lingvo.wikisort.org - Language
The Kartvelian languages (/kɑːrtˈvɛliən, -ˈvil-/; Georgian: ქართველური ენები, romanized: kartveluri enebi; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languages[1]) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primarily in Georgia. There are approximately 5.2 million Kartvelian speakers worldwide, with large groups in Russia, Iran, the United States, the European Union, Israel,[2] and northeastern Turkey.[3] The Kartvelian family has no known relation to any other language family, making it one of the world's primary language families.[4]
| Kartvelian | |
|---|---|
| ქართველური | |
| Geographic distribution | Western Trans-Caucasus, Northeast Anatolia |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Kartvelian |
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-5 | ccs |
| Glottolog | kart1248 |
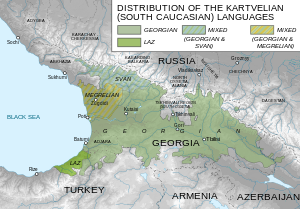 | |
The most widely spoken of these languages is Georgian. The earliest literary source in any Kartvelian language is the Old Georgian Bir el Qutt inscriptions, written in ancient Georgian Asomtavruli script at the once-existing Georgian monastery near Bethlehem,[5] dated to c. 430 AD.[6] The Georgian script is used to write all Kartvelian languages.
Social and cultural status
Georgian is the official language of Georgia (spoken by 90% of the population) and the main language for literary and business use in Georgia. It is written with an original and distinctive alphabet, and the oldest surviving literary text dates from the 5th century AD. The old Georgian script seems to have been derived from the Greek script,[7] but this is not certain.
Mingrelian has been written with the Georgian alphabet since 1864, especially in the period from 1930 to 1938, when the Mingrelians enjoyed some cultural autonomy, and after 1989.
The Laz language was written mainly between 1927 and 1937, and now again in Turkey using the Latin alphabet. Laz, however, is disappearing as its speakers are integrating into mainstream Turkish society.
Classification
| Part of a series on |
| Georgians ქართველები |
|---|
 |
| Nation |
| Georgia |
| Ancient Kartvelian people |
|
| Subgroups |
|
| Culture |
|
| Languages |
|
| Religion |
|
| Symbols |
|
| History of Georgia |
The Kartvelian language family consists of four closely related languages:
- Svan (ლუშნუ ნინ, lušnu nin), with approximately 35,000–40,000 native speakers in Georgia, mainly in the northwestern mountainous region of Svaneti and the Kodori Gorge in Abkhazia
- Georgian-Zan (also called Karto-Zan)
- Georgian (ქართული ენა, kartuli ena) with approximately 4 million native speakers, mainly in Georgia. There are Georgian-speaking communities in Russia, Turkey, Iran, Israel, and EU countries, but the current number and distribution of them are unknown.
- Judaeo-Georgian (ყივრული ენა, kivruli ena) with some 85,000 speakers, is the only Kartvelian Jewish dialect, its status being the subject of debate among scholars.[8]
- Zan (also called Colchian)
- Mingrelian (მარგალური ნინა, margaluri nina), with some 500,000 native speakers in 1989, mainly in the western regions of Georgia, namely Samegrelo and Abkhazia (at present in Gali district only). The number of Mingrelian speakers in Abkhazia was very strongly affected by the war with Georgia in the 1990s which resulted in the expulsion and flight of the ethnic Georgian population, the majority of which were Mingrelians. Nevertheless, Georgians in Abkhazia (mostly Mingrelians) make up 18% of the population, in Gali district 98.2%.[9] The Mingrelians displaced from Abkhazia are scattered elsewhere in the Georgian government territory, with dense clusters in Tbilisi and Zugdidi.
- Laz (ლაზური ნენა, lazuri nena), with 22,000 native speakers in 1980, mostly in the Black Sea littoral area of northeast Turkey, and with some 2,000 in Adjara, Georgia.[citation needed]
- Georgian (ქართული ენა, kartuli ena) with approximately 4 million native speakers, mainly in Georgia. There are Georgian-speaking communities in Russia, Turkey, Iran, Israel, and EU countries, but the current number and distribution of them are unknown.
Genealogical tree
| Proto-Kartvelian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proto-Georgian-Zan (Proto-Karto-Zan) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Svan | Mingrelian | Laz | Georgian | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The connection between these languages was first reported in linguistic literature by Johann Anton Güldenstädt in his 1773 classification of the languages of the Caucasus, and later proven by G. Rosen, Marie-Félicité Brosset, Franz Bopp and others during the 1840s. Zan is the branch that contains the Mingrelian and Laz languages.
On the basis of glottochronological analysis, Georgi Klimov dates the split of the Proto-Kartvelian into Svan and Proto-Georgian-Zan (Proto-Karto-Zan) to the 19th century BC,[10][11] and the further division into Georgian and Zan to the 8th century BC,[11] although with the reservation that such dating is very preliminary and substantial further study is required.[10]
Higher-level connections
No relationship with other languages, including the two North Caucasian language families, has been demonstrated so far.[7] According to the Nostratic hypothesis, advocated by Illič-Svityč and his school, the six language families Altaic, Uralic, Indo-European, Dravidian, Semito-Hamitic and Kartvelian go back to a common proto-language and are thus genetically related.[12][13] Note however that both the concept of a Nostratic family and Kartvelian's relation to it are not considered likely by other linguists.
Certain grammatical similarities with Basque, especially in the case system, have often been pointed out. However, the hypothesis of a relationship, which also tends to link the Caucasian languages with other non-Indo-European and non-Semitic languages of the Near East of ancient times, is generally considered to lack conclusive evidence.[7] Any similarities to other linguistic phyla may be due to areal influences. Heavy borrowing in both directions (i.e. from North Caucasian to Kartvelian and vice versa) has been observed; therefore, it is likely that certain grammatical features have been influenced as well. If the Dené–Caucasian hypothesis, which attempts to link Basque, Burushaski, the North Caucasian families and other phyla, is correct, then the similarities to Basque may also be due to these influences, however indirect. Certain Kartvelian–Indo-European lexical links are revealed at the protolanguage level,[14] which are ascribed to the early contacts between Proto-Kartvelian and Proto-Indo-European populations.[15]
Phonetics and phonology
Regular correspondences
| Proto-Kartv. | Geo. | Zan | Svan |
|---|---|---|---|
| *ა (*a) [ɑ] |
a [ɑ] |
o [ɔ] |
a [ɑ] |
| *ე (*e) [ɛ] |
e [ɛ] |
a [ɑ] |
e [ɛ] |
| *ი (*i) [i] |
i [i] |
i [i] |
i [i] |
| *ო (*o) [ɔ] |
o [ɔ] |
o [ɔ] |
o [ɔ] |
| *უ (*u) [u] |
u [u] |
u [u] |
u [u] |
| Proto-Kartv. | Geo. | Zan | Svan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voiced stops |
*ბ (*b) [b] |
b [b] |
b [b] |
b [b] |
| *დ (*d) [d] |
d [d] |
d [d] |
d [d] | |
| *გ (*g) [ɡ] |
g [ɡ] |
g [ɡ] |
g / ǯ [ɡ] / [d͡ʒ] | |
| Voiced affricates |
*ძ (*ʒ) [d͡z] |
ʒ [d͡z] |
ʒ [d͡z] |
ʒ / z [d͡z] / [z] |
| *ძ₁ (*ʒ₁) [ɖʐ] |
ǯ [d͡ʒ] |
ǯ / ž [d͡ʒ] / [ʒ] | ||
| *ჯ (*ǯ) [d͡ʒ] |
ǯ [d͡ʒ] |
ǯg / ʒg [d͡ʒɡ] / [d͡zɡ] |
ǯg / sg [d͡ʒɡ] / [sɡ] | |
| Voiced fricatives |
*ზ (*z) [z] |
z [z] |
z [z] |
z [z] |
| *ზ₁ (*z₁) [ʐ] |
ž [ʒ] |
ž [ʒ] | ||
| *ღ (*ɣ) [ɣ] |
ɣ [ɣ] |
ɣ [ɣ] |
ɣ [ɣ] | |
| *უ̂ (*w) [w] |
v [v] |
v [v] |
w [w] | |
| Ejective stops |
*პ (*ṗ) [pʼ] |
ṗ [pʼ] |
ṗ [pʼ] |
ṗ [pʼ] |
| *ტ (*ṭ) [tʼ] |
ṭ [tʼ] |
ṭ [tʼ] |
ṭ [tʼ] | |
| *კ (*ḳ) [kʼ] |
ḳ [kʼ] |
ḳ [kʼ] |
ḳ / č' [kʼ] / [t͡ʃʼ] | |
| *ყ (*qʼ) [qʼ] |
qʼ [qʼ] |
qʼ / ʔ / ḳ [qʼ] / [ʔ] / [kʼ] |
qʼ [qʼ] | |
| Ejective affr. |
*წ (*ċ) [t͡sʼ] |
ċ [t͡sʼ] |
ċ [t͡sʼ] |
ċ [t͡sʼ] |
| *წ₁ (*ċ₁) [ʈʂʼ] |
čʼ [t͡ʃʼ] |
čʼ [t͡ʃʼ] | ||
| *ლʼ (*ɬʼ) [t͡ɬʼ] |
h [h] | |||
| *ჭ (*čʼ) [t͡ʃʼ] |
čʼ [t͡ʃʼ] |
čʼḳ / ċḳ [t͡ʃʼkʼ] / [t͡sʼkʼ] |
čʼḳ / šḳ [t͡ʃʼkʼ] / [ʃkʼ] | |
| Voiceless stops and affr. |
*ფ (*p) [p] |
p [p] |
p [p] |
p [p] |
| *თ (*t) [t] |
t [t] |
t [t] |
t [t] | |
| *ც (*c) [t͡s] |
c [t͡s] |
c [t͡s] |
c [t͡s] | |
| *ც₁ (*c₁) [ʈʂ] |
č [t͡ʃ] |
č [t͡ʃ] | ||
| *ჩ (*č) [t͡ʃ] |
č [t͡ʃ] |
čk [t͡ʃk] |
čk / šg [t͡ʃk] / [ʃɡ] | |
| *ქ (*k) [k] |
k [k] |
k [k] |
k / č [k] / [t͡ʃ] | |
| *ჴ (*q) [q] |
x [x] |
x [x] |
q [q] | |
| Voiceless fricatives |
*ხ (*x) [x] |
x [x] | ||
| *შ (*š) [ʃ] |
š [ʃ] |
šk / sk [ʃk] / [sk] |
šg / sg [ʃɡ] / [sɡ] | |
| *ს (*s) [s] |
s [s] |
s [s] |
s [s] | |
| *ს₁ (*s₁) [ʂ] |
š [ʃ] |
š [ʃ] | ||
| *ლʿ (*lʿ) [ɬ] |
∅ | l [l] | ||
| Liquids | *ლ (*l) [l] |
l [l] |
l [l] | |
| *რ (*r) [r] |
r [r] |
r [r] |
r [r] | |
| Nasals | *მ (*m) [m] |
m [m] |
m [m] |
m [m] |
| *ნ (*n) [n] |
n [n] |
n [n] |
n [n] |
Grammar
Noun classification
The Kartvelian languages classify objects as intelligent ("who"-class) and unintelligent ("what"-class) beings. Grammatical gender thus is not correlated to masculine not feminine as in many languages with grammatical gender associated with vegetance, animacy, or sentience.
| Concrete | Abstract | ||
| Animate | Inanimate | ||
| Human and "human-like" beings (e.g. God, deities, angels) | Animals | Inanimate physical entities | Abstract objects |
| Intelligent | Unintelligent | ||
| "who"-class | "what"-class | ||
Declension
| Case | Singular | Plural | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mingrelian | Laz | Georgian | Svan | Mingrelian | Laz | Georgian | Svan | ||
| Nominative | -i | -i/-e | -i | -i | -ep-i | -ep-e | -eb-i | -är | |
| Ergative | -k | -k | -ma | -d | -ep-k | -epe-k | -eb-ma | -är-d | |
| Dative | -s | -s | -s | -s | -ep-s | -epe-s | -eb-s | -är-s | |
| Genitive | -iš | -iš | -is | -iš | -ep-iš | -epe-š(i) | -eb-is | -are-š | |
| Lative | -iša | -iša | — | — | -ep-iša | -epe-ša | — | — | |
| Ablative | -iše | -iše | — | — | -ep-iše | -epe-še(n) | — | — | |
| Instrumental | -it | -ite | -it | -šw | -ep-it | -epe-te(n) | -eb-it | -är-šw | |
| Adverbial | -o(t)/-t | -ot | -ad/-d | -d | -ep-o(t) | — | -eb-ad | -är-d | |
| Finalis | -išo(t) | — | -isad | -išd | -ep-išo(t) | — | -eb-isad | -är-išd | |
| Vocative | — | — | -o (/-v) | — | — | — | -eb-o | — | |
| Case | Singular | Plural | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mingrelian | Laz | Georgian | Svan | Mingrelian | Laz | Georgian | Svan | ||
| Nominative | ǯveš-i | mǯveš-i | ʒvel-i | ǯwinel | ǯveš-ep-i | mǯveš-ep-e | ʒvel-eb-i | ǯwinel-är | |
| Ergative | ǯveš-k | mǯveš-i-k | ʒvel-ma | ǯwinel-d | ǯveš-ep-k | mǯveš-epe-k | ʒvel-eb-ma | ǯwinel-är-d | |
| Dative | ǯveš-s | mǯveš-i-s | ʒvel-s | ǯwinel-s | ǯveš-ep-s | mǯveš-i-epe-s | ʒvel-eb-s | ǯwinel-är-s | |
| Genitive | ǯveš-iš | mǯveš-iš | ʒvel-is | ǯwinl-iš | ǯveš-ep-iš | mǯveš-epe-š | ʒvel-eb-is | ǯwinel-är-iš | |
| Lative | ǯveš-iša | mǯveš-iša | — | — | ǯveš-ep-iša | mǯveš-epe-ša | — | — | |
| Ablative | ǯveš-iše | mǯveš-iše | — | — | ǯveš-ep-iše | mǯveš-epe-še | — | — | |
| Instrumental | ǯveš-it | mǯveš-ite | ʒvel-it | ǯwinel-šw | ǯveš-ep-it | mǯveš-epe-te | ʒvel-eb-it | ǯwinel-är-šw | |
| Adverbial | ǯveš-o | mǯveš-ot | ʒvel-ad | ǯwinel-d | ǯveš-ep-o | — | ʒvel-eb-ad | ǯwinel-är-d | |
| Finalis | ǯveš-išo | — | ʒvel-isad | ǯwinel-išd | ǯveš-ep-išo | — | ʒvel-eb-isad | ǯwinel-är-išd | |
| Vocative | — | — | ʒvel-o | — | — | — | ʒvel-eb-o | — | |
Verb
Kartvelian verbs can indicate one, two, or three grammatical persons. A performer of an action is called the subject and affected persons are objects (direct or indirect). The person may be singular or plural. According to the number of persons, the verbs are classified as unipersonal, bipersonal or tripersonal.
- Unipersonal verbs have only a subject and so are always intransitive.
- Bipersonal verbs have a subject and one object, which can be direct or indirect. The verb is:
- transitive when the object is direct;
- intransitive if the object is indirect.
- Tripersonal verbs have one subject and both direct and indirect objects and are ditransitive.
| Unipersonal | Bipersonal | Tripersonal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| intransitive | transitive | intransitive | ditransitive | |
| Subject | + | + | + | + |
| Direct object | + | + | ||
| Indirect object | + | + | ||
Subjects and objects are indicated with special affixes.
| Subject set | |||||||||
| Singular | Plural | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old Geo. | Mod. Geo. | Ming./Laz | Svan | Old Geo. | Mod. Geo. | Ming./Laz | Svan | ||
| S1 | v- | v- | v- | xw- | v-...-t | v-...-t | v-...-t | xw-...-(š)d (excl.)
l-...-(š)d (incl.) | |
| S2 | x/h- | ∅,(h/s)- | ∅ | x-/∅ | x/h-...-t | ∅,(h/s)-...-t | ∅-...-t | x/∅-...-(š)d | |
| S3 | -s,-a/o,-n,-ed | -s,-a/o | -s,-u,-n | (l)-...-s/(a) | -an,-en,-es,-ed | -en,-an,-es | -an,-es | (l)-...-x | |
| Object set | |||||||||
| O1 | m- | m- | m- | m- | m- (excl.)
gv- (incl.) |
gv- | m-...-t,-an,-es | n- (excl.)
gw- (incl.) | |
| O2 | g- | g- | g- | ǯ- | g- | g-...-t | g-...-t,-an,-es | ǯ-...-x | |
| O3 | x/h,∅- | ∅,s/h/∅- | ∅ | ∅,x- | x/h,∅- | ∅,s/h/∅-...-t | ∅-...-t,-an,-es | ∅,x-...-x | |
By means of special markers Kartvelian verbs can indicate four kinds of action intentionality ("version"):
- subjective—shows that the action is intended for oneself,
- objective—the action is intended for another person,
- objective-passive—the action is intended for another person and at the same time indicating the passiveness of subject,
- neutral—neutral with respect to intention.
| Version | Mingrelian | Laz | Georgian | Svan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjective | -i- | -i- | -i- | -i- |
| Objective | -u- | -u- | -u- | -o- |
| Objective-passive | -a- | -a- | -e- | -e- |
| Neutral | -o-/-a- | -o- | -a- | -a- |
Case patterns
Subject, direct object and indirect object are coded by the three core-cases, namely ergative, nominative and dative. Although the term "ergative" is traditional, strictly speaking no Kartvelian language features ergative alignment. Rather, they display a mixture of nominative-accusative and active alignment,[18] depending on two factors:
- the class to which the verb belongs, based on its morphological and syntactic properties (class 1 including all transitive verbs, while intransitive verbs are divided between class 2 and 3);
- the series to which the tense/aspect/mood form (traditionally known as screeve) belongs.
Georgian and Svan have accusative alignment in the Present series (often termed Series I) and active alignment in the Aorist series (Series II).
| Subject | Direct object | Indirect object | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 3 | Class 2 | |||
| Series I | Nominative | Dative | |||
| Series II | Ergative | Nominative | Dative | ||
Laz has extended the case marking of Series II to Series I, thus featuring active alignment regardless of tense.
| Subject | Direct object | Indirect object | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 3 | Class 2 | |||
| Series I | Ergative | Nominative | Dative | ||
| Series II | Ergative | Nominative | Dative | ||
Mingrelian, on the other hand, has extended the use of the ergative to all intransitive verbs, becoming fully accusative in all series, although with different case marking.
| Subject | Direct object | Indirect object | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 3 | Class 2 | |||
| Series I | Nominative | Dative | |||
| Series II | Ergative | Nominative | Dative | ||
Examples from inherited lexicon
| Proto-Kartv.
form |
Karto-Zan | Svan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-form | Georgian | Mingrelian | Laz | |||
| 1. one, 2. other | *s₁xwa [ʂxwɑ] |
*s₁xwa [ʂxwɑ] |
sxva [sxvɑ] (other) |
šxva [ʃxva] (other) |
čkva / škva [t͡ʃkvɑ] / [ʃkvɑ] (other, one more) |
e-šxu [ɛ-ʃxu] (one) |
| one | n/a | *erti [ɛrti] |
erti [ɛrti] |
arti [ɑrti] |
ar [ɑr] |
n/a |
| two | *yori [jɔri] |
*yori [jɔri] |
ori [ɔri] |
žiri / žəri [ʒiri] / [ʒəri] |
žur / ǯur [ʒur] / [d͡ʒur] |
yori [jɔri] |
| three | *sami [sɑmi] |
*sami [sɑmi] |
sami [sɑmi] |
sumi [sumi] |
sum [sum] |
semi [sɛmi] |
| four | *otxo [ɔtxɔ] |
*otxo [ɔtxɔ] |
otxi [ɔtxi] |
otxi [ɔtxi] |
otxo [ɔtxɔ] |
w-oštxw [w-ɔʃtxw] |
| five | *xuti [xuti] |
*xuti [xuti] |
xuti [xuti] |
xuti [xuti] |
xut [xut] |
wo-xušd [wɔ-xuʃd] |
| six | *eks₁wi [ɛkʂwi] |
*eks₁wi [ɛkʂwi] |
ekvsi [ɛkvsi] |
amšvi [ɑmʃwi] |
aši [ɑʃi] |
usgwa [usɡwɑ] |
| seven | *šwidi [ʃwidi] |
*šwidi [ʃwidi] |
švidi [ʃvidi] |
škviti [ʃkviti] |
škvit [ʃkvit] |
i-šgwid [i-ʃɡwid] |
| eight | *arwa [ɑrwɑ] |
*arwa [ɑrwɑ] |
rva [rvɑ] |
ruo / bruo [ruɔ] / [bruɔ] |
ovro / orvo [ɔvrɔ] / [ɔrvɔ] |
ara [ɑrɑ] |
| nine | *ts₁xara [t͡ʂxɑrɑ] |
*ts₁xara [t͡ʂxɑrɑ] |
tsxra [t͡sxrɑ] |
čxoro [t͡ʃxɔrɔ] |
čxoro [t͡ʃxɔrɔ] |
čxara [t͡ʃxɑrɑ] |
| ten | *a(s₁)ti [ɑ(ʂ)ti] |
*ati [ɑti] |
ati [ɑti] |
viti [viti] |
vit [vit] |
ešd [ɛʃd] |
| twenty | n/a | *ots₁i [ɔt͡ʂi] |
otsi [ɔt͡si] |
etsi [ɛt͡ʃi] |
etsi [ɛt͡ʃi] |
n/a |
| hundred | *as₁i [ɑʂi] |
*as₁i [ɑʂi] |
asi [ɑsi] |
oši [ɔʃi] |
oši [ɔʃi] |
aš-ir [ɑʃ-ir] |
| Personal Pronouns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-Kartv. | Georgian | Mingrelian | Laz | Svan | |
| I | *me [mɛ] |
me [mɛ] |
ma [mɑ] |
ma(n) [mɑ] |
mi [mi] |
| You (sg.) | *sen [sɛn] |
šen [ʃɛn] |
si [si] |
si(n) [si] |
si [si] |
| That | *e- [ɛ-] |
e-sa [ɛ-sɑ] |
e-na [ɛ-nɑ] |
(h)e-ya [(h)ɛ-jɑ] |
e-ǯa [ɛ-d͡ʒɑ] |
| We | *čwen [t͡ʃwɛn] |
čven [t͡ʃvɛn] |
čki(n) / čkə(n) [t͡ʃki(n)] / [t͡ʃkə(n)] |
čkin / čku / šku [t͡ʃkin] / [t͡ʃku] / [ʃku] |
näy
[næj] |
| You (pl.) | *stkwen [stkwɛn] |
tkven [tkvɛn] |
tkva(n) [tkvɑ(n)] |
tkvan [tkvɑn] |
sgäy [sɡæj] |
| Possessive Pronouns | |||||
| Proto-Kartv. | Georgian | Mingrelian | Laz | Svan | |
| My | *č(w)e-mi [t͡ʃ(w)ɛ-mi] |
če-mi [t͡ʃɛ-mi] |
čki-mi [t͡ʃki-mi] |
čki-mi / ški-mi [t͡ʃki-mi] / [ʃki-mi] |
mi-šgu [mi-ʃɡu] |
| Your (sg.) | *š(w)eni [ʃ(w)ɛni] |
šeni [ʃɛni] |
skani [skɑni] |
skani [skɑni] |
i-sgu [i-sɡu] |
| His/her/its | *m-is₁ [m-iʂ] |
m-is-i [m-is-i] |
mu-š-i [mu-ʃ-i] |
(h)e-mu-š-i [(h)ɛ-mu-ʃ-i] |
m-ič-a [m-it͡ʃ-ɑ] |
| Our | *čweni [t͡ʃwɛni] |
čveni [t͡ʃvɛni] |
čkini / čkəni [t͡ʃkini] / [t͡ʃkəni] |
čkini / čkuni / škuni [t͡ʃkini] / [t͡ʃkuni] / [ʃkuni] |
gu-šgwey (excl.) [ɡu-ʃɡwɛj] ni-šgwey (incl.) |
| Your (pl.) | *stkweni [stkwɛni] |
tkveni [tkvɛni] |
tkvani [tkvɑni] |
tkvani [tkvɑni] |
i-sgwey [i-sɡwɛj] |
See also
- Proto-Kartvelian language
Citations
- Boeder (2002), p. 3
- "Israel". Ethnologue.
- "Browse by Language Family". Ethnologue.
- Dalby (2002), p. 38
- Lang (1966), p. 154
- Hewitt (1995), p. 4.
- Encyclopædia Britannica, 15th edition (1986): Macropedia, "Languages of the World", see section titled "Caucasian languages".
- Judeo-Georgian at Glottolog
- "Государственный комитет Республики Абхазия по статистике". ugsra.org.
- Klimov (1998b), p. 14
- Klimov (1994), p. 91
- András Róna-Tas: The Reconstruction of Proto-Turkic and the Genetic Question. In: Lars Johanson – Éva Á. Csató (eds): The Turkic Langueges. London – New York: Routledge, 1998. 77.
- Allan R. Bomhard, John C. Kerns. (1994) The Nostratic Macrofamily: A Study in Distant Linguistic Relationship.
- Gamkrelidze & Ivanov (1995), pp. 774–776
- Gamkrelidze & Ivanov (1995), p. 768
- Fähnrich (2002), p. 5
- Fähnrich (2002), p. 5-6
- Testelets (2020), pp. 513-516
- Harris (1985), p. 46
- Harris (1985), p. 55
- Harris (1985), p. 58
General references
- Boeder, W. (1979). "Ergative syntax and morphology in language change: the South Caucasian languages". In Plank, F. (ed.). Ergativity: towards a theory of grammatical relations. Orlando: Academic Press. pp. 435–480.
- Boeder, W. (2002). "Speech and thought representation in the Kartvelian (South Caucasian) languages". In Güldemann, T.; von Roncador, M. (eds.). Reported Discourse. A Meeting-Ground of Different Linguistic Domains. Typological Studies in Language, vol. 52. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: Benjamins. pp. 3–48.
- Boeder, W. (2005). "The South Caucasian languages", Lingua, vol. 115, iss. 1–2 (Jan.-Feb.), pp. 5–89
- Dalby, A. (2002). Language in Danger; The Loss of Linguistic Diversity and the Threat to Our Future. Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231129008.
- Deeters, Gerhard (1930). Das kharthwelische Verbum: vergleichende Darstellung des Verbalbaus der südkaukasischen Sprachen. Leipzig: Markert und Petters.
- Delshad, F. (2010). Georgica et Irano-Semitica (in German). Wiesbaden.
- Fähnrich, H. (2002). Kartwelische Wortschatzstudien. Jena: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität.
- Fähnrich, H. & Sardzhveladze, Z. (2000). Etymological Dictionary of the Kartvelian Languages (in Georgian). Tbilisi.
- Gamkrelidze, Th. (Jan.–Mar. 1966) "A Typology of Common Kartvelian", Language, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 69–83
- Gamkrelidze, Th. & Ivanov, V. (1995). Indo-European and the Indo-Europeans: A Reconstruction and Historical Analysis of a Proto-Language and a Proto-Culture. 2 vols. Berlin / New York: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Harris, Alice C. (1985). Diachronic syntax: the Kartvelian case. Academic Press.
- Harris, A.C., ed. (1991). The Indigenous Languages of the Caucasus, Vol.1: The Kartvelian languages. Caravan Books.
- Hewitt, B.G. (1995). Georgian: A Structural Reference Grammar. John Benjamins Publishing. ISBN 978-90-272-3802-3.
- Kajaia, O. (2001). Megrelian-Georgian dictionary (in Georgian). Vol. 1. Tbilisi.
- Kartozia, G. (2005). The Laz language and its place in the system of Kartvelian languages (in Georgian). Tbilisi.
- Klimov, G. (1964). Etymological Dictionary of the Kartvelian Languages (in Russian). Moscow.
- Klimov, G. (1994). Einführung in die kaukasische Sprachwissenschaft. Hamburg: Buske.
- Klimov, G. (1998). Etymological Dictionary of the Kartvelian Languages. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Klimov, G. (1998). Languages of the World: Caucasian languages (in Russian). Moscow: Academia.
- Lang, D.M. (1966). The Georgians. New York: Praeger.
- Ruhlen, M. (1987). A Guide to the World's Languages, Vol. 1: Classification. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Testelets, Y.G. (2020). "Kartvelian (South Caucasian) Languages". In Polinsky, M. (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of Languages of the Caucasus. Oxford Handbooks Series. Oxford University Press.
- Tuite, K. (1998). Kartvelian Morphosyntax. Number agreement and morphosyntactic orientation in the South Caucasian languages. Studies in Caucasian Linguistics, 12. Munich: LINCOM Europa.
External links
- Lazuri Nena – The Language of the Laz by Silvia Kutscher.
- The Arnold Chikobava Institute of Linguistics, Georgian Academy of Sciences
- Arthur Holmer, The Iberian-Caucasian Connection in a Typological Perspective
- The rise and fall and revival of the Ibero-Caucasian hypothesis by Kevin Tuite (Université de Montréal).
На других языках
- [en] Kartvelian languages
[fr] Langues kartvéliennes
Les langues kartvéliennes forment une des trois familles de langues spécifiques au Caucase avec les langues abkhazo-adygiennes et les langues nakho-daghestaniennes.[it] Lingue cartveliche
Le lingue cartveliche[1] (in georgiano: ქართველური ენები?, kartveluri enebi; note anche come caucasiche meridionali[2] .mw-parser-output .chiarimento{background:#ffeaea;color:#444444}.mw-parser-output .chiarimento-apice{color:red}o iberiche[senza fonte][3]) sono una famiglia di lingue parlate nella zona meridionale del Caucaso, principalmente in Georgia. Il numero totale di parlanti nel mondo ammonta a circa 5,2 milioni di persone, con grandi comunità in Turchia, in Azerbaigian, in Iran, in Russia e in Israele.[4][ru] Картвельские языки
Картве́льские языки́ (или южнокавказские; груз. ქართველური ენები) — семья языков, распространённых на западе и в центре Южного Кавказа (Закавказья), в основном на территории современной Грузии, частично — в Турции (Лазистан, Тао-Кларджети), носителями которых являются грузины и их субэтносы.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
