W. Schneider, eds. (2004). A Handbook of Varieties of English, Volume 1: Phonology. De Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-017532-5.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - Hankey, Clyde T. (1965). "Miscellany: 'tiger,' 'tagger,' and [aɪ] in western Pennsylvania". American Speech. 40 (3): 226–229. doi:10.2307/454074. JSTOR 454074.
- Brown, C (1982). A search for sound change: A look at the lowering of tense vowels before liquids in the Pittsburgh area. Master's thesis. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh.
- Labov, Ash & Boberg (2006:72)
- Hankey, Clyde T. (1972). Notes on west Penn-Ohio phonology. In: Studies in Linguistics in Honor of Raven I. McDavid, Jr., ed. by L.M. Davis. University of Alabama Press. pp. 49–61. ISBN 978-0-8173-0010-4.
- Fasold, Ralph W. (1980). "The conversational function of Pennsylvania Dutch intonation". Paper Presented at New Ways of Analyzing Variation (NWAVE IX) at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI.
- In Russian, Slovak, and many other Slavic languages, the word babushka (a familial/cute extension of the word baba) means "grandmother" or (endearingly) "old woman." In Pittsburgh and much Northern U.S. English, the word also denotes a type of headscarf that might be worn by an old woman. Predominantly used in the northeast United States, babushka is most heavily in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin, and Michigan. It is sometimes used as a derogatory term for an elderly woman, similar to calling someone an "old hag."[citation needed]
- Kurath (1949) mentions that speakers in a large portion of Pennsylvania use the term, but that it is "very common in the Pittsburgh area[,]...[in] the adjoining counties of Ohio and on the lower Kanawha"
- Johnstone, Barbara; Andrus, Jennifer; Danielson, Andrew E. (2006-06-01). "Mobility, Indexicality, and the Enregisterment of 'Pittsburghese'" (PDF). Journal of English Linguistics. 34 (2): 77–104. doi:10.1177/0075424206290692. ISSN 0075-4242. S2CID 3851451. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-02-28.
- (Kurath 1949); this may be heard from the western edge of the Alleghenies to beyond the Ohio line
- "Something different, Something delicious: City Chicken", Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, p. 4, 2 November 1932, retrieved 16 September 2016
- This is heard in Southwestern Pennsylvania and Northern West Virginia. It origins are not entirely known, but rumored to have begun during the Depression Era, when people took meat scraps and fashioned a makeshift drumstick out of them.
- Johnstone, Barbara (2013). Speaking Pittsburghese: The Story of a Dialect. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-199-94568-9.
- Crozier, Alan (1984). "The Scotch-Irish influence on American English". American Speech. 59 (4): 310–331. doi:10.2307/454783. JSTOR 454783.
- Kurath (1949) claims these forms are used from the western edge of the Alleghenies to beyond the Ohio line; and Crozier claims that they are restricted to southwestern Pennsylvania, from Scots-Irish English origins.
- Cassidy, F. G. and. J.H. Hall., Eds. (1991). Dictionary of American Regional English, Vol. II: D-H. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-20512-3.
- Johnstone, Barbara (2015). Pittsburgh Speech and Pittsburghese. Walter de Gruyter GmbH. ISBN 978-1-614-51178-6.
- Kurath 1949): This term is used from the western edge of the Alleghenies to beyond the Ohio line.
- This can mean "comfort", as in "He's been in poor hap since his wife died" (Maxfield 1931), or "comforter or quilt," as in "It was cold last night but that hap kept me warm." Hap is used for "comfort" in western Pennsylvania (Maxfield 1931); and a "quilt" is known as a hap only in western Pennsylvania.
- Cassidy, F. G. and J. H. Hall, Eds. (1996). Dictionary of American Regional English, Volume III: I-O. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-20519-2.
- Johnstone, Andrus and Danielson 2006
- The word is often followed by off to mean (as a verb) "to annoy, irritate, play tricks on; to disparage; to reject", or (as a noun) "an annoying or irritating person;" as well as around to mean "annoy, tease, or engage in a frivolous endeavor." These phrases are probably influenced by jack off and jack around, respectively. "Jus' jaggin'" is a common expression, the same as standard "just kidding". Descended from Scots-Irish usage in English, this is chiefly a Pennsylvania term, especially southwestern Pennsylvania, but also portions of Appalachia.
- Freeman, Jan. "The jimmies story". Boston.com.
- Wisnosky 2003; Johnstone, Andrus and Danielson 2006
- The OED (1991) lists kolbasa as a variable pronunciation of kielbasa, and notes that the former pronunciation is Polish and the latter Russian.
- Parker, Jeanie (September 2, 2000). "Gardening: The fruit of the Osage orange tree has many odd reputed uses". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. PG Publishing. Retrieved 26 February 2014.
- McElhinny 1999; Wisnosky 2003; Johnstone, Andrus and Danielson 2006
- The distribution of n'at is Southwestern Pennsylvania, possibly Scots-Irish. Macaulay (1995) finds it in the regular speech and narratives of Scottish coal miners in Glasgow, a principal area from which Scottish settlers emigrated to Northern Ireland, and from there, to the American colonies.
- Hall, J. H., ed. (2002). Dictionary of American Regional English, Volume IV: P-Sk. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-00884-7.
- Dressman, Michael R. (1979). "Redd up". American Speech. 54 (2): 141–145. doi:10.2307/455213. JSTOR 455213.
- Also see McElhinny (1999); Johnstone, Andrus and Danielson (2006).
- An example of this term is "Yinz better redd up this room". Dressman notes that it is common to the Pittsburgh area and throughout Pennsylvania, but less so in Philadelphia. It is also scattered about New England States and in New Brunswick, though its occurrence is heaviest in Pennsylvania. Hall states that its distribution is "scattered, but chiefly N. Midland, esp PA". Dressman suggested that it was brought to the U.S. by Scots. It's almost certainly of Scandinavian/Viking origin; the Danish "rydde op" means to clean up. "Redd up" and its associated variants probably entered the English language from old Norse.
- Editors of the American Heritage Dictionaries (2006). The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (Fourth ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-618-70173-5. Retrieved 26 October 2012.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - "Definition of SPICKET".
- Yinzer Basics: Pittsburghese for Beginners
- "Yunzonics: Translating Pennsylvanian". tomtwine.com. Thomas H. Twine. Archived from the original on 23 September 2009. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- McElhinny 1999; Wisnosky 2003; Johnstone, Andrus and Danielson 2006: Used Southwestern Pennsylvania and elsewhere in Appalachia, yinz is a particularly salient feature of Pittsburgh speech
- Robert P. Marzec (30 December 2004). The Mid-Atlantic Region. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 271. ISBN 978-0-313-32954-8. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
- Montgomery 2001
- Metcalf, Allan (2000). How We Talk: American Regional English Today. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-618-04362-0. Retrieved 26 October 2012.
- Montgomery 1989; McElhinny 1999; Montgomery 1999
- Adams, Michael (2003). "Lexical Doppelgängers". Journal of English Linguistics. 28 (3): 295–310. doi:10.1177/00754240022005054. S2CID 220752970.
- Still, Brian (15 October 2010). Usability of Complex Information Systems: Evaluation of User Interaction. CRC Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-1-4398-2894-6. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
Further reading
- Johnstone, B.; Andrus, J.; Danielson, A. (2006). "Mobility, indexicality, and the enregisterment of "Pittsburghese"". Journal of English Linguistics. 34 (2): 77–104. doi:10.1177/0075424206290692. S2CID 3851451.
- Kurath, H. (1949). Western Pennsylvania. A Word Geography of the Eastern United States. Ann Arbor, University of Michigan Press: 35-36.
- Kurath, H. and R. I. McDavid. (1961). Western Pennsylvania. The pronunciation of English in the Atlantic United States. Ann Arbor, University of Michigan Press: 17-18.
- Labov, W., S. Ash and C. Boberg. (2005). The atlas of North American English: phonetics, phonology, and sound change. Mouton de Gruyter.
- Labov, William; Ash, Sharon; Boberg, Charles (2006), The Atlas of North American English, Berlin: Mouton-de Gruyter, pp. 187–208, ISBN 978-3-11-016746-7
- Layton, N. N. (1999). The dialect of western Pennsylvania: evaluation of ten sounds. Master's thesis. Goteburg, Sweden: University of Goteburg.
- Macauley, R. (1985). The narrative skills of a Scottish coal miner. Focus on: Scotland. Ed. by M. Gorlach. Philadelphia, John Benjamins: 101-124.
- Maxfield, E. K. (1931). "The speech of south-western Pennsylvania". American Speech. 7 (1): 18–20. doi:10.2307/451308. JSTOR 451308.
- McElhinny, B (1999). "More on the third dialect of English: linguistic constraints on the use of three phonological variables in Pittsburgh". Language Variation and Change. 11 (2): 171–195. doi:10.1017/s0954394599112031. S2CID 145656857.
- Montgomery, M. B. (1997). A tale of two Georges: the language of Irish Indian traders in colonial North America. Focus on: Ireland. Ed. by J. Kallen. Philadelphia, John Benjamins. 21: 227-254.
- Montgomery, M. B. (1989). "Exploring the roots of Appalachian English". English World-Wide. 10 (2): 227–278. doi:10.1075/eww.10.2.03mon.
- Montgomery, M. B. (2001). ""My mother, whenever she died, she had pneumonia": The history and functions of whenever". Journal of English Linguistics. 29 (3): 234–249. doi:10.1177/00754240122005350. S2CID 143776545.
- Montgomery, M. B. (2002). "The structural history of y'all, you all, and you'uns". Southern Journal of Linguistics. 26: 19–27.
- Murray, T. E.; Frazer, T. C.; Simon, B. L. (1996). "Need + past participle in American English". American Speech. 71 (3): 255–271. doi:10.2307/455549. JSTOR 455549.
- Murray, T. E.; Simon, B. L. (1999). "Want + past participle in American English". American Speech. 74 (2): 140–164. JSTOR 455576.
- Murray, T. E.; Simon, B. L. (2002). "At the intersection of regional and social dialects: the case of like + past participle in American English". American Speech. 77 (1): 32–69. doi:10.1215/00031283-77-1-32. S2CID 143892781.
- Newlin, C (1928). "Dialects on the western Pennsylvania frontier". American Speech. 4 (2): 104–110. doi:10.2307/452864. JSTOR 452864.
- Shields, K. Jr. (1985). "Germanisms in Pennsylvania English: an update". American Speech. 60 (3): 228–237. doi:10.2307/454887. JSTOR 454887.
- Simpson, J.A. and E.S.C. Weiner, Eds. (1991). Compact Oxford English Dictionary. 2nd Ed. Cambridge: Oxford UP.
- Tenny, C (1998). "Psych verbs and verbal passives in Pittsburghese". Linguistics. 36: 591–597.
- Thomas, E. (2001). An acoustic analysis of vowel variation in New World English. Durham, Duke UP.
- Wisnosky, M. (2003). 'Pittsburghese' in Pittsburgh humor. Master's thesis in Linguistics. Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh.
- Heinz History Center staff (2015). Pittsburghese from Ahrn to Yinz. Senator John Heinz History Center. ISBN 978-0936340210.
- Blackley, Katie (28 September 2017). "Redd Up Your Pittsburghese: A Deep Dive Into How Yinz Talk". WESA-FM. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
External links
- Pittsburgh Speech & Society, University of Pittsburgh
- "It's Not the Sights, It's the Sounds", New York Times article, March 17, 2006 /9"Pittsburgh is the Galapagos Islands of American dialect")
- "American Varieties: Steel Town Speak", part of PBS's Do You Speak American?
- Pittsburghese: Welcome!, Duquesne University
- Pittsburghese.com
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
